Bitumen Melting Inside a Tank, CFD Simulation ANSYS Fluent Training
$100.00 Student Discount
The present problem simulates bitumen melting inside a bitumen tank using ANSYS Fluent software.
Click on Add To Cart and obtain the Geometry file, Mesh file, and a Comprehensive ANSYS Fluent Training Video.To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Bitumen Melting Description
The present simulation is about bitumen melting inside a bitumen tank via ANSYS Fluent. Bitumen is a material that increases in concentration when exposed to cold. In other words, the cold gradually causes the bitumen to freeze inside the tank.
Therefore, hot water flow pipes are used inside these tanks to upper the bitumen temperature inside the tanks and thus prevent it from freezing. In this project, a 2D bitumen tank is designed with periodic conditions.
Inside the tank, several rows of hot water pipes are designed. The bitumen material enters the tank at a low temperature, and its temperature increases when it receives heat from the pipe wall. This simulation uses a solidification and melting model to define phase change materials.
To define bitumen as a phase change material (PCM), the maximum temperature at which the solid phase temperature prevails (solidus temperature) is 340.15 K, the minimum temperature at which the liquid phase dominates (liquidus temperature) is 341.15 K, and the latent heat of pure solvent melting heat is defined as 450367 j.kg-1.
Bitumen flow enters the tank with a speed of 0.1 m.s-1 and a temperature of 343.15 K, and contacts the wall of hot water pipes with a constant temperature of 523.15 K.
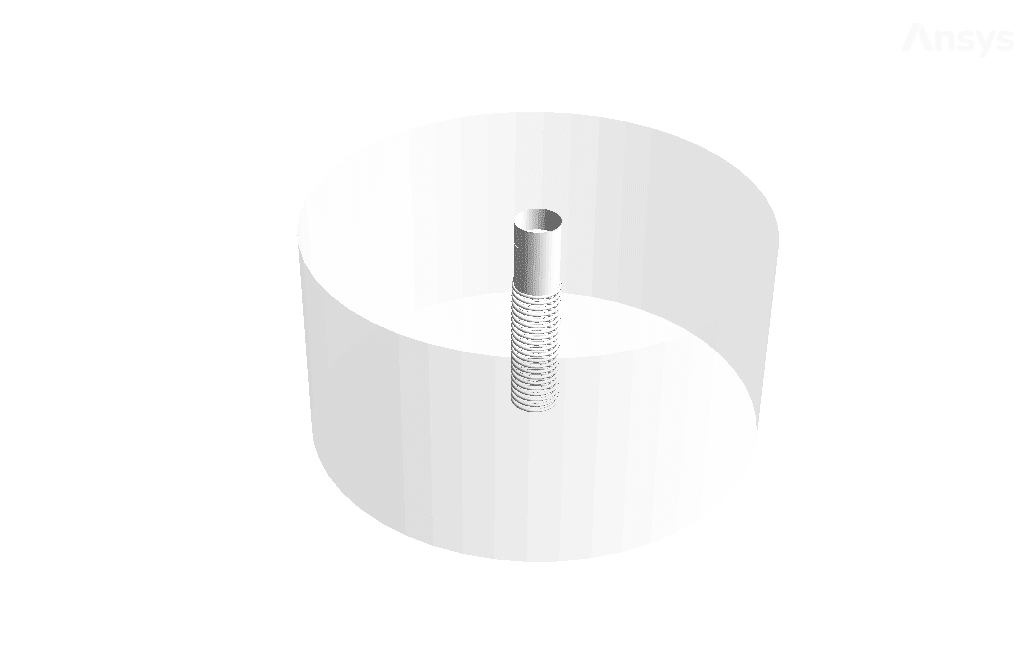
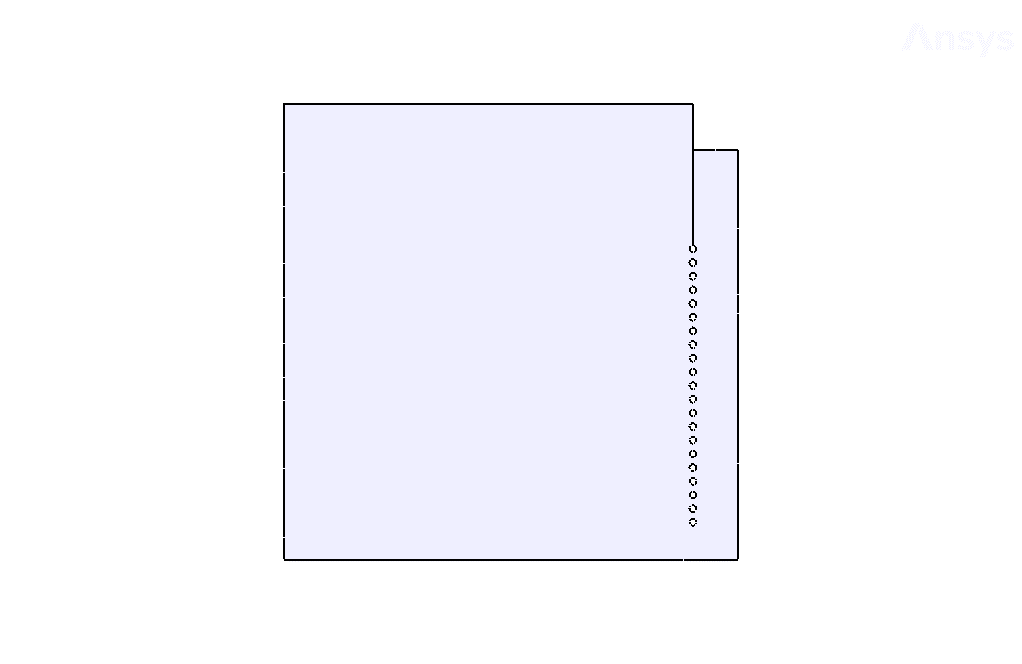
Geometry & Mesh
The present geometry is designed in a 2D model via Design Modeler. The computational zone is the interior of a tank with several rows of pipes. This geometry is designed as a 2D plane with periodic conditions and can turn into a 3D cylindrical tank when checking the results.
