Ffwocs Williams & Hawkings (FW-H) Acoustic Model, ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial
$100.00 Student Discount
- The current CFD Analysis simulates the flow around a cylinder to investigate its aeroacoustics condition.
- The simulation is dependent on time so is performed in transient form.
- The Ffwocs Williams & Hawkings Acoustic Model has been used for acoustic modeling.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Description
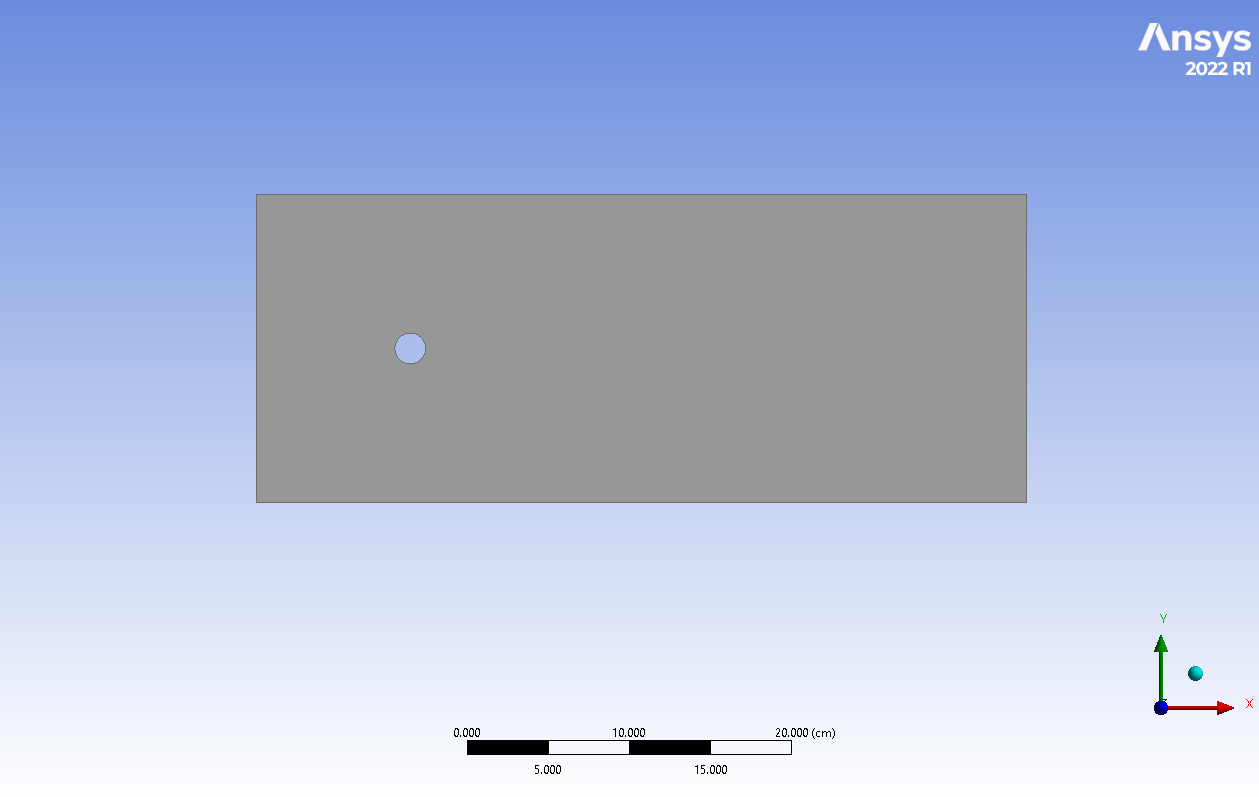
In this project, the airflow around a cylinder is simulated to investigate its acoustic condition using Ffwocs Williams & Hawkings (FW-H) model.
