Francis Turbine Acoustics Analysis, ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Training
$200.00 Student Discount
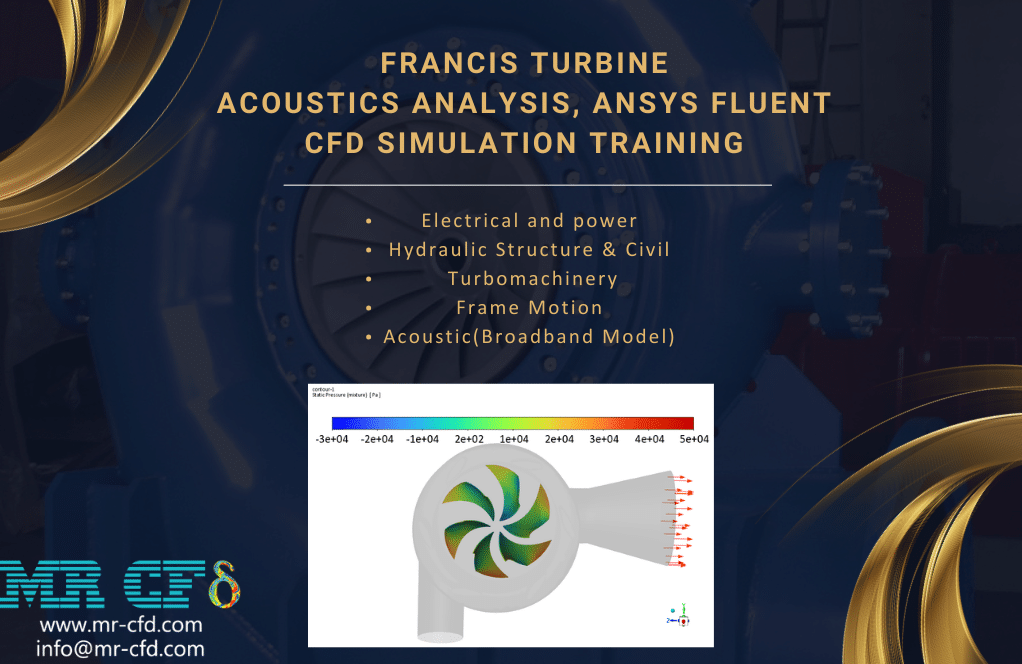
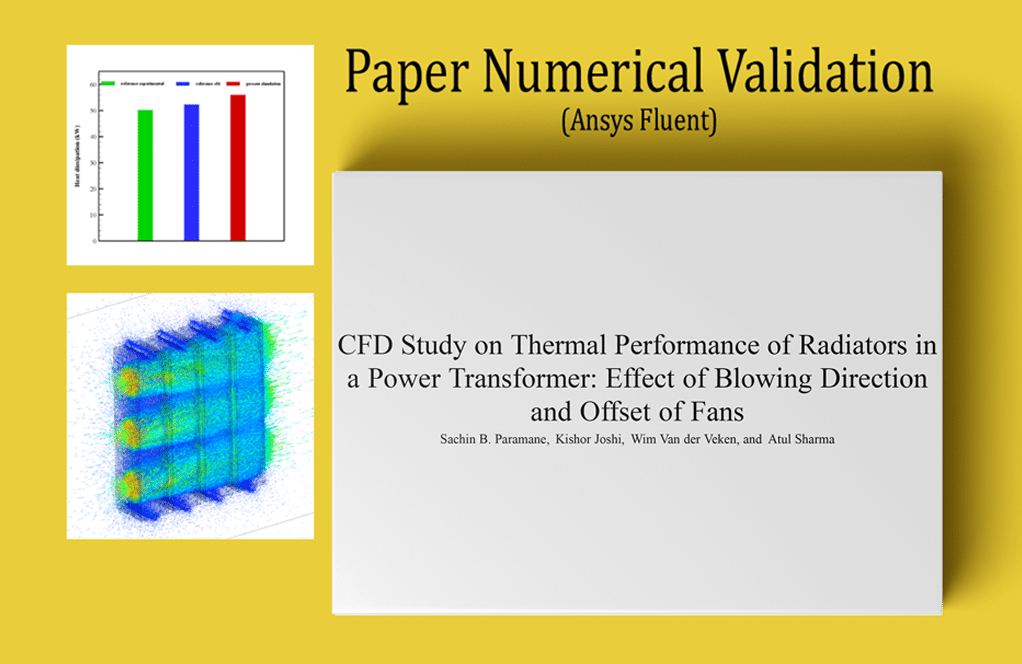
- The present problem simulates the aeroacoustics and sound generation by a water flow inside a Francis Turbine using ANSYS Fluent software.
