Gas Particle Movement Through the Nozzle Simulation
$100.00 Student Discount
In this project, gas-particles movement through the convergence-divergence nozzle has been simulated and the results of this simulation have been investigated.
Click on Add To Cart and obtain the Geometry file, Mesh file, and a Comprehensive ANSYS Fluent Training Video.To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Gas Particle Movement Through the Nozzle, CFD Simulation Tutorial by Ansys Fluent
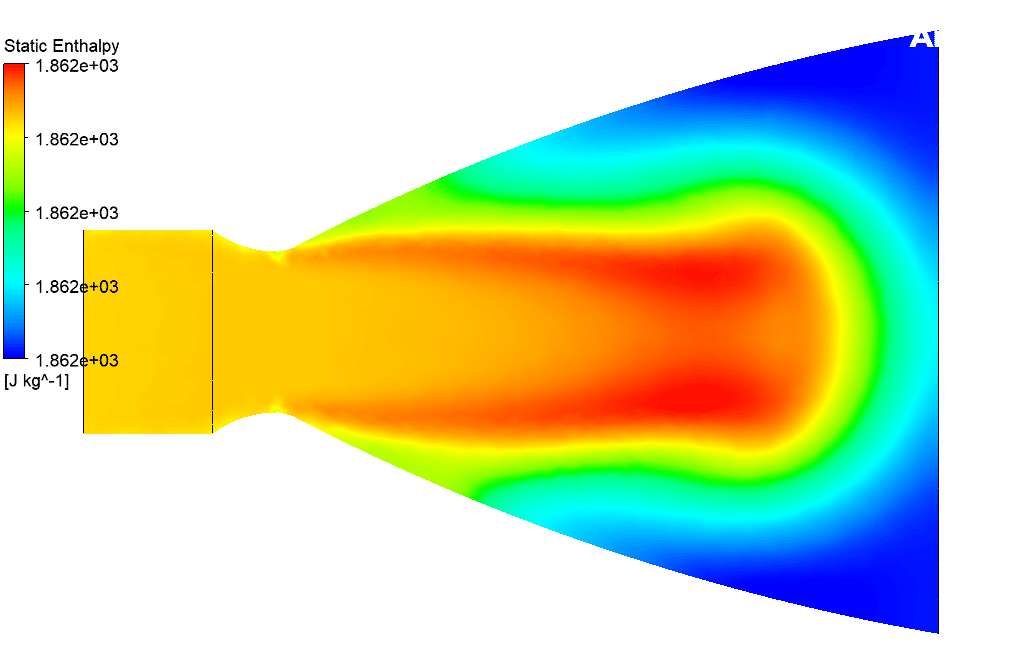