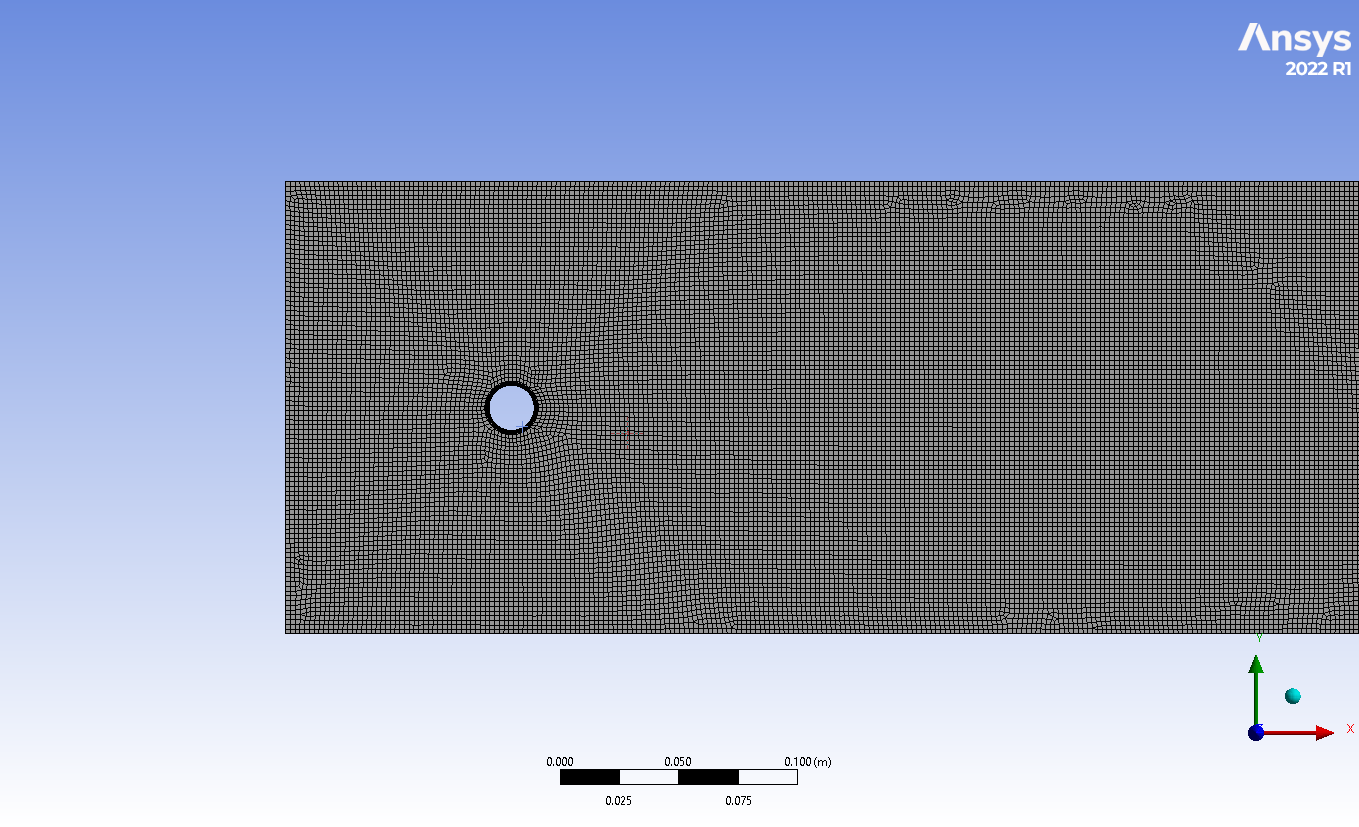
The two-dimensional geometry is designed in ANSYS Design Modeler software. Also, the structured grid is carried out using ANSYS Meshing meshing. As a result, 23264 elements were generated.
This product is the 2nd episode of the Acoustic Model Training Course.
Methodology of Ffwocs Williams & Hawkings Acoustic Model CFD Simulation
The simulation is Transient(unsteady) to capture fluid behavior over time. The Pressure-based solver type is used due to the incompressibility of the working fluid. Also, Fwocs Williams & Hawkings (FW-H) is employed.