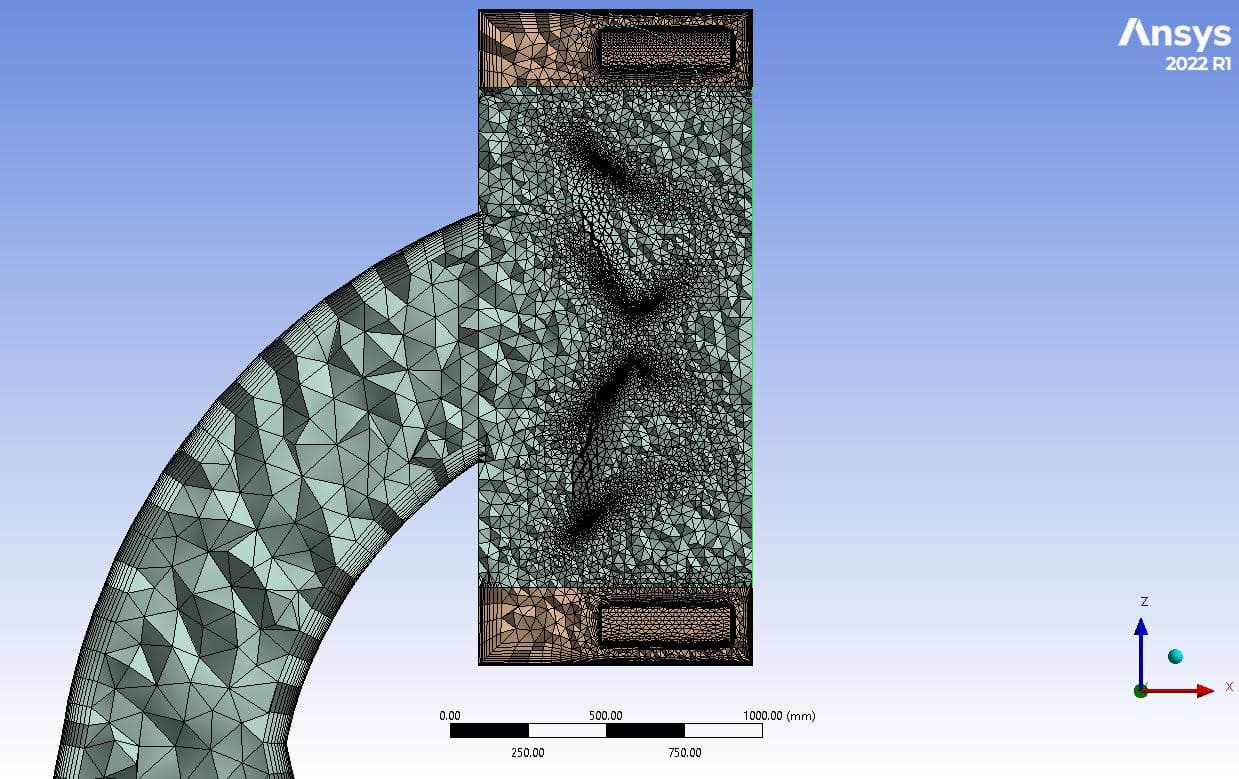
- We have designed the geometry using ANSYS Design Modeler software and created the mesh on this geometry using ANSYS Meshing software. The mesh type is unstructured with 4,914,404cells.
- We use the Frame Motion (MRF) to define rotation movement.
- We use the VOF Multi-Phase Model to define water liquid and water vapor.
- The Broadband Noise Sources model is also used to define the acoustic model
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Francis Turbine Acoustics Analysis, ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Training
description
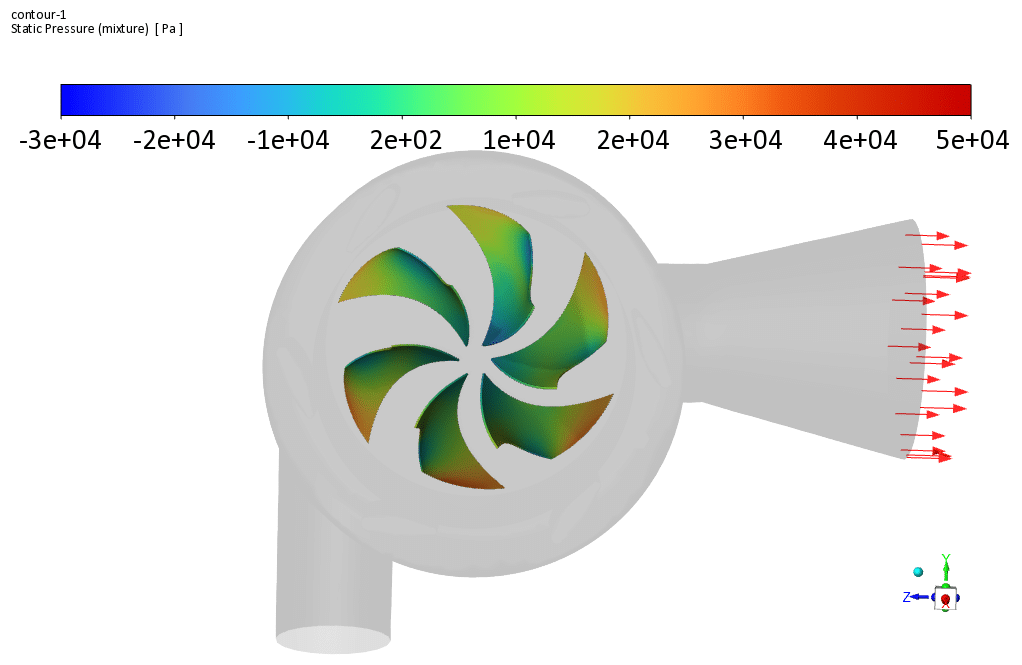
