Flow Conditioner by Perforated Plate: Paper Validation
$210.00 $126.00 HPC
- The current CFD analysis numerically validates the paper “Comparison of velocity and turbulence profiles downstream of perforated plate flow conditioners” by Spearman et al. using ANSYS Fluent software.
- The model designed and meshed the pipe geometry with perforated plate flow conditioner in SpaceClaim and ANSYS Meshing, generating 583,842 tetrahedral cells.
- A pressure-based solver with k-ε standard turbulence modeling and gravity effects (-9.81 m/s²) is employed, using water as the working fluid with velocity inlet profile and pressure outlet boundary conditions coupled via SIMPLE algorithm.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Flow Conditioner by Perforated Plate CFD Simulation by ANSYS Fluent : Paper Validation
Project Description
This project involved CFD validation of a perforated plate flow conditioner against experimental data from Spearman et al(Comparison of velocity and turbulence profiles downstream of perforated plate flow conditioners
perforated plate). The study aimed to validate numerical simulation results for flow conditioning performance downstream of flow-disturbing installations. The validation focused on analyzing velocity and pressure profiles to assess how effectively the CFD model captures the flow development characteristics observed in laboratory experiments, which is crucial for industrial flow measurement applications.
Geometry and Mesh
The computational geometry was created using ANSYS SpaceClaim with dimensions of 4,822.2 × 102.6 × 205.2 mm, representing a pipe section with an integrated perforated plate flow conditioner. The perforated plate contained multiple holes arranged in concentric patterns to provide graded resistance across the flow cross-section. The computational mesh was generated using ANSYS Meshing, resulting in 583,842 tetrahedral elements with appropriate refinement around the perforated plate holes and near-wall regions to accurately capture complex flow phenomena.
Setup
The CFD simulation used a pressure-based solver with steady-state conditions and gravity enabled at -9.81 m/s². Water was specified as the working fluid material. The k-epsilon standard turbulence model was employed to capture turbulence effects downstream of the perforated plate. Boundary conditions included velocity inlet with profile specification and pressure outlet. The SIMPLE algorithm was used for pressure-velocity coupling to ensure proper solution convergence and accuracy in predicting flow development characteristics.
Results
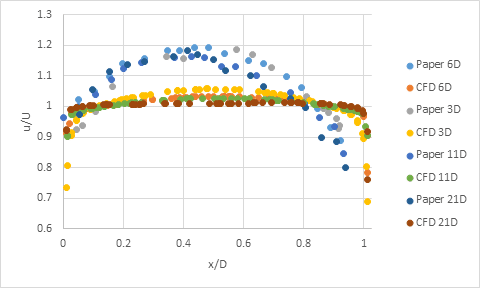
The simulation results demonstrated good agreement with experimental findings regarding velocity and pressure profile development downstream of the flow conditioner. The velocity contours showed characteristic jet formation through perforated holes and subsequent mixing, with flow approaching developed conditions at 3D downstream, consistent with experimental observations. The pressure distribution results showed the expected pressure drop across the perforated plate and subsequent recovery downstream. As noted in the reference material, dimensionless velocity values showed minimal variation at different downstream distances, with differences typically less than 5-10% between locations, validating the CFD methodology for flow conditioner design applications.
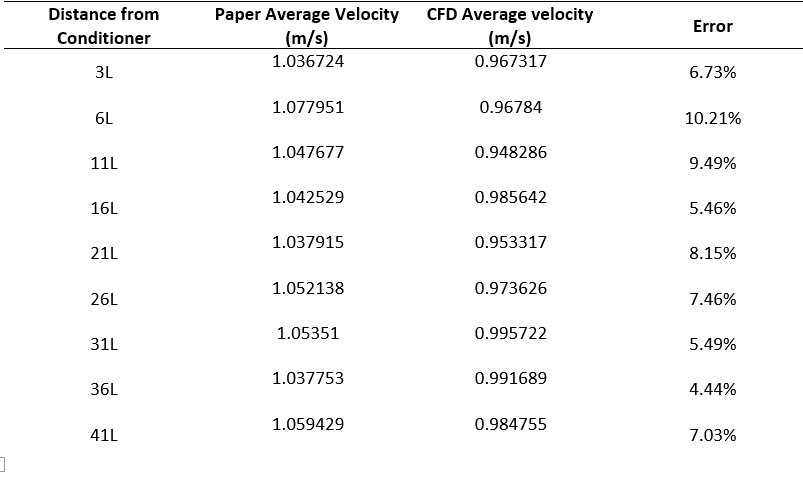
Also, the error values are shown in the table below:
You must be logged in to post a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.