Conclusion
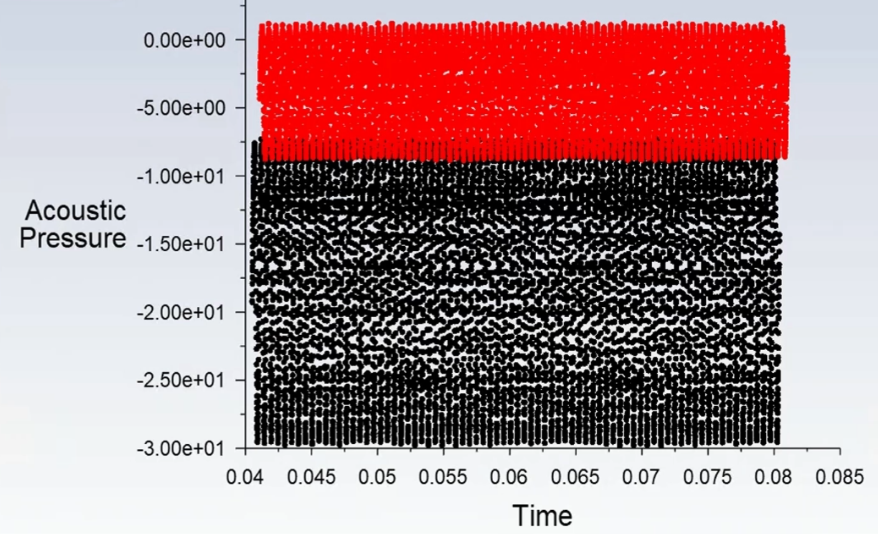
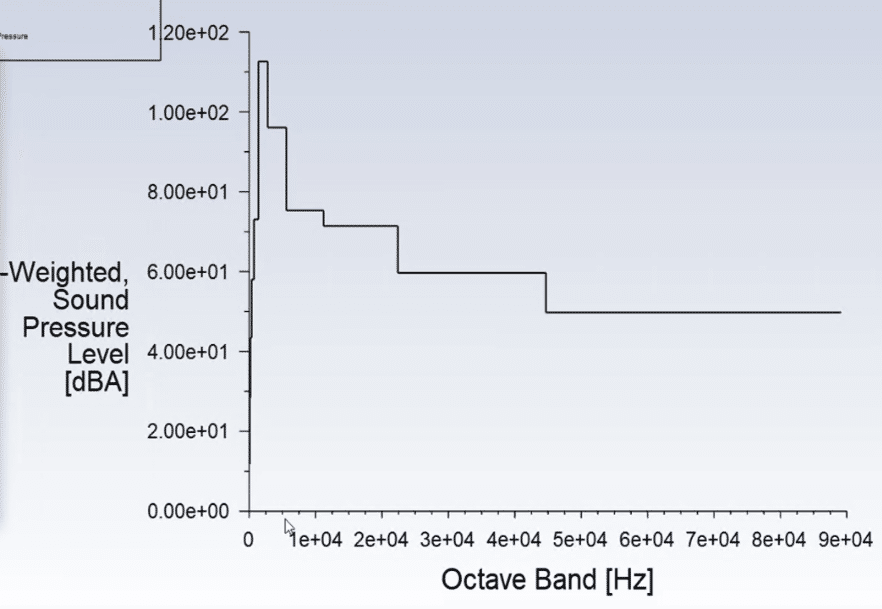
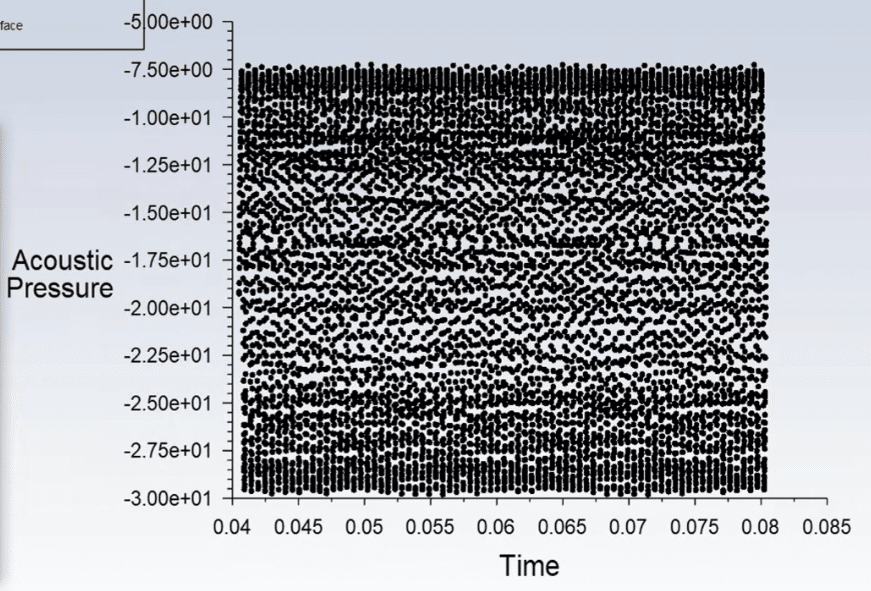
At the end of the simulation, the sound pressure level, A-weighted and acoustic pressure recorded by the defined receivers are extracted. The graph of acoustic pressure is extracted in terms of time. In the first step, the data has been taken to the frequency domain using Fourier transform. The acoustic signal information is plotted in decibels in the frequency domain in the graph you see in the results (sound pressure level plot). As it is clear from the graph, the most sound that is present by the microphone installed at the receiver location occurred in a frequency range smaller than 2e+4.