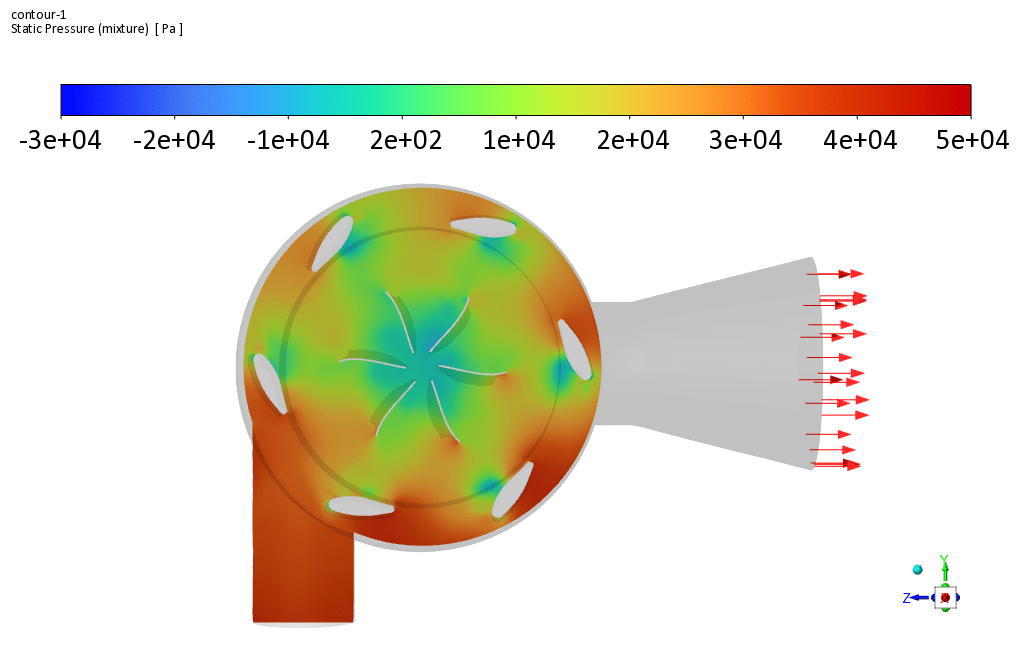
Francis turbines are one of the types of water turbines that can use kinetic and potential energy for power generation at the same time due to the location of their blades.
In this type of turbine, water flows into the spiral chamber because, due to the blades’ circular structure, the flow of fluid colliding with the blades must be rotational to improve the system’s operational efficiency. The water flow is then transferred to the turbine runner blades with a specific flow rate, and as a result, the desired work is produced by rotating these blades by the water flow.
