Distal-End Side-to-Side and End-to-Side Anastomoses for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in a Pulsatile Flow, CFD Simulation: Paper Validation
$120.00 $48.00 HPC
- This project presents a CFD study based on the article “Analysis of Computational Fluid Dynamics and Particle Image Velocimetry Models of Distal-End Side-to-Side and End-to-Side Anastomoses for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in a Pulsatile Flow.”
- The objective is to reproduce and validate the hemodynamic behavior of distal-end side-to-side (deSTS) and end-to-side (ETS) anastomoses.
- All simulations were carried out in ANSYS Fluent using steady, laminar, and incompressible flow assumptions.
- The results include comparisons of velocity profiles and wall shear stress (WSS) to ensure accuracy with the reference study.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Distal-End Side-to-Side and End-to-Side Anastomoses for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in a Pulsatile Flow
Description
In distal project, a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation was performed based on the reference study titled “Analysis of Computational Fluid Dynamics and Particle Image Velocimetry Models of Distal-End Side-to-Side and End-to-Side Anastomoses for Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting in a Pulsatile Flow” by Shintani et al. (Circulation Journal, 2018). The purpose of this work was to reproduce and validate the hemodynamic behavior of two coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) configurations: the distal-end side-to-side (deSTS) and end-to-side (ETS) anastomoses. The analysis aimed to verify the numerical results of the present simulation against the reference data using ANSYS Fluent. The study focused on steady, laminar, and incompressible flow conditions to evaluate velocity profiles and wall shear stress (WSS) distributions and to confirm the accuracy of the CFD methodology for modeling physiological blood flow in coronary bypass geometries.
Geometry and Mesh
The geometry was created in ANSYS Design Modeler based on typical coronary artery and graft dimensions described by Shintani et al. The model represented a circular graft connected to the host artery at a realistic physiological angle to simulate both ETS and deSTS configurations. An unstructured tetrahedral mesh was generated in ANSYS Meshing to discretize the fluid domain and capture flow gradients accurately near the anastomotic region. The mesh consisted of approximately 2,049,525 elements, providing sufficient resolution to ensure mesh-independent results. The fine elements near the vessel wall allowed precise evaluation of velocity distribution and wall shear stress levels, ensuring high-quality CFD data for validation purposes.
Model and Solver Settings
The computational model assumed a laminar, incompressible, Newtonian fluid with properties corresponding to blood: a density of 1060 kg/m³ and a dynamic viscosity of 0.004 Pa·s. The inlet velocity was set to 0.0097 m/s, and a pressure outlet boundary condition with a gauge pressure of 0 Pa was used at the outlet. Vessel walls were modeled as rigid with no-slip conditions. The simulations were carried out using the pressure-based solver in ANSYS Fluent under steady-state conditions. Convergence was considered achieved when all residuals fell below 1×10⁻⁵. This setup provided accurate and numerically stable results for the velocity field and wall shear stress distribution across the anastomotic region.
Results
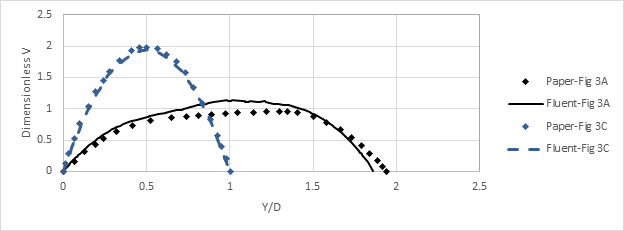
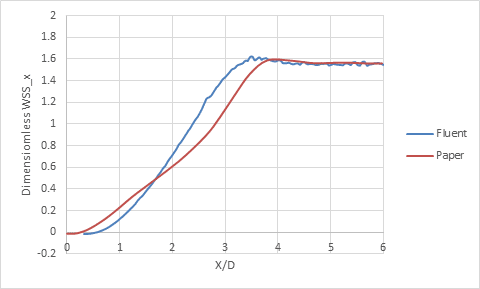
The CFD results showed excellent agreement with those reported by Shintani et al., confirming the reliability of the numerical approach. The velocity profiles closely matched the data presented in the velocity profile comparison at two sections, demonstrating correct prediction of flow behavior at the anastomotic junctions. Similarly, the dimensionless wall shear stress comparison verified that the distribution of WSS in the current model corresponded well to the reference results. Regions of low WSS were identified near the heel and distal end of the graft, consistent with the areas prone to disturbed flow, while higher WSS values appeared along the regions of direct flow impingement. These results validate the CFD model’s capability to accurately capture the complex hemodynamics characteristic of coronary bypass flows.
Velocity Profile Comparison at two Sections
Dimensionless Wall Shear Stress Comparison
You must be logged in to post a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.