A-weighting is an established, standard curve that attempts to alter the sound pressure levels recorded by a microphone measurement to more closely match the perception of the human ear. This graph also confirms the previous results, and as it is known, the highest frequency that the human ear can hear at the location of the desired receiver happened at frequencies smaller than 1e+4.
Data is dedicated to recording the nearer and farthest receivers and clearly shows how the acoustic pressure level decreases by getting farther from the acoustic source (cylinder).


Bennett Gaylord –
I’m amazed by the detail in the acoustic simulation results! Can the FW-H model be applied to other shapes, like an airfoil, and how are the receivers for measuring acoustic pressure placed in the simulation domain?
MR CFD Support –
We appreciate your kind words about our product! Yes, the FW-H acoustic model can also be applied to other shapes, such as airfoil geometries, to study the noise generated by the flow around them. As for the placement of receivers in the simulation domain, they are strategically distributed to measure the acoustic pressure at various locations, and their positioning is dependent on the specific requirements of the study to best capture the relevant acoustic data.
Kirk Ankunding MD –
This Fw-H model tutorial really simplifies the complex subject of acoustic modeling. The step-by-step approach and the graphs included helped me grasp the concept of A-weighting and how different frequencies affect sound perception. Great job expounding FW-H application!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our FW-H model tutorial was helpful for you and that you found the graphs and explanations clear. It’s encouraging to know that our approach to teaching acoustic modeling is effective. If you have any further questions or need more insights, feel free to reach out!
Prof. Alexis Stanton –
I really appreciated the thorough explanation of the FW-H Acoustic Model simulation. Delving into acoustic phenomena and seeing those decibel graphs was fascinating. Congratulations on a job well done!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are pleased to hear that you found the simulation tutorial informative and engaging. Should you have any further interest in acoustic simulation or any other CFD topics, feel free to explore more of MR CFD’s training courses. We are always here to help you deepen your understanding.
Dr. Gracie Schulist V –
I recently purchased the FW-H Acoustic Model CFD Simulation tutorial and was impressed with the clarity of the explanation provided. The step-by-step guidance through the two-dimensional simulation was especially helpful for visualizing the complex acoustic phenomena involved.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that you found the FW-H Acoustic Model tutorial clear and helpful. We always strive to provide detailed and instructive content to aid our customers in understanding complex simulations. If you further explore the field of acoustics or have any additional questions, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
Ms. Alia Hilpert –
This tutorial on the FW-H Acoustic Model seems quite comprehensive! Do the simulation results include a detailed analysis of the frequency-specific acoustic attenuation over distance?
MR CFD Support –
Yes, the simulation results provide a detailed analysis of frequency-specific acoustic attenuation. The recorded data covers both near and far receivers, demonstrating how sound pressure levels decrease with distance from the source.
Jana Keebler IV –
The tutorial was clear and I got results similar to those described. However, is there a way to reduce the high-frequency noise observed in the results?
MR CFD Support –
Indeed, in cases where high-frequency noise is present in the simulation results, several approaches can be applied. You may consider refining the mesh around the noise source, using a high-order scheme for the discretization of the acoustic variables, implementing acoustic dampening materials or barriers in the simulation domain if applicable, or applying a low-pass filter during post-processing to remove unwanted high-frequency components. It is great to hear that the tutorial was helpful, and your results matched those illustrated!