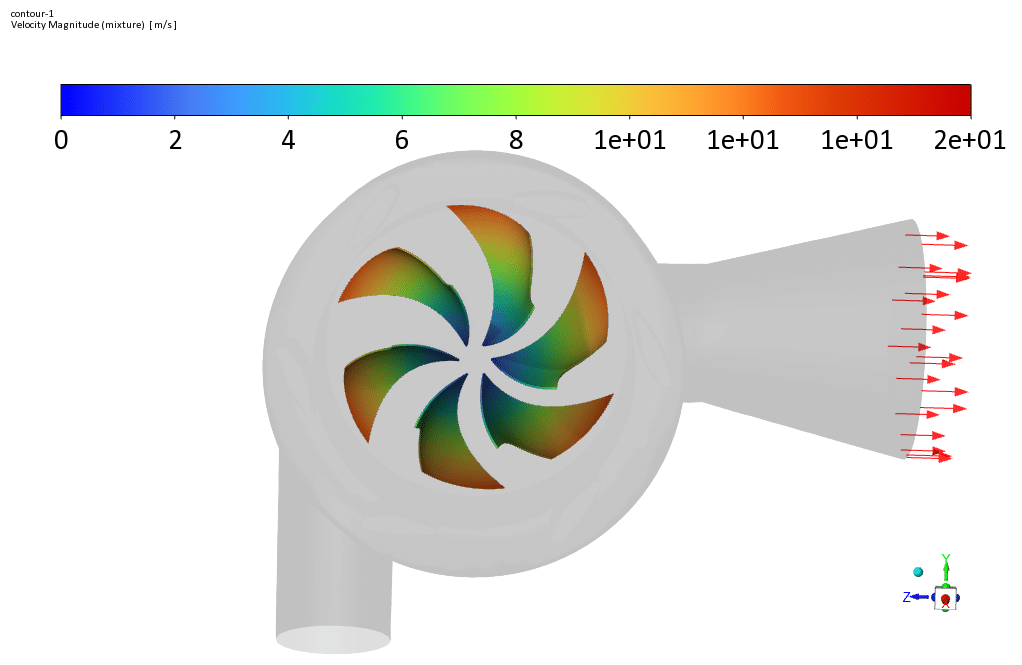
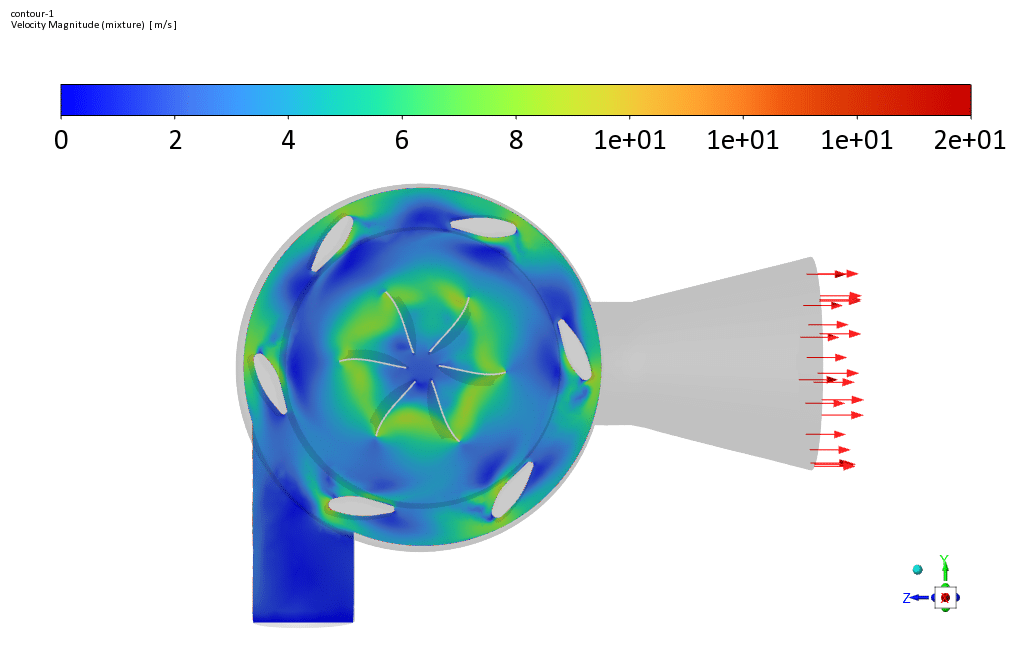
Finally, the outflow of water from the turbine runner blades will be axial. In the present simulation, a flow of water with a mass flow rate of 1.996 m/s enters the turbine’s inner chamber with a rotational speed of 158 rpm for the blades.
The geometry is designed using Design Modeler software. In the design of the present model, two main parts have been considered, which include fixed walls that have fixed vanes with fixed angles and moving walls that have rotating vanes.
The model meshing has been done using ANSYS Meshing software, and the mesh type is unstructured. The element number is 4,914,404. Also, the mesh quality is considered finer in the areas close to the blades.
Methodology
Frame motion (MRF) defines the blades’ rotation inside the chamber and creates the resulting rotational flow around the blades. It is assumed that the area of water flow around the blades has a rotational motion relative to the blades, While the rotating blades have a rotational speed of zero relative to this rotating area.