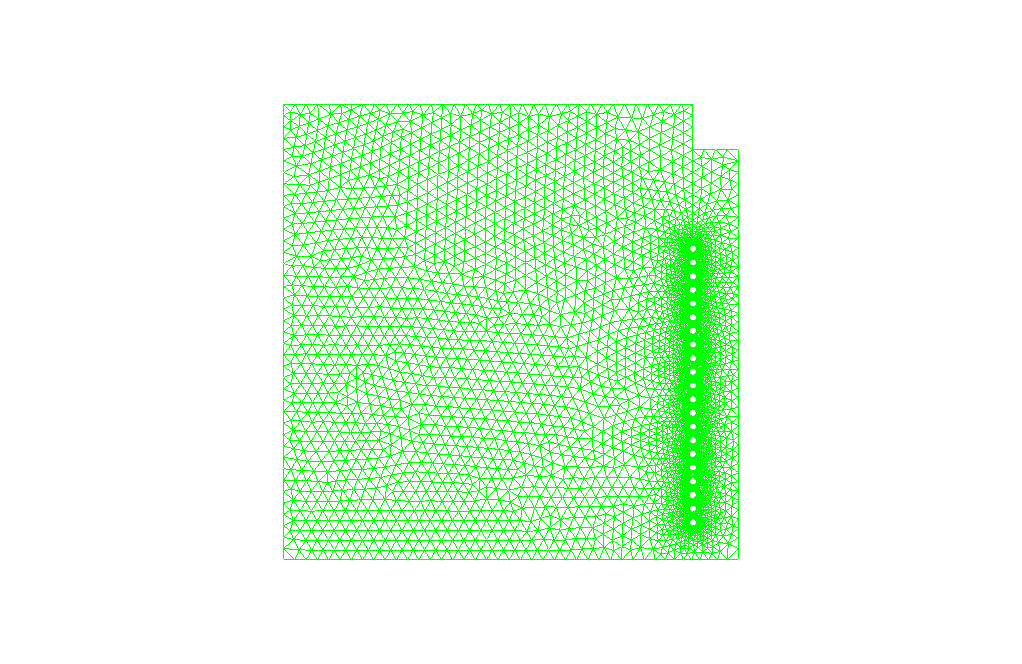
The mesh of the present model has been done via ANSYS Meshing. Mesh is structured, and the number of production cells equals 10541.
 Set-up & Solution
Set-up & Solution
Assumptions used in this simulation:
- Pressure-based solver is used.
- The present simulation is unsteady.
- The effect of gravity is ignored.
