Cycloidal Rotor: 3D CFD Simulation of Geometrical Effects on Performance
$1,080.00 $648.00 HPC
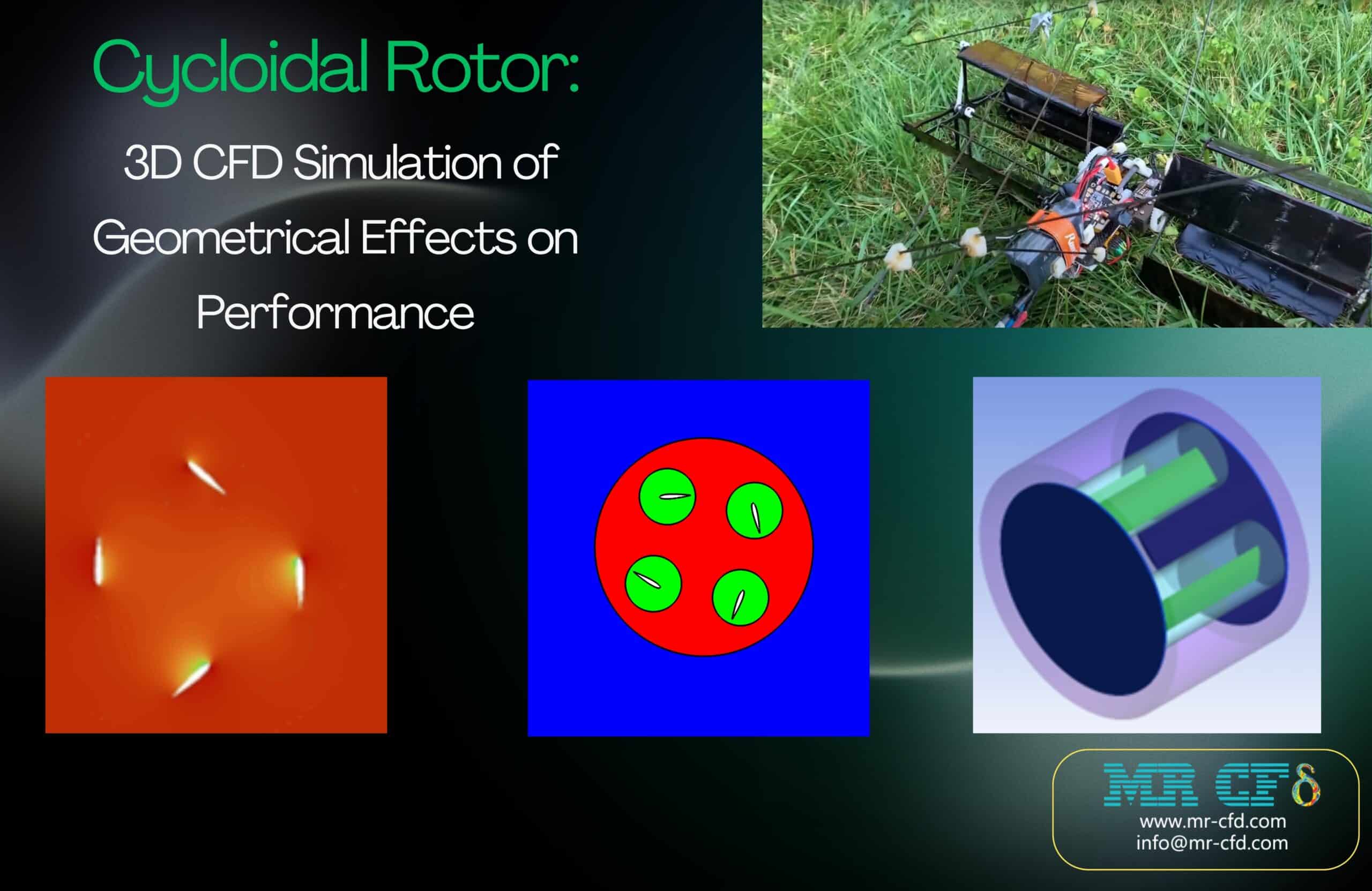
- The 3D cycloidal rotor CFD simulation models a pitching four-blade rotor to analyze flow behavior and aerodynamic performance.
- The rotor produces lift by dynamically adjusting blade pitch while rotating, enabling multidirectional thrust.
- Three disc configurations were tested to assess their effect on efficiency.
- Results highlight how disc presence alters thrust and torque characteristics, providing insights for design optimization.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Cycloidal Rotor: 3D CFD Simulation of Geometrical Effects on Performance
Description
A cycloidal rotor is a device that can have multiple blades that rotate both around the axis of the device and around its own axis. Approximately the blades change their pitch twice during each full turn so they can generate lift or thrust in any direction perpendicular to the rotor’s axis.. Today, cycloidal rotors are used for the propulsion of aerial vehicles, including drones and water vehicles. A unique aspect is that it can change the amount and direction of thrust without requiring any tilt of the aircraft’s structure.
This project presents a three-dimensional transient CFD simulation of a cycloidal rotor in hover to investigate the aerodynamic effects of different end-disc configurations on rotor performance. The study extends previous validated 2D work by resolving the full 3D flow field around the rotating, pitching blades and the surrounding end plates. The main objectives are to quantify thrust and moment variations for three configurations, no disc, single-side disc, and double-side disc, and to assess how the discs influence efficiency and loading distribution.
Geometry and Mesh
The 3D model consists of a cycloidal rotor with multiple identical blades arranged on a circular path, each defined by an airfoil section and rotating about its own pitch axis while the rotor spins about the main shaft. Three geometrical variants are created: blades without end discs, blades with one disc on a single side, and blades with discs on both sides of the rotor span. An unstructured mesh with local refinement around the blades and in the tip and wake regions is generated, using sliding or rotating fluid zones to accommodate blade motion while maintaining acceptable element quality throughout the cycle.
Model and Solver Settings
The simulations employ an incompressible, transient, pressure-based CFD solver with appropriate turbulence modeling (e.g., SST k–ω) to capture separation and unsteady vortical structures around the pitching blades. The same physical models, temporal resolution, boundary conditions, and numerical schemes as the previously validated 2D cycloidal rotor study are adopted here to ensure consistency; the 2D configuration was first validated against published data, and the proven setup from that work is directly extended to the present 3D cases. This approach ensures that any performance differences arise primarily from three-dimensional geometry and end-disc effects rather than changes in modeling strategy.
Results
The 3D simulations reveal distinct changes in thrust and moment when end discs are added compared to the baseline rotor without discs. For the cases with one and two discs, the discs alter the tip vortex structure and induced flow, leading to reduced thrust and increased aerodynamic moment relative to the no-disc configuration, indicating a drop in overall efficiency. Comparison between 2D and 3D results shows noticeable differences in predicted thrust and momentum, highlighting the importance of three-dimensional effects and demonstrating that end-disc geometry has a significant impact on cycloidal rotor performance in hover.
You must be logged in to post a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.