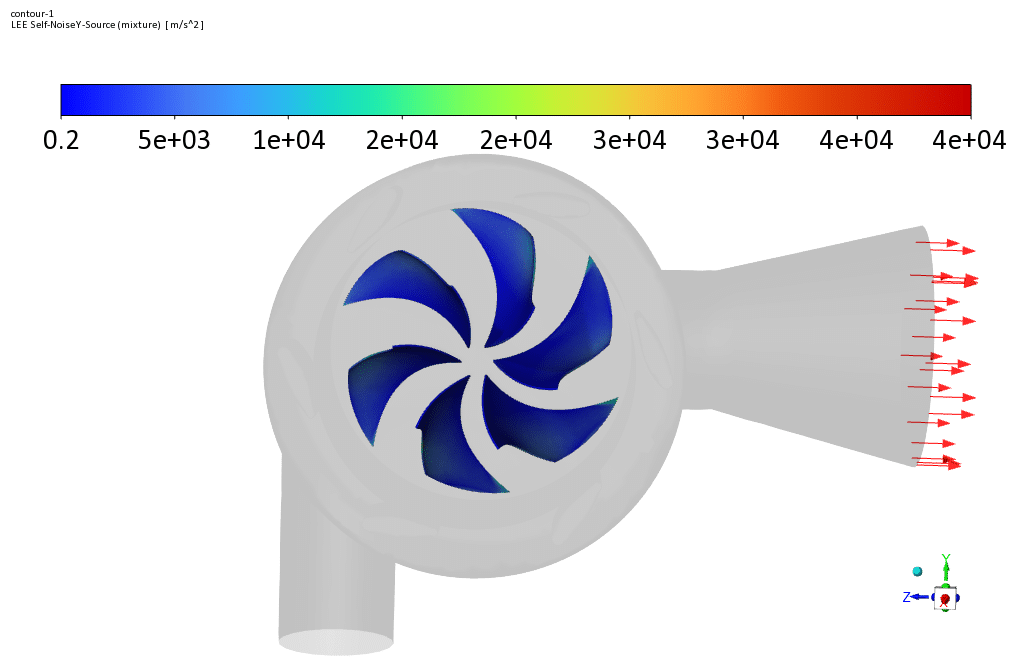
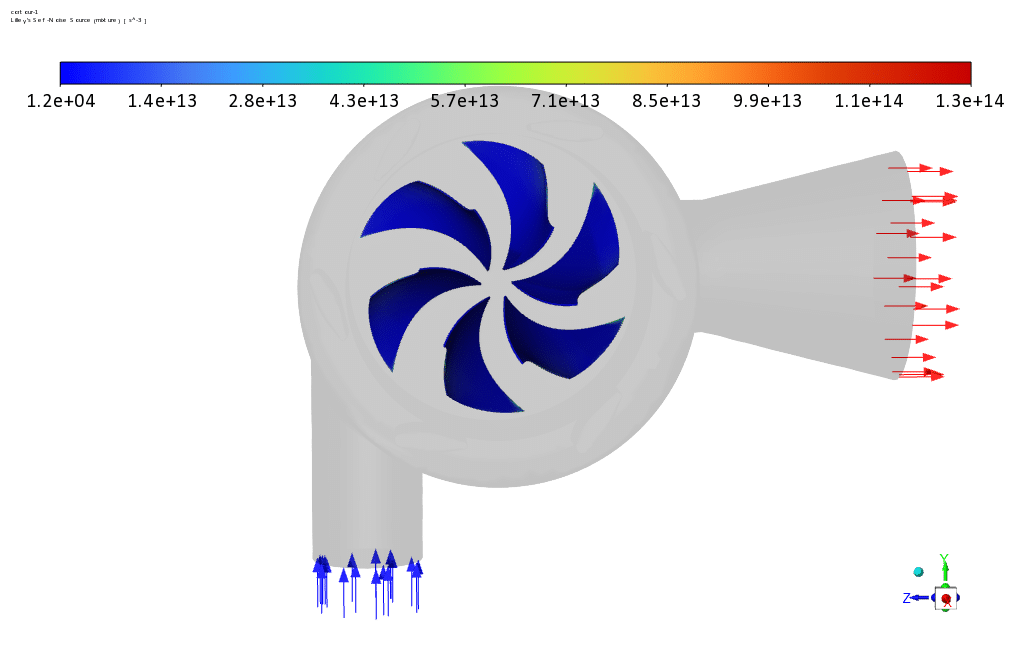
We use the VOF Multi-Phase Model to define water liquid and water vapor. The Broadband Noise Sources model is used to define the acoustic model.
Conclusion
Since we have investigated the issue of the turbomachine in this case already, this acoustic review continues on the same settings.