| Models | ||
| Viscous | k-epsilon | |
| k-epsilon model | RNG | |
| Near-wall treatment | standard wall function | |
| Solidification & Melting Model | On | |
| Energy | On | |
| Boundary conditions | ||
| Inlet | Velocity Inlet | |
| velocity magnitude | 0.1 m.s-1 | |
| temperature | 343.15 K | |
| Inner Wall | Wall | |
| wall motion | stationary wall | |
| thermal condition | coupled | |
| Outer Wall | Wall | |
| wall motion | stationary wall | |
| heat flux | 0 W.m-2 | |
| Tubes’ Wall | Wall | |
| wall motion | stationary wall | |
| temperature | 523.15 K | |
| Outlet | Pressure Outlet | |
| gauge pressure | 0 pascal | |
| Methods | ||
| Pressure-Velocity Coupling | Coupled | |
| pressure | second-order | |
| momentum | first-order upwind | |
| energy | first-order upwind | |
| turbulent kinetic energy | first-order upwind | |
| turbulent dissipation rate | first-order upwind | |
| Initialization | ||
| Initialization methods | Standard | |
| gauge pressure | 0 pascal | |
| velocity (axial & radial) | 0 m.s-1 | |
| temperature | 293.15 K | |
Bitumen Melting Results
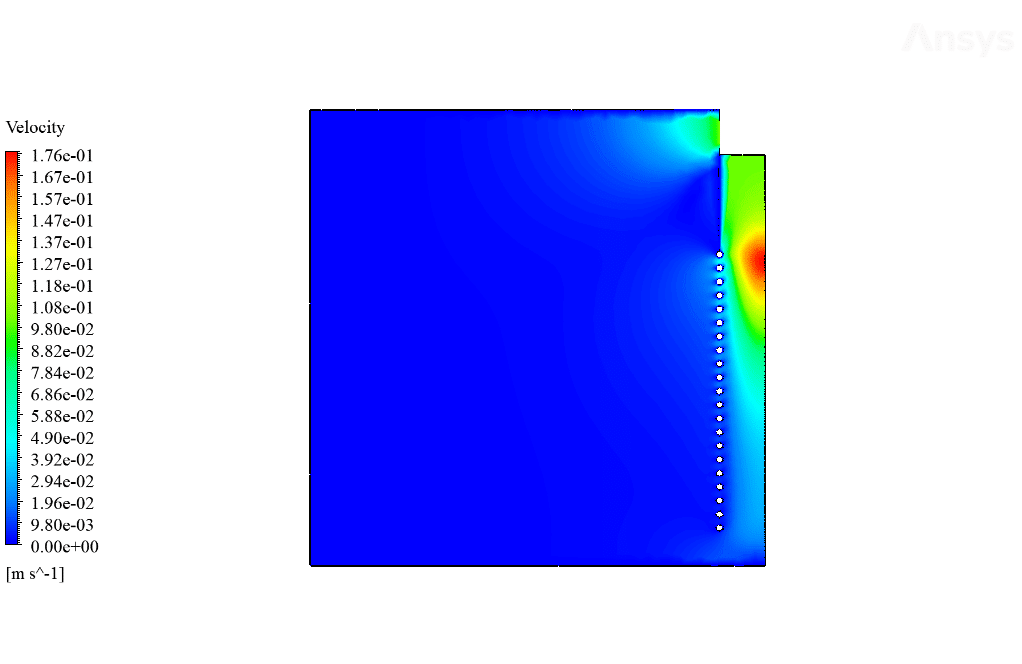
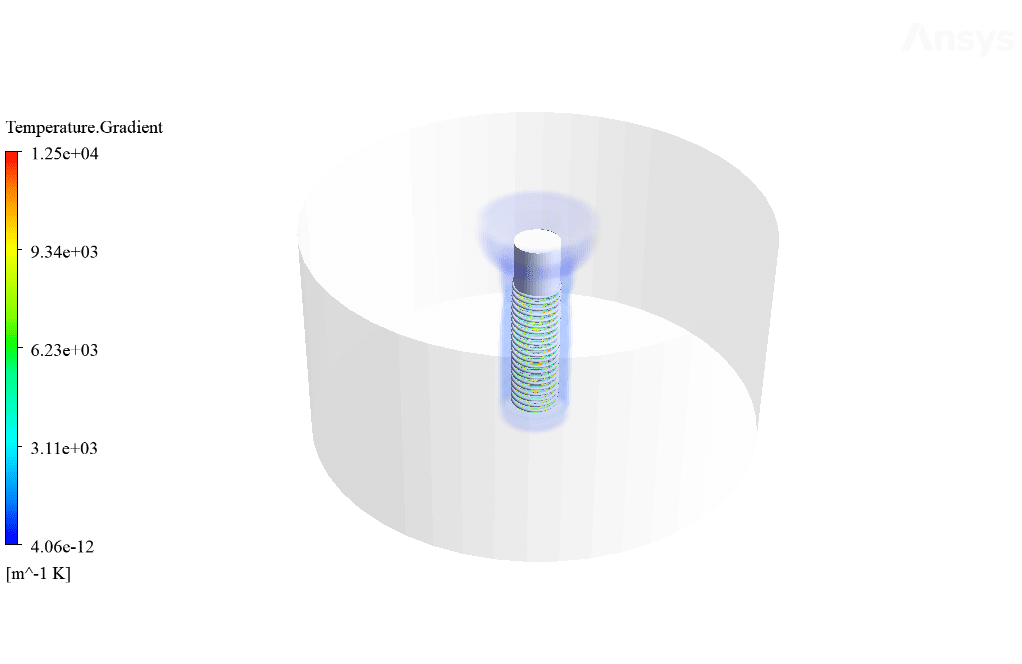
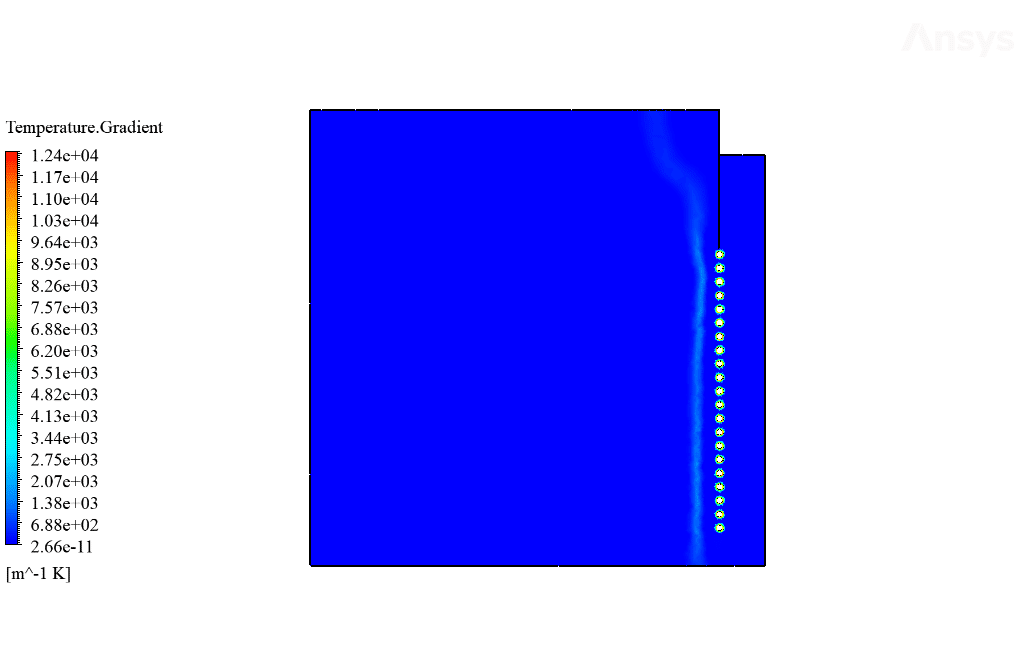
After calculation, 2D and 3D contours related to temperature, temperature gradient, pressure, velocity, liquid fraction, and liquid fraction gradient are obtained. The contours show that in the vicinity of the hot pipes, the bitumen rises in temperature. An increase in temperature causes the bitumen to begin to melt. As a result, it prevents the bitumen from freezing.
