Flap, Two-way FSI, ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation
$210.00 $84.00 HPC
- This product numerically simulates a Flap motion or deformation using ANSYS software.
- This project is implemented as a Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) approach.
- We perform the Fluid simulation in ANSYS Fluent and the Solid simulation in ANSYS Transient Structural.
- The System Coupling is used to define Data Transfer between fluid and structural calculations.
- We use a 2-Way FSI for data transfer in both from fluid to solid and from solid to fluid.
- We design the 3-D model in the Design Modeler software and mesh it in the ANSYS Meshing software.
- We use the Dynamic Mesh option to account for fluid domain deformation.
- The run calculation is in an Unsteady State (transient).
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Description
In this project, we present the CFD simulation of the motion or deformation of a Flap under Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) in ANSYS software.
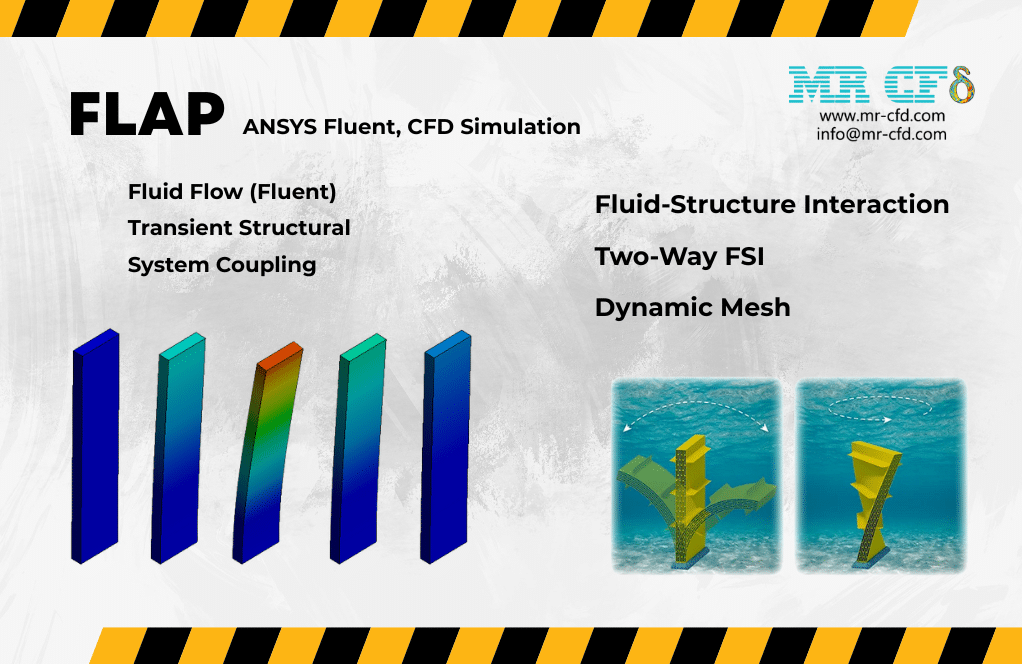
We consider a simple vertical flap exposed to the surrounding airflow. As a result, the hydrodynamic forces from the airflow are imposed on the steel flap body. Therefore, the flap body undergoes deformation, and its external boundaries can be displaced in the airflow.
In such a condition, we need to implement the simulations of the fluid and structure simultaneously. So, we model a computational domain consisting of the fluid zone for the airflow and the solid zone for the flap body. For this, it is known as fluid-structure interaction (FSI).
Since we intend to evaluate both the effect of the hydrodynamic force from the fluid on the flap body and the effect of the deformation and displacement of the solid boundary on the adjacent flowing fluid, we utilize a Two-Way FSI.
Methodology
In the first step, we model the computational domain in Design Modeler software. We design a large-scale domain for fluid flow involving a flap as a solid object inside it. This flap from the bottom becomes a clamped connection to the fluid region and has freedom of motion only from the top and sides.
We use the solid body for simulation in ANSYS Transient Structural and the fluid zone around it for simulation in ANSYS Fluent software.
In the second step, we describe the simulation in Fluent software. Before that, we mesh the fluid domain in ANSYS Meshing software, so that about 500,000 elements are generated.
For FSI simulations in Fluent, we use the Dynamic Mesh model. Since the motion of the solid body causes the mesh deformation in the fluid domain, the dynamic mesh technique allows this deformation to occur over time.
In the dynamic mesh, we apply the System Coupling to the moving structure boundary to define the two-way FSI. Next, we use the Smoothing and Remeshing methods to define how the mesh domain deforms.
In the third step, we describe the simulation in Mechanical (Transient Structural) software.
We define the clamped component of the flap structure as a Fixed Support at the bottom. However, we define the outer wall of the flap body as a System Coupling Region. As a result, the flap structure is allowed to move under the influence of the airflow in all directions, except for the constrained base.
In the final step, we describe the procedure in the System Coupling tool. By this, the Fluent and mechanical calculations are linked.
In the coupling system, we define two Data Transfers. One is the data transfer in the form of Force from fluid to structural, and the other is the data transfer in the form of Displacement, from structural to fluid.
It means that first the fluid flow exerts a force on the structure body, and then the structure undergoes displacement and affects the fluid adjacent to it.
Conclusion
After the calculation process, we represent both Fluid analysis and Structural analysis.
So, in Transient Structural, we obtain the contours of Total Deformation and Von Mises Stress on the flap structure body. The behavior of the flap structure shows the deformation and movement of the flap body over time under the influence of hydrodynamic forces.
In addition, the results demonstrate that the maximum deformation occurs in the upper part of the flap, which has the highest degree of freedom, while the maximum stress appears on the lower part of the flap, which is due to the fixed support.
However, in Fluent, we obtain the Pressure and Velocity distribution of the airflow around the flap, as well as the surface pressure on the flap body. These contours are specific to the last second of the calculation process.
You must be logged in to post a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.