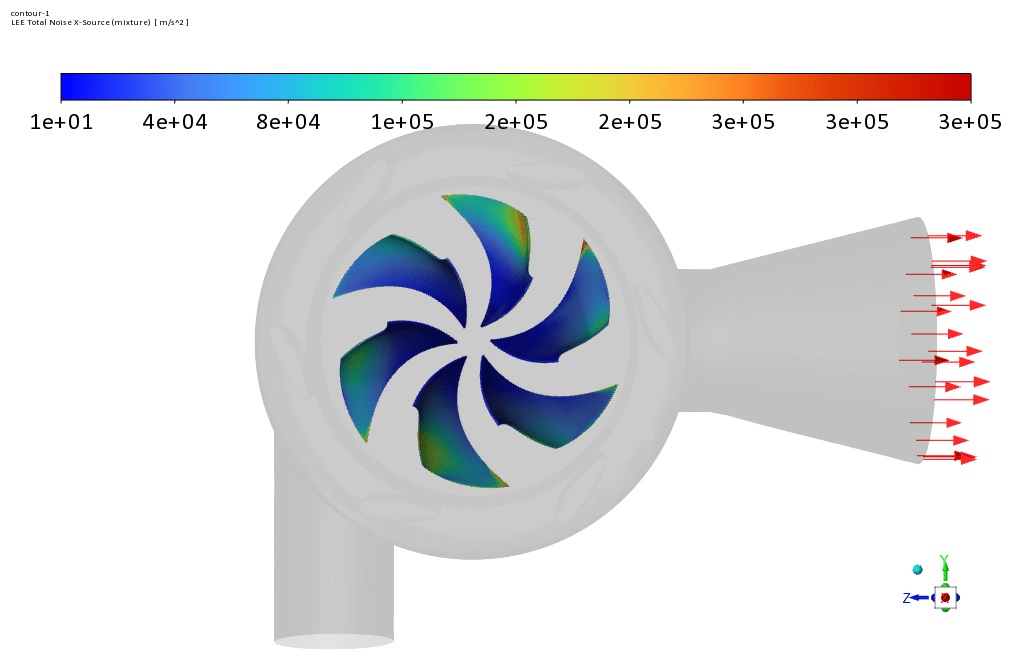
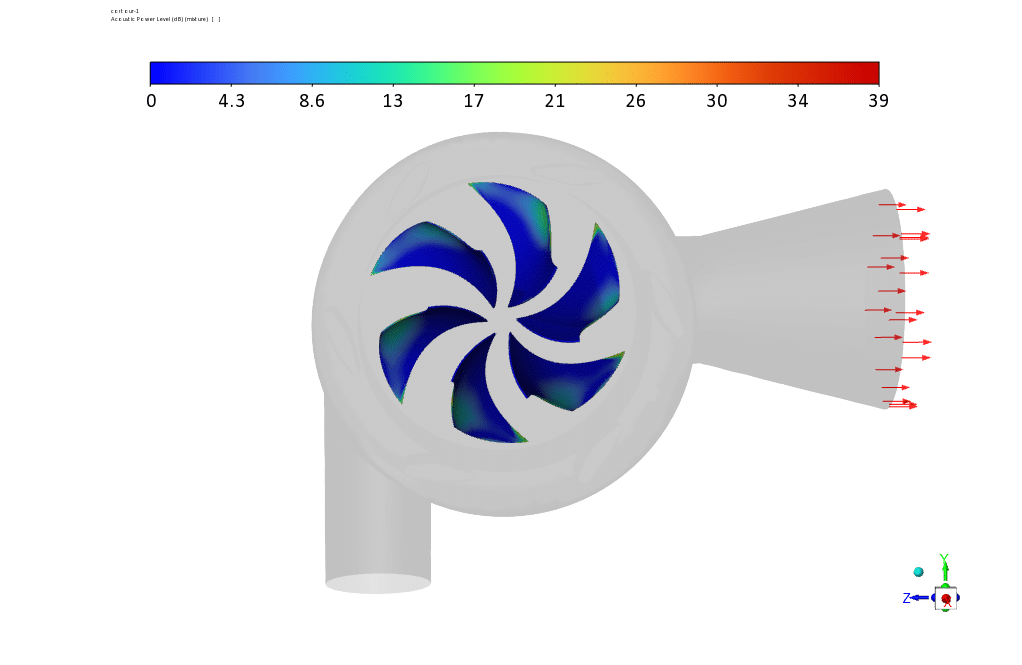
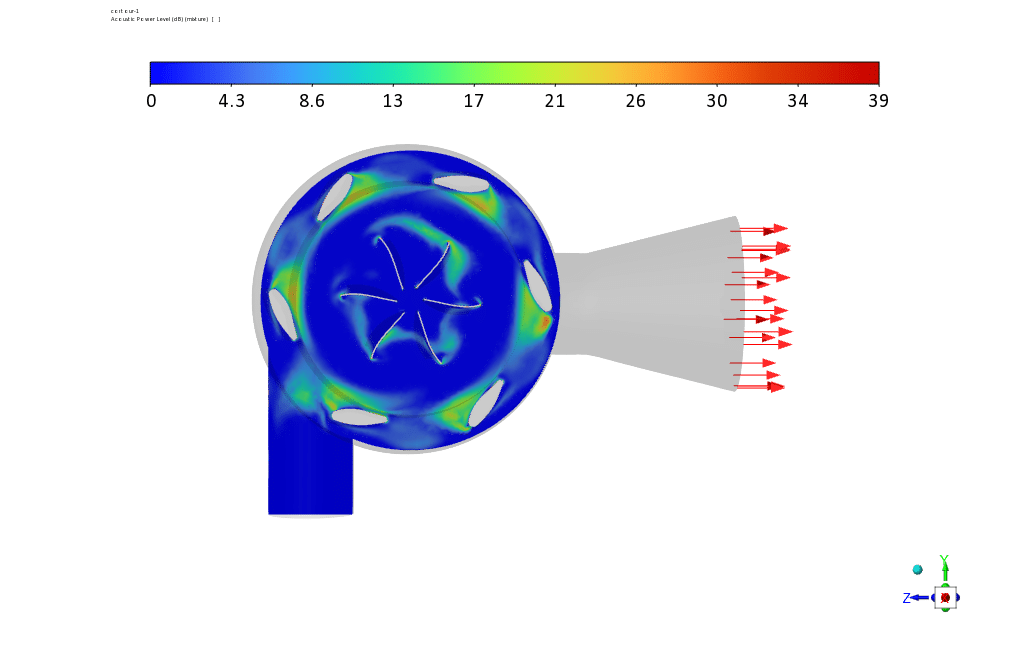
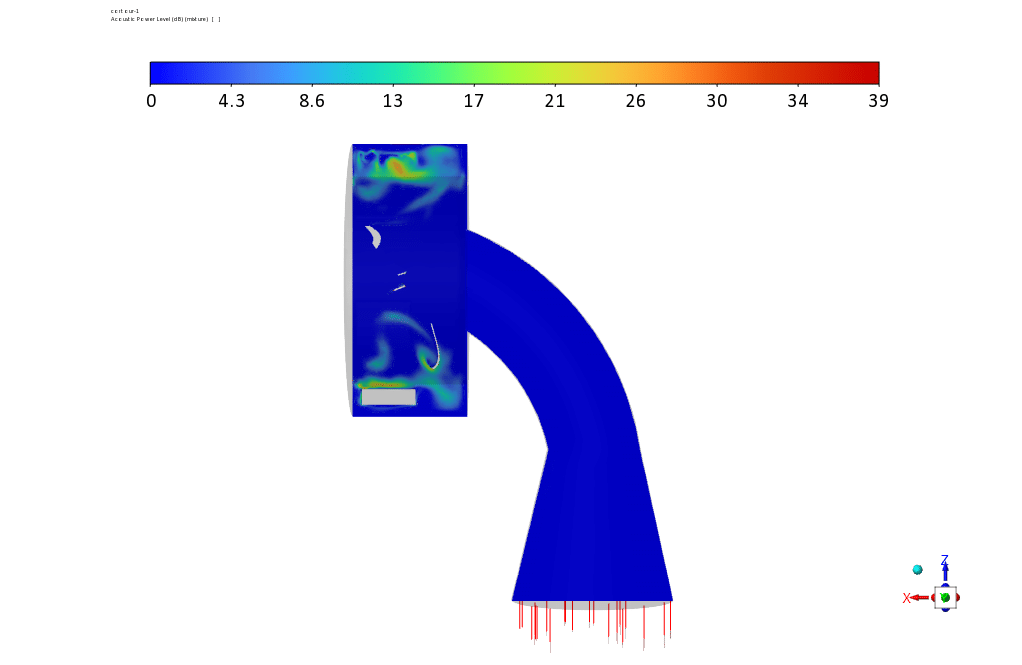
Observations show that the rotors have a greater share of the components that create sound and show more acoustic power in the related contour. Contour linear Euler’s equations show how fast the sound propagates in the space between the rotor and the stator.
Ahmad Rutherford –
I was truly impressed with the thoroughness of the Francis Turbine Acoustics Analysis CFD Simulation training. The methodology incorporating Frame Motion to simulate blade rotation creates a highly realistic depiction of operational dynamics. Outstanding work!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words and for recognizing the effort we put into creating detailed simulations. We’re really glad to hear that you found the training both impressive and valuable!
Tate Jacobson –
The thoroughness of the simulation training for the Francis Turbine is an asset to any engineer’s education. The detail about meshing and the use of MRF were particularly absorbing, and the acoustic analysis adds a crucial, often overlooked aspect to turbine design.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your compliment on our Francis Turbine Acoustics Analysis training material. We’re delighted to hear that our attention to detail and incorporation of comprehensive acoustic analysis has been valuable in your engineering studies. We appreciate your feedback!
Berta Jaskolski –
The tutorial provided clear examples and results illustrating acoustics in Francis Turbines. I was quite impressed with the elucidation of complex topics such as Broadband Noise Sources and the use of rotational frame motion.
MR CFD Support –
We greatly appreciate your kind words and are thrilled to know that the training for Acoustics Analysis of Francis Turbine using ANSYS Fluent was helpful to you. Your satisfaction with our tutorial is our top priority. Thank you for taking the time to provide your feedback!
Aglae Russel DVM –
The training for the Francis turbine simulation was very comprehensive. The practical application of the Model Frame of Reference and the acoustic analysis was particularly enlightening. I managed to apply the acquired knowledge in my own turbine project with excellent results.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback on our Francis Turbine Acoustics Analysis training! We’re delighted to hear that you were able to successfully apply the concepts learned to your own projects. Your success is our greatest reward. Keep up the great work!
Miss America Homenick II –
What’s the importance of the Broadband Noise Sources model in this simulation, and can the sound propagation affect the efficiency of the Francis turbine in practice?