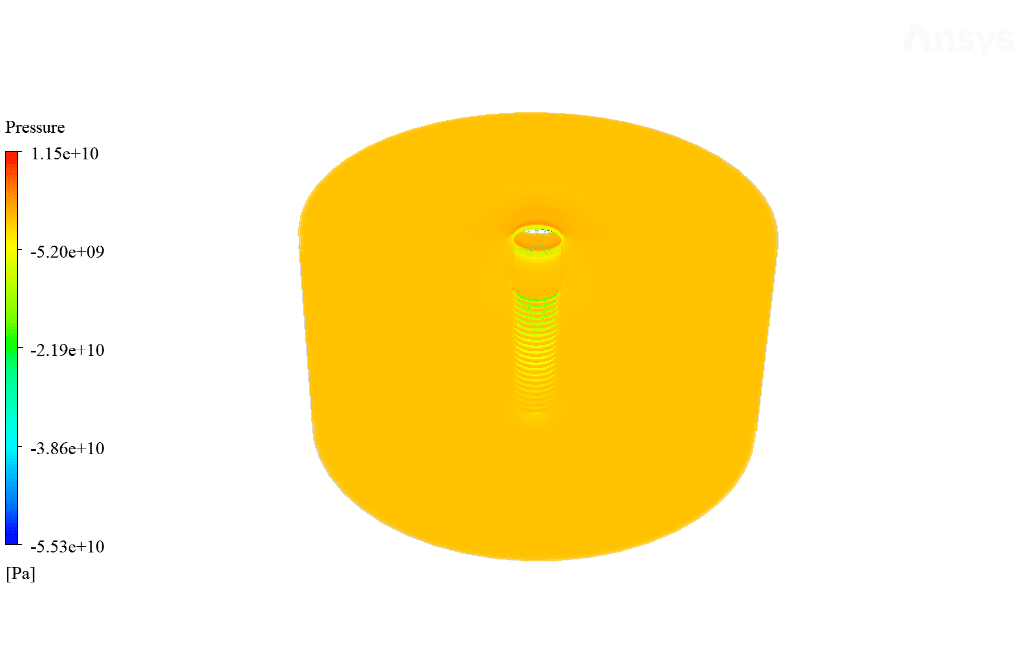

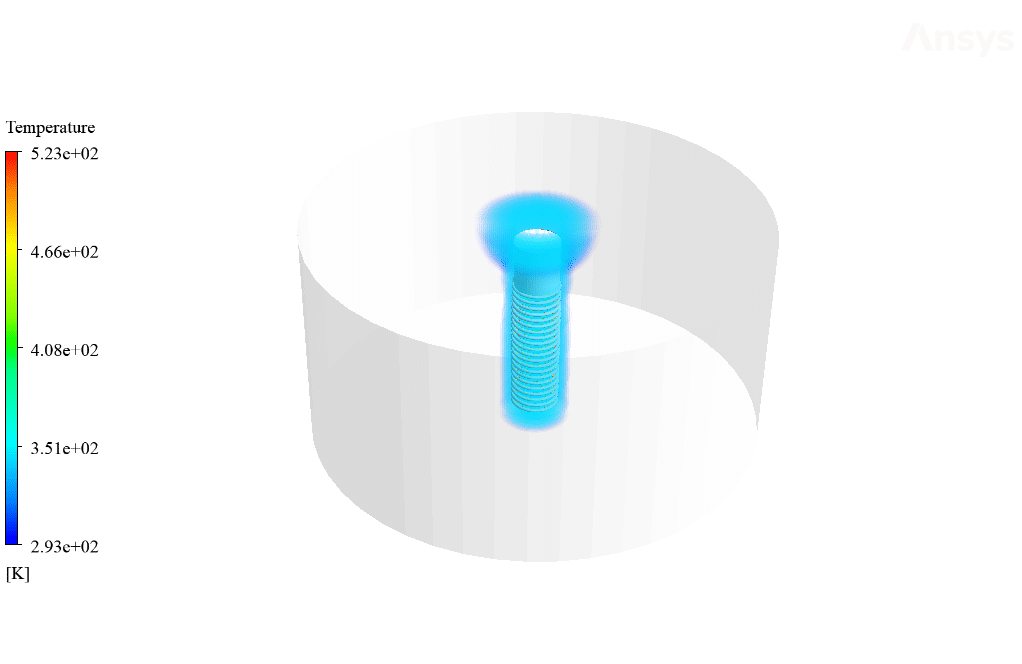
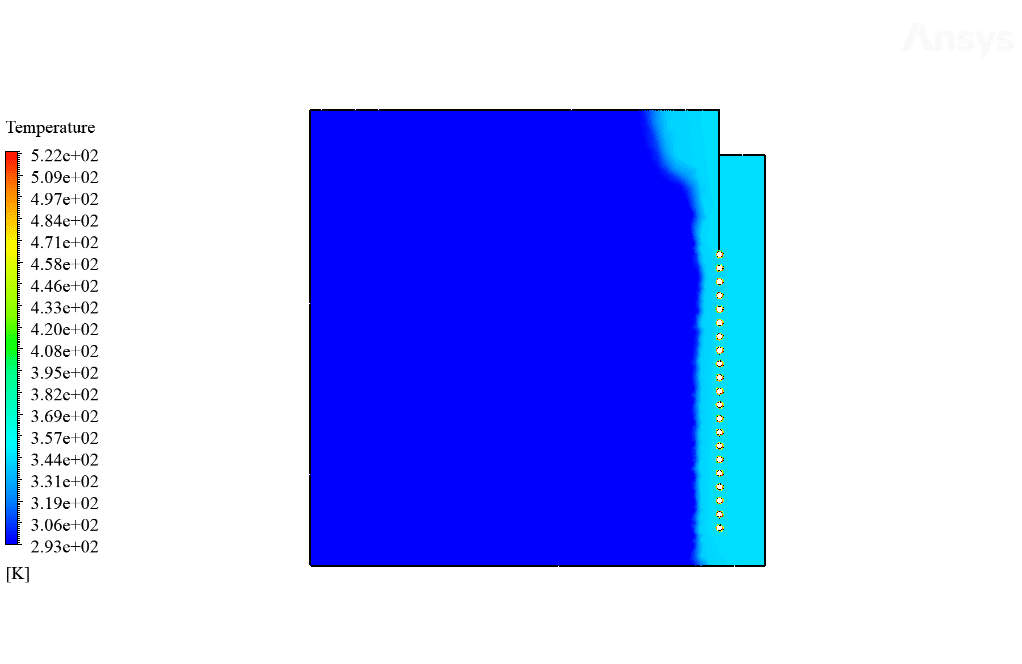

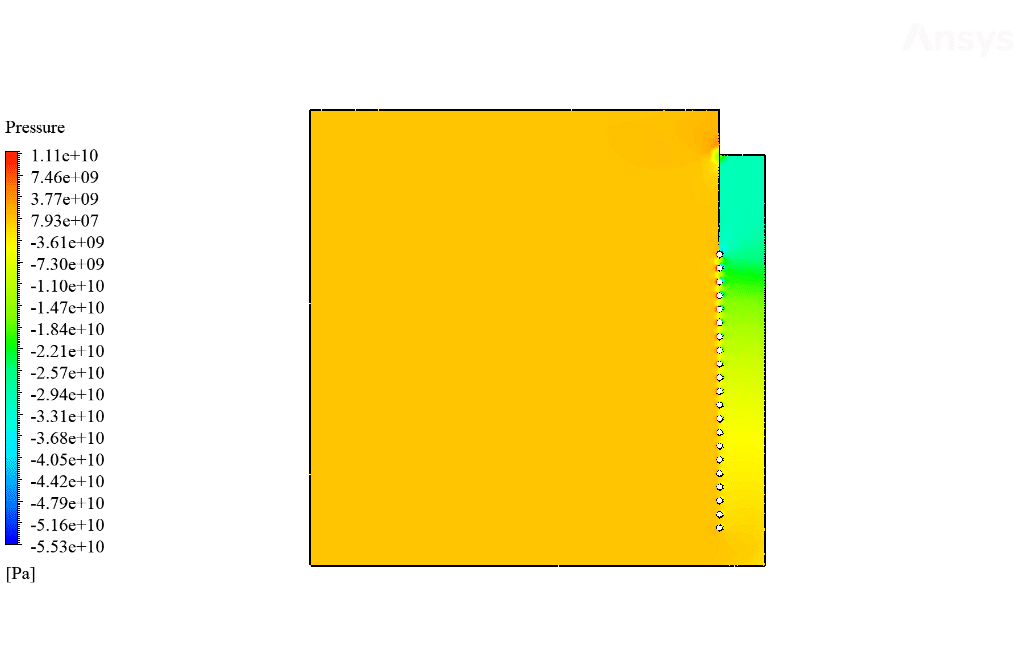
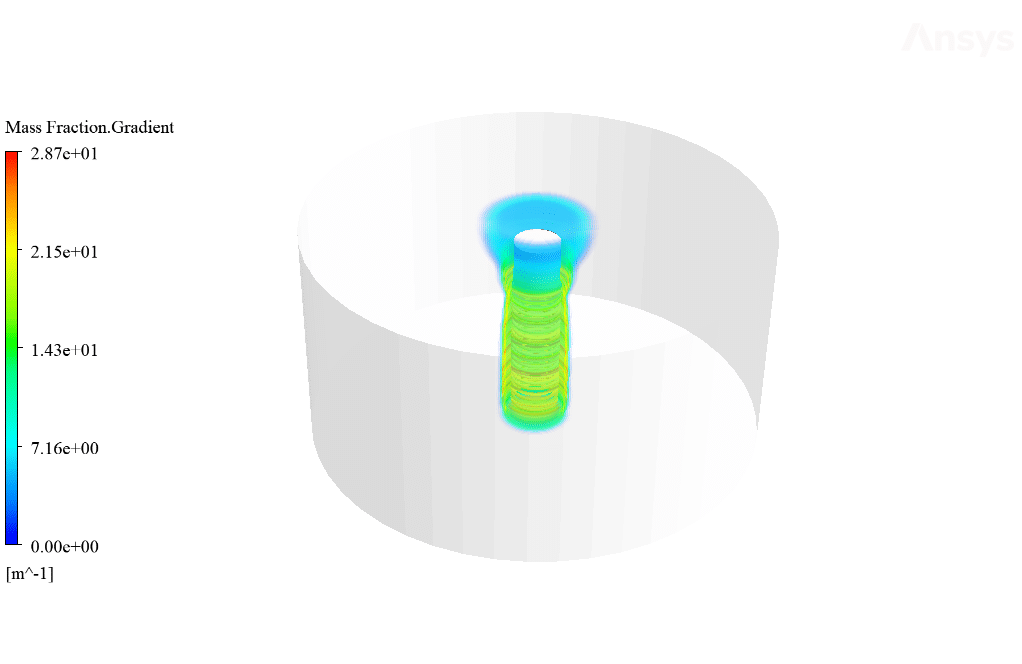
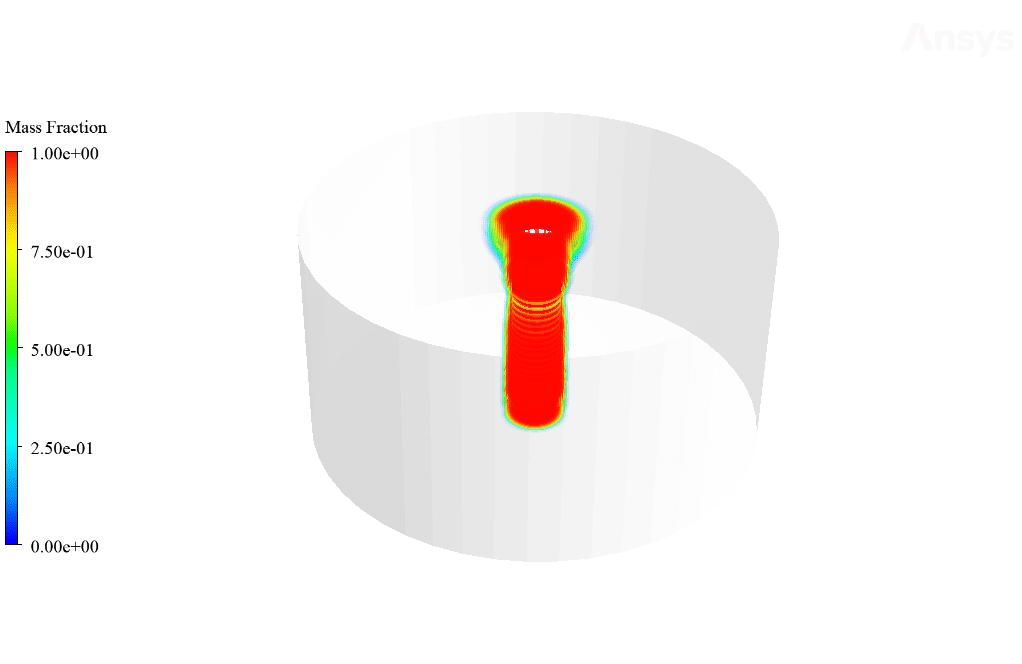
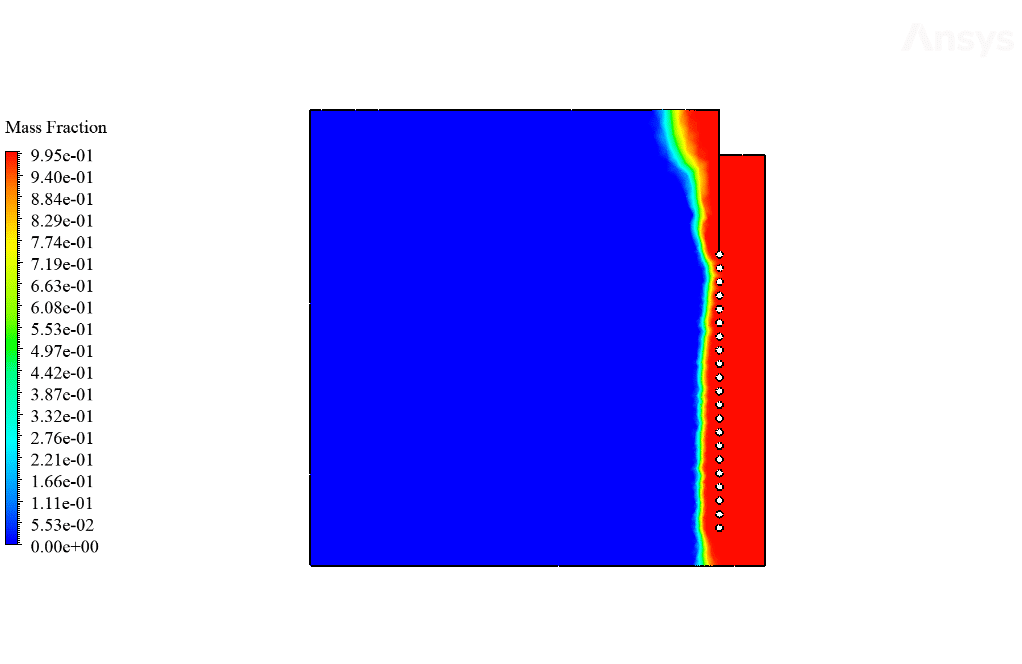
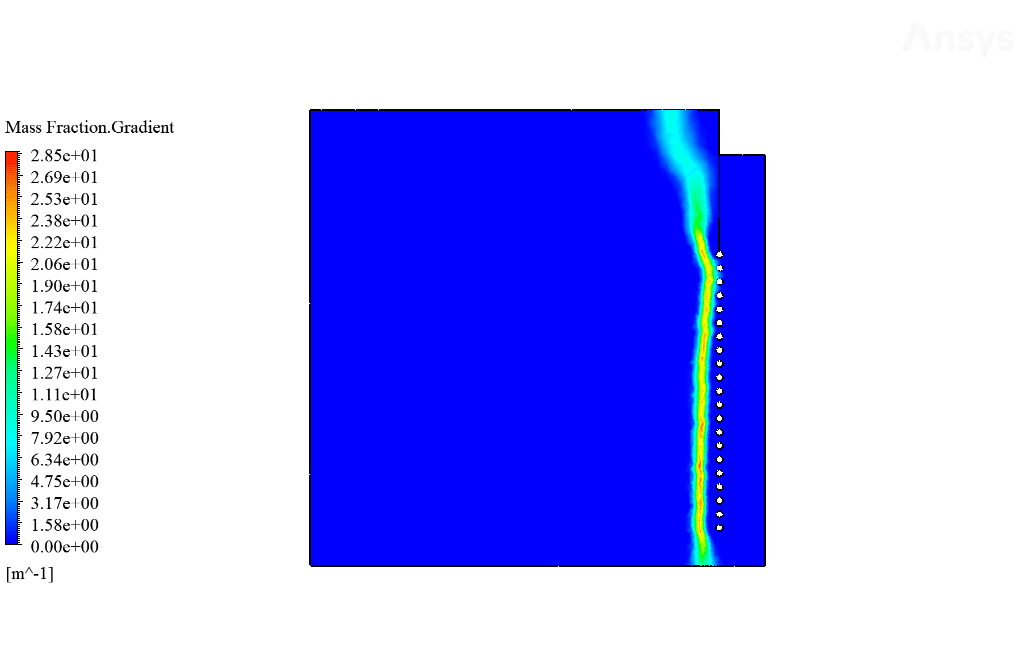

Ulices Purdy IV –
I am very impressed by the clarity of the process on how the bitumen freezing problem is addressed using hot water flow pipes. It is fascinating to see how computational simulations like this can inform and optimize practical industrial processes.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for taking the time to review our Bitumen Melting CFD simulation training. We’re delighted to hear that you are impressed with the practical applications of the simulation and appreciate the clarity of the presentation. It’s feedback like yours that affirm the value of our efforts. If you have any further questions or need further assistance, please do not hesitate to reach out.