Deondre O’Hara DVM –
I’m curious about how the simulation captures the reduction in acoustic pressure levels at varying distances from the cylinder. Could you elaborate on that?
MR CFD Support –
In this simulation, multiple receivers are placed at various distances from the cylinder to capture the change in acoustic pressure levels. As sound travels through the air, its intensity decreases with distance due to the spreading of sound wave fronts and energy dissipation in the medium. This phenomenon is accurately captured in the FW-H simulation by comparing the sound pressure levels recorded at each receiver, demonstrating a decrease in levels as the receiver gets farther from the source. The FW-H model incorporated in ANSYS Fluent calculates this effect, providing a realistic prediction of the acoustic environment around the cylinder.
Matilda Conroy –
This tutorial was a fantastic learning tool for understanding acoustic simulation using the FW-H model. The structured approach and detail-oriented instructions which guided through the whole process of setting up the simulation to interpreting the results were exceptional.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re delighted to hear that you found the FW-H acoustic model tutorial informative and helpful. Your understanding and appreciation of the detailed instructions is much appreciated. If you need further assistance with your acoustic simulations, don’t hesitate to reach out!
Scarlett Donnelly –
I loved learning how sound behaves around structures thanks to this FW-H Acoustic Model course. The combination of fluid dynamics and acoustics in this tutorial is fascinating and the step-by-step method made complex concepts understandable. The graph results helped me grasp how different frequencies are distributed, which is fantastic for practical applications.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your wonderful review! We’re delighted to hear that the FW-H Acoustic Model course was both educational and enjoyable for you. It’s great to know the tutorials and graphical results were effective in clarifying the intricate interplay between fluid dynamics and acoustics. We appreciate your feedback and are glad you found practical value in the course materials.
Maurice Keebler –
I’m very impressed with how the FW-H Acoustic Model simulates the sound pressures around the cylinder and provides insights into the acoustic profile. The use of A-weighting to adjust for the human ear’s perception is particularly smart. Great job on demonstrating the impact of distance on acoustic pressure levels in the results too.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are glad that you appreciate the attention to detail in the simulation and the effort to align it with human auditory perception. It is our aim to provide thorough and practical analysis tools, and we’re pleased to know that our work resonates with our users. Your satisfaction is the best reward for our efforts!
Freida Dibbert –
I’m thoroughly impressed with the acoustic analysis capabilities! The FW-H model seems to grasp the subtleties of sound pressure level alterations well. The detailed outcome showcasing how noise diminishes with distance from the source is particularly remarkable. Could you clarify if this simulation accounts for variables such as temperature and humidity that also affect the propagation of sound?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the insightful comments and the compliment! This specific CFD simulation focuses on acoustic pressure levels using the Ffowcs Williams and Hawkings (FW-H) model, typically under assumed constant atmospheric conditions. Factors like temperature and humidity can indeed have an impact on sound propagation. However, this model typically does not include these environmental factors in the calculations for the sake of simplicity, numerical stability, and computational efficiency. If a user required a simulation that considered these additional variables, a more comprehensive and customized model setup would be necessary.
Retta Schultz –
I loved learning from your Ffwocs Williams & Hawkings acoustic model tutorial! The simplification of complex acoustic phenomena into understandable terms was phenomenal and the structured mesh design was well-explained. I particularly found the demonstration on how to extract and interpret sound pressure levels and acoustic signals incredibly useful for my own studies in acoustics engineering.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that our tutorial on the Ffwocs Williams & Hawkings acoustic model was helpful to you. Our team works hard to ensure complex concepts are made accessible and understandable, and we’re glad you appreciated the structured approach. If you ever have more questions or need further assistance in your acoustics engineering studies, we’re here to help!
Prof. Candido Green –
Amazing tutorial! Not only did it strengthen my understanding of acoustics in CFD simulations, but it also guided me fluently through FW-H model application. Thank you for this invaluable learning resource.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that our tutorial was helpful and enhanced your knowledge. Your feedback inspires us to continue creating high-quality learning materials. If you have any more questions or need further assistance, feel free to reach out.