MR CFD Support –
The Broadband Noise Sources model is crucial for predicting the location and strength of sound sources within the flow, which relates to the turbulence-generated noise. Sound propagation can contribute to the overall vibration and noise levels in the surrounding environment, potentially impacting stability, lifespan, and environmental factors. In practice, while acoustic energy is typically much less than the kinetic energy converted in the turbine, understanding the noise characteristic helps in designing quieter and more environmentally friendly installations while maintaining efficiency.
Kattie Bahringer –
This training sounds fascinating! I’m eager to learn more about the analysis. Could you please explain a bit about how the Broadband Noise Sources model contributes to understanding the turbine acoustics in this simulation?
MR CFD Support –
Certainly! The Broadband Noise Sources model is crucial in predicting acoustic noise in turbulent flows, such as those in turbine systems. In this simulation, it helps calculate the generation and propagation of noise based on the flow field data. By analyzing the sources of broadband noise within the turbine, we gain insights into the noise characteristics, highlighting which components – such as the rotors – generate more sound. This information is vital for optimizing turbine designs to reduce noise levels, enhancing their environmental and operational compatibility.
Laila Luettgen IV –
I really learned a lot about Francis turbines and the acoustic analysis in this CFD simulation training. The detailed presentation of the methodology including the use of the VOF model for multiphase simulation and the MRF concept for blade motion was incredibly beneficial. The sound propagation visualizations were particularly illuminating and enhanced my understanding of the complexities within turbine acoustics!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive review! We are thrilled to hear that the training has contributed to your understanding of Francis turbines and acoustics analysis. It is rewarding to know that our detailed presentation and visualizations have enhanced your CFD simulation knowledge. If you require further training or have any more questions, please don’t hesitate to reach out. Your success is very important to us!
Kenton Daniel –
The training content was quite extensive. The step-by-step explanation of the simulation setup for the Francis Turbine, particularly the mingling of kinetic and potential energy for power generation was enlightening. Appreciated the nuances in the design considerations for the fixed and rotating vanes, which seems crucial for capturing the acoustics accurately. Also, the high fidelity of the unstructured mesh was keenly instrumental for the correct acoustical analyses, great job on maintaining quality there. The inclusion of rotor-stator interaction in the acoustic analysis added depth to the overall understanding.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback on the Francis Turbine Acoustic Analysis training module. We’re thrilled to know that the detailed content and the methodologies applied in the simulation provided you with clear insights into the workings of the turbine. Your appreciation for the mesh quality and the in-depth analysis of rotor-stator acoustics is greatly valued. It’s always our goal to deliver comprehensive training that not only guides you through the process but also enhances your understanding of the complex dynamics involved in CFD simulations.
Lewis Lehner –
Absolutely fascinating how you covered the acoustics analysis of a Francis Turbine using ANSYS Fluent. The detail on using the MRF and Broadband Noise Sources model for such complex simulations is impressive, and the inclusions regarding sound propagation speed add invaluable depth. Thank you for offering a resource that merges the technical robustness of mechanical design with the precision of acoustic analysis. Great work!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you very much for your kind words. We’re thrilled to hear that you found the Francis Turbine Acoustics Analysis training both thorough and informative. We’re dedicated to providing high-quality resources that bridge complex topics with ease of understanding. Your feedback is greatly appreciated, and we look forward to helping you with any future learning endeavors!
Thalia Spencer DDS –
I appreciate the detailed explanations of the Francis Turbine Acoustics Analysis training. The insights gained from both hydrodynamic and acoustic modeling aspects were incredibly useful for my research on turbine efficiency and noise pollution.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your feedback! We’re delighted to hear that the Francis Turbine Acoustics Analysis training proved beneficial for your research. If you have any questions in the future or need further assistance, please don’t hesitate to reach out. Your success is our top priority.
Terrance Mann –
I’m amazed at the impressive level of detail in this simulation training. The inclusion of the acoustic analysis adds a valuable dimension to understanding Francis Turbines. Great job!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback. We are delighted to hear that you appreciate the level of detail in our simulation training and found the acoustic analysis component beneficial. Understanding every aspect of the simulation is crucial, and we are glad to provide valuable insights into Francis Turbines. If you have any further questions or need assistance, feel free to reach out!
Jennie Walsh IV –
The Francis Turbine simulation exceeded my expectations. The detailed acoustic analysis helped me grasp the intricacies of turbine noise generation, and the implementation of the Broadband Noise Sources model was insightful. Excellent work on presenting the complex interaction between fluid dynamics and acoustics in such an understandable manner!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re delighted to hear you found our Francis Turbine acoustics analysis demonstration both insightful and understandable. Our team strives to deliver clear and comprehensive training, so it’s rewarding to know we’re achieving that goal. Your positive feedback motivates us to continue providing high-quality CFD simulation training.