Fluent Meshing Training Course: Session 9, Regions
Free
- In this session, a heat exchanger geometry created in Design Modeler was processed through the Create Regions workflow in Fluent Meshing.
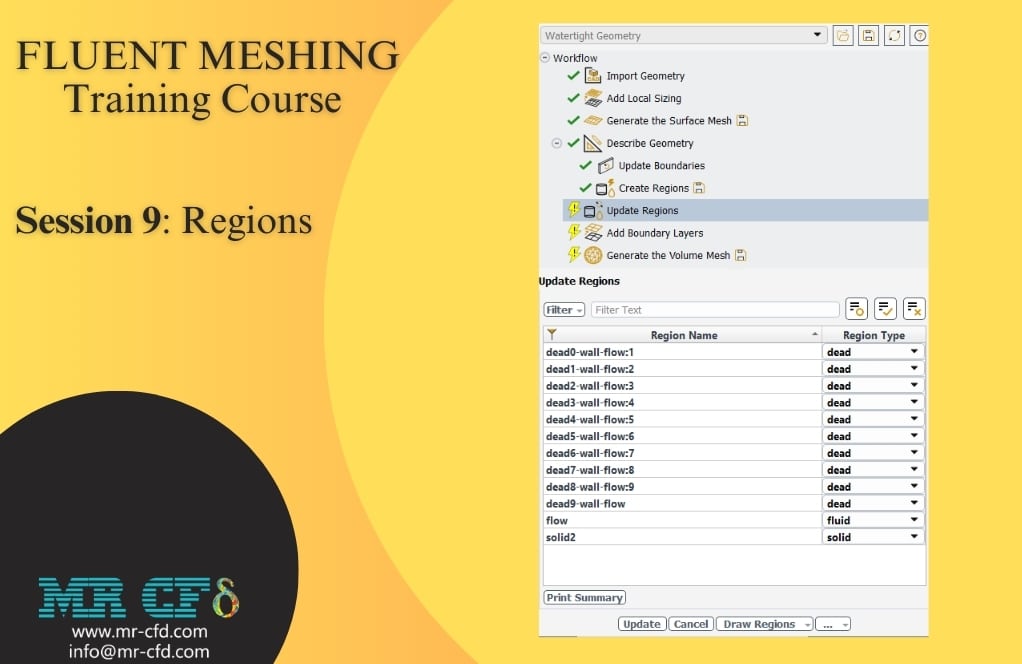
- After completing surface meshing and boundary updates, the Create Regions step identified three types of zones: fluid zones (flow areas), solid zones (material bodies), and dead zones (isolated volumes from geometry suppression).
- Key settings included setting “Estimated Number of Fluid Regions” to 1 for a single continuous fluid domain and “Retain Dead Region Names” to “No” for cleaner mesh processing.
- The Update Regions interface allowed conversion of dead zones to fluid or solid zones as needed, ensuring proper region assignment before volume mesh generation.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Fluent Meshing Training Course: Session 9, Regions
In this session, a heat exchanger geometry was created in Design Modeler and imported into Fluent Meshing. Named selections were applied in the CAD environment to facilitate automatic boundary recognition. Local sizing was added to control surface discretization and generate a surface mesh. The geometry was defined as both fluid and solid domains to prepare for region identification and assignment.
Region Types in Fluent Meshing
Fluent Meshing identifies three primary types of regions within the computational domain:
Fluid Zones: Represent areas where fluid flow occurs and are the primary regions of interest for CFD simulations. These include flow passages, channels, pipes, and any volume where fluid motion is expected.
Solid Zones: Represent solid materials that may participate in heat transfer or act as flow obstructions. These include walls, structural components, heat exchanger tubes, and any solid bodies within the domain.
Dead Zones: Isolated volumes that don’t connect to any boundary conditions and cannot participate in the flow solution. These often result from geometry suppression, modeling choices, or gaps in the CAD geometry.
Create Regions Settings
Estimated Number of Fluid Regions: This parameter tells Fluent Meshing how many separate fluid volumes to expect in the geometry. Set to “1” for single continuous fluid domains like simple pipes or channels, while higher numbers are used for multiple separate fluid regions such as heat exchangers with shell and tube sides. This setting helps with memory allocation and processing optimization.
Retain Dead Region Names: Controls how Fluent handles isolated volumes that don’t connect to boundaries. Setting to “No” (recommended) removes dead/isolated regions for cleaner mesh and faster processing. Setting to “Yes” keeps all regions visible for debugging and quality control purposes, particularly useful when troubleshooting complex geometries.
You must be logged in to post a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.