Prof. Jazmyne Farrell –
I was truly impressed by the clarity and thoroughness of the bitumen melting simulation. The detailed setup and the resulting contours provide great insights!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you! We’re pleased to hear that you found the simulation details clear and insightful. Your positive feedback is highly appreciated, and we hope our products continue to meet your expectations!
Alanis Luettgen –
I’ve learned so much about bitumen melting from your simulation! Thanks for the comprehensive training materials and the effective teaching strategy that helped me fully grasp the concept.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are delighted to hear that our training materials on ‘Bitumen Melting Inside a Tank’ using ANSYS Fluent were helpful to you. Our team works hard to create comprehensive and user-friendly educational content, and it’s always rewarding to receive positive feedback. If you have any further questions or need more assistance, feel free to reach out!
Tristin Marks –
I am impressed with the thorough set-up for the bitumen tank simulation! Can you explain why the gravity effect was ignored in this simulation?
MR CFD Support –
The effect of gravity was likely ignored in this simulation because the primary focus was on the heat transfer and melting process, rather than on the fluid dynamics influenced by gravity. In many simulations where buoyancy or sedimentation are not of primary concern, gravity can be omitted to simplify the computational model. It allows more computational resources to focus on the critical aspects, such as the temperature distribution and phase change in this case.
Leonor Steuber –
This CFD training opened my eyes to the capabilities of ANSYS Fluent in modeling phase change phenomena! It’s astonishing how accurately the temperature gradients and melting effects of bitumen were captured, which paves the way for better designing and operating bitumen tanks with more efficiency.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our ANSYS Fluent training on bitumen melting was informative and eye-opening for you. Understanding phase change in materials is crucial for industrial applications, and we’re glad that this simulation could effectively demonstrate these effects. Your appreciation motivates us to keep providing quality educational content.
Oswaldo Schamberger –
Bravo on such a thorough simulation training! The level of specificity in temperature ranges for the phase change and the careful attention to the meshing details shows significant expertise on MR CFD’s part. It seems like an invaluable resource for understanding heat transfer in industrial applications.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to know that the specifics of the bitumen melting simulation — from phase changes to meshing quality — were informative and useful for your understanding of heat transfer processes. Your recognition underscores our dedication to delivering high-quality CFD training and simulations to assist with real-world industrial challenges.
Mrs. Matilde Shields V –
The training product covers bitumen melting simulation. The CF analysis helped immensely to understand the phase change. I appreciate the detailed approach captured in both the 2D and 3D contours.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to hear that our bitumen melting simulation training was helpful and that the results provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the phase changing process. If you need any further assistance or have more interest in CFD simulations, don’t hesitate to explore our other products and training modules.
Lavina Brekke –
This is an incredibly detailed simulation on bitumen melting. It’s clear a lot of thought went into setting up the boundary conditions and solidification models. The training must provide a deep dive into phase change materials and their behavior in different conditions.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for taking the time to review our Bitumen Melting CFD Simulation using ANSYS Fluent. We are glad to hear that you found the level of detail and complexity in the simulation impressive. Our goal is to provide thorough training material that deepens understanding of phase change materials under various circumstances. Your feedback is very much appreciated!
Elena Bednar –
The project accurately captures the solidification and melting of bitumen in industrial scenarios. The comprehensive model setup and utilization of ANSYS software allowed me to understand not only the temperature gradients effectively but also the impact of heat pipes intervention—preventing bitumen from freezing. Excellent demonstrations using both 2D and 3D contours efficiently illustrate crucial concepts and results. This simulation serves as a valuable resource for understanding bitumen behavior under thermal influence.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that our Bitumen Melting CFD Simulation training material was informative and effectively illustrated the concepts for you. Your understanding and the practical application of the knowledge are what we aim for, and knowing our efforts are appreciated is highly encouraging. Please, feel free to share more about your CFD journey or reach out if you have any more questions.
Emmanuel Pacocha –
Are the hot water pipes the only source of heat contributing to preventing the bitumen from freezing in the tank, or are there other heating sources applied in this simulation?
MR CFD Support –
Yes, in this simulation the hot water pipes inside the tank are the sole source of heat provided to prevent the bitumen from freezing. There are no other heating sources applied in the simulation.
Laury Rohan Jr. –
The training explains solidification and melting. Does it also teach how to verify the accuracy of the phase change simulation in ANSYS Fluent?
MR CFD Support –
Yes, the training includes evaluating the simulation’s accuracy, focusing on verification techniques such as checking energy conservation, comparing simulation results with known benchmarks or experimental data, and ensuring proper mesh independence.
Benny Ward –
I’ve taken this course recently, and wow, I’m impressed by the depth of information provided. The details in the simulation setup and the step-by-step procedures were so useful. The way phase changes were handled was particularly enlightening. I can tell a lot of hard work went into creating this training module.
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear that you found the Bitumen Melting course enlightening and informative! It is always our goal to provide detailed and practical knowledge that our users can apply to their own projects. Thank you for taking the time to provide such positive feedback. If you need any more assistance or have further inquiries about advanced applications, please don’t hesitate to reach out!