Jessica Bode –
I’m really impressed by this tutorial—especially the practical application of the FW-H acoustic model for assessing the sound pressure levels around the cylinder. It’s great to have a clear visualization of how noise frequencies are distributed, which is critical in acoustic engineering. Having the Fourier transform data to support frequency domain analysis makes it even more valuable for real-world engineering issues. Thanks for such a comprehensive and enlightening tutorial.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our Ffwocs Williams & Hawkings (FW-H) Acoustic Model tutorial met your expectations and provided the comprehensive insights you were looking for. Your recognition of the practical applications and the detailed frequency analysis is greatly appreciated. At MR CFD, we strive to ensure our tutorials are enlightening and practical, and we’re glad to know we succeeded with this tutorial. If you ever have more questions or need further assistance, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
Tracy Bartoletti –
I really appreciate how the FW-H acoustic model CFD simulation helped me understand acoustic pressure levels related to airflow around a cylinder. It’s great to see how the simulation captures the sound’s frequencies that the human ear can perceive.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our training product on the FW-H acoustic model in ANSYS Fluent was informative and beneficial for your understanding of acoustics related to fluid dynamics.
Ms. Kirsten Hammes –
The tutorial was terrific at explaining the acoustic modeling process. Especially useful was seeing the practical aspects of employing the FW-H acoustic model. Thanks to the clear steps and well-illustrated results sections, I better understand how noise profiles can be analyzed in industrial applications.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the positive feedback on our FW-H Acoustic Model tutorial! We’re delighted to hear that it helped improve your understanding of acoustic simulations in industry. If you have any further questions or need additional guidance through your CFD learning journey, please feel free to reach out to us.
Dr. Samson Larkin MD –
The tutorial was superbly clear, allowing me to fully grasp the FW-H Acoustic model implementation. The sound pressure level graph provided was particularly helpful in understanding the frequency response around the cylinder. Great work on presenting how acoustic perception is modelled!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive words! We’re glad to hear that the FW-H Acoustic model simulation tutorial was able to provide you with a clear understanding and that the sound pressure level graph was of use to you. If you have any further questions or need additional clarification as you apply the model to new situations, please don’t hesitate to reach out. It’s always very rewarding for us to see our customers making good use of our tutorials!
Gay Conn –
The tutorial seems very informative. Does it also provide a comparison between the FFWH model results and experimental or theoretical data to validate the acoustic predictions?
MR CFD Support –
The tutorial provides a detailed analysis of the acoustic pressure levels using the FW-H acoustic model. However, it doesn’t explicitly mention a comparison with experimental or theoretical data in the description provided. It focuses on teaching the simulation methodology and result analysis. For details on validation, you may need to refer to academic literature where FW-H model predictions are typically compared against experimental data to assess their accuracy.
Gisselle Daniel –
Amazing tutorial! Was very impressed with the detailed explanation of the FW-H acoustic model and the comprehensive acoustic analysis. Keep up the excellent work!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the wonderful feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that you found our FW-H acoustic model tutorial helpful and informative. We strive to provide comprehensive analyses in our courses, and we are glad that it met your expectations. If you have any more questions or need further assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out. Happy learning!
Marion Corkery –
I’m fascinated by the detailed acoustic analyses. Could you explain how you determined the location of the microphones or receivers to accurately measure the sound pressure levels in your CFD study?
MR CFD Support –
In the CFD study, the locations of the microphones or receivers are carefully chosen based on several factors. These might include the primary noise sources, the geometry of the analyzed object (e.g., the cylinder), and the specific requirements of the acoustic analysis. The aim is to place the receivers at points where accurate measurements of the acoustic pressures can be obtained, both near and far from the noise source, to understand the propagation and attenuation characteristics of the sound waves emitted. The placement ensures that the resultant data effectively represents a range of frequencies and acoustic behaviors pertinent to the study objectives.
Obie Predovic –
I was impressed with how the Ffwocs Williams & Hawkings model helped in analyzing acoustic conditions around the cylinder. The detailed analysis of the frequency domain and A-weighting provided clear and valuable insights. Great work!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled to know that you found the Ffwocs Williams & Hawkings model and our analysis of acoustic conditions useful. Our goal is to provide clear insights and understanding with our simulations and it’s wonderful to hear such positive feedback!
Prof. Walker Rutherford –
The tutorial was brilliant! It really demystified the process for setting up and analyzing acoustic simulations using the FW-H model in ANSYS Fluent. Very clear step-by-step guidance and valuable insights into interpreting the results.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that our Acoustic Model training course provided you with clear and valuable guidance. At MR CFD, we always strive to support our users in mastering CFD simulations. We appreciate your feedback and are glad you found the tutorial useful. If you have any more questions or need further assistance in your CFD journey, please don’t hesitate to reach out!
Miss Ellen Von –
I am absolutely thrilled with the clarity provided in your FW-H Acoustic Model tutorial! The step-by-step guidance has significantly bolstered my understanding of acoustics in fluid dynamics. Could you share how exactly the receivers are positioned in the simulation setup?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words about the FW-H Acoustic Model tutorial! We’re pleased to know it has improved your understanding of acoustics in fluid simulations. In this project, the receivers are strategically placed at varying distances from the cylinder to measure the acoustic pressure levels. Their positions are defined within the simulation environment, ensuring that one captures the acoustic field near the cylinder and another measures the acoustic field further away. This arrangement helps in understanding how the sound pressure level varies with distance.
Sanford Bode –
After going through the excellent FW-H acoustic simulation tutorial, I’m intrigued by how the A-weighting curve adjustments are accurately accounted for in Fluent. Is there a specific setting or functionality in ANSYS Fluent that applies this curve, or do we use external tools for that correction?
MR CFD Support –
The A-weighting adjustments are not directly applied within ANSYS Fluent. After the simulation, you would typically use post-processing tools either within Fluent’s result processing options or external software like ANSYS CFD-Post or a dedicated acoustic analysis software to apply A-Weighting to the frequency spectrum obtained from the simulation results.
Clare Zulauf –
I’m impressed with the way the FW-H acoustic model captures the sound generated around the cylinder. The detail in the analysis is fantastic!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the positive feedback! We’re happy to hear that you are impressed with the precision and thoroughness of the FW-H acoustic model analysis in capturing sound interaction around the cylinder. If you have further interest in our products or require additional information, feel free to reach out!
Lacey Maggio –
I appreciate the detailed approach to acoustic simulation using the FW-H acoustic model. Could you please elaborate on the relevance of using the A-weighting curve in this particular simulation?
MR CFD Support –
The A-weighting curve is relevant in this simulation as it applies a frequency weighting that mimics the human ear’s response to sound of varying frequencies. By using A-weighting in the simulation, the extracted sound pressure levels are adjusted to reflect the perceived loudness that would be experienced by a person, making the results more valuable for applications where human hearing perception is critical, such as noise pollution studies or acoustic comfort analysis.
Rickie Huels –
This tutorial made it easy to understand the FW-H acoustic model. The details of transforming data into the frequency domain using Fourier transform were particularly clear.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to hear that the tutorial helped you understand the FW-H acoustic model and that the transformation process using Fourier transform was explained clearly. We aim to provide detailed and informative content, and it’s always great to know that our efforts are appreciated by our customers. If you have any more questions or need further assistance, please don’t hesitate to ask.
Pattie Batz –
I’m delighted with the clarity of the graphs and the information provided in the acoustic signal frequencies. The A-weighting explanation was quite helpful for comprehending how it correlates to human hearing. Great job on this comprehensive tutorial!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words and positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that you found the A-weighting explanation useful and that our tutorial on the FW-H Acoustic Model met your expectations. If you have any more questions or need further assistance with your CFD learning journey, feel free to reach out to us. Your success is our biggest reward!
Alfreda Watsica Sr. –
I’ve completed the FW-H Acoustic Model CFD Simulation tutorial and the results are fantastic. The explanation was clear and the final graphs truly highlighted the noise patterns. Great resource for understanding acoustics in fluid dynamics!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words! We are thrilled to hear that our FW-H Acoustic Model CFD Simulation tutorial was helpful and provided clear results. If you ever have more questions or need further assistance, do not hesitate to reach out. Happy simulating!
Eula Boyer –
This sounds amazing! The FW-H acoustic model tutorial must have been quite insightful, especially when analyzing the sound frequency distribution and attenuation with distance. Your team has constructed an articulated and comprehensive training material here.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words and for recognizing the effort we put into the FW-H acoustic model tutorial! We’re glad that you found the tutorial insightful and helpful in understanding the intricacies of acoustic simulations. We look forward to providing you with more quality learning materials in the future.