Crystallization CFD Simulation of Loratadine Using the PBM in ANSYS Fluent
$300.00 $180.00 HPC
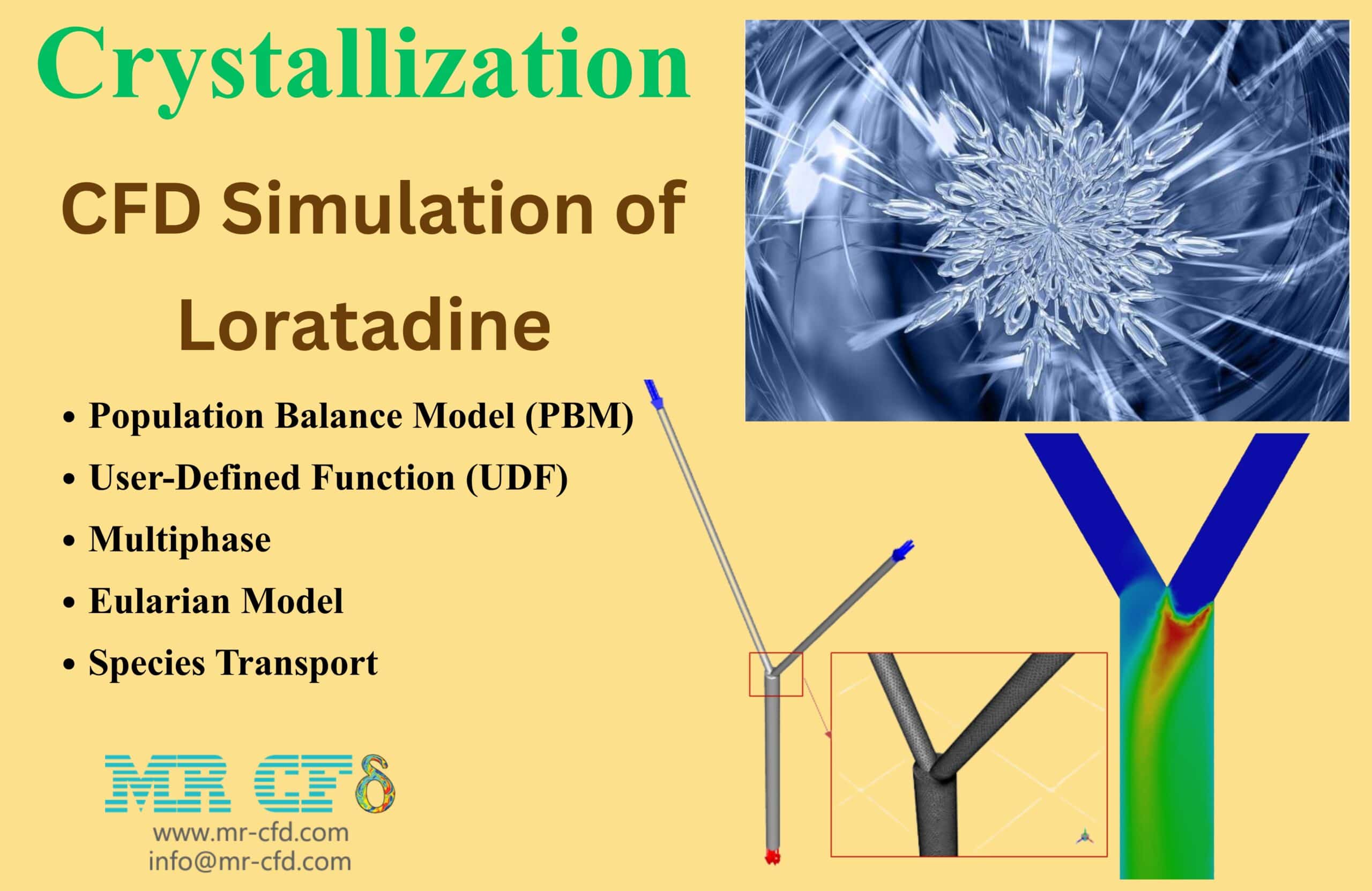
- This project investigates the crystallization of Loratadine in a dual-inlet nozzle using the Population Balance Model (PBM) in ANSYS Fluent.
- The study focuses on the effects of mixing and flow dynamics on nucleation and crystal growth.
- A tetrahedral mesh with 506,677 cells was used for accurate flow and particle tracking.
- A User-Defined Function (UDF) defined the kinetics of crystal formation based on local conditions.
- The results show realistic particle size distribution and effective prediction of crystallization behavior.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Crystallization Process Analysis with PBM: Numerical Study of Loratadine in a Dual-Inlet Nozzle
Description
This project presents a numerical simulation of the crystallization process of Loratadine in a dual-inlet nozzle using the Population Balance Model (PBM) in ANSYS Fluent. The main objective is to study the particle size distribution and the effects of mixing on crystal formation during the interaction of ethanol and water streams. These fluids mix to create supersaturation conditions that lead to nucleation and growth of Loratadine crystals. The simulation provides useful insights into the relationship between hydrodynamics, turbulence, and crystallization kinetics, helping to improve the design and control of similar industrial processes.
Geometry and Mesh
The computational domain represents a dual-inlet nozzle where ethanol and water enter through separate inlets and mix before exiting through a single outlet. The geometry was created in ANSYS DesignModeler, and the mesh was generated using ANSYS Meshing. A tetrahedral mesh was applied to capture the complex flow behavior inside the nozzle, with refinement in the mixing region to improve accuracy. The total number of elements was 506,677, ensuring an adequate balance between accuracy and computational cost. The mesh quality was verified to maintain low skewness and ensure stable convergence during the simulation.
Model and Solver Settings
The simulation of crystallization used the Eulerian multiphase model combined with the realizable k–ε turbulence model to capture phase interactions and turbulent mixing. The Discrete Population Balance Model (PBM) was employed to track Loratadine crystal sizes across 10 bins ranging from 1×10⁻⁸ m to 8.1681×10⁻⁸ m. A User-Defined Function (UDF) was used to define the nucleation and growth kinetics of the crystals, allowing the rates to depend on local supersaturation and flow conditions. The primary phase consisted of an ethanol–water mixture, which used the spices Model, while the secondary phase represented the dispersed Loratadine particles. The solver was transient and pressure-based, with a time step of 1×10⁻⁷ s and second-order upwind discretization for improved accuracy.
Results
The simulation showed effective mixing and crystallization of Loratadine inside the nozzle. The particle size distribution was divided into 10 bins, from 1×10⁻⁸ m (Bin-9) to 8.1681×10⁻⁸ m (Bin-0). Smaller particles dominated the early stage due to nucleation, while larger particles appeared later as growth progressed. The UDF accurately captured the dependence of crystal growth on local flow conditions. Flow results revealed strong mixing zones near the inlets and a uniform crystal distribution toward the outlet. The model successfully represented the interaction between flow dynamics and particle growth, confirming the reliability of the PBM–UDF approach.
Bin Sizes for loratadine (10):
Bin Number Bin Size (m)
—————————
Bin-0 8.168097e-08
Bin-1 6.4680612e-08
Bin-2 5.1218559e-08
Bin-3 4.0558379e-08
Bin-4 3.2116915e-08
Bin-5 2.5432383e-08
Bin-6 2.0139111e-08
Bin-7 1.5947534e-08
Bin-8 1.2628355e-08
Bin-9 1e-08
—————————
You must be logged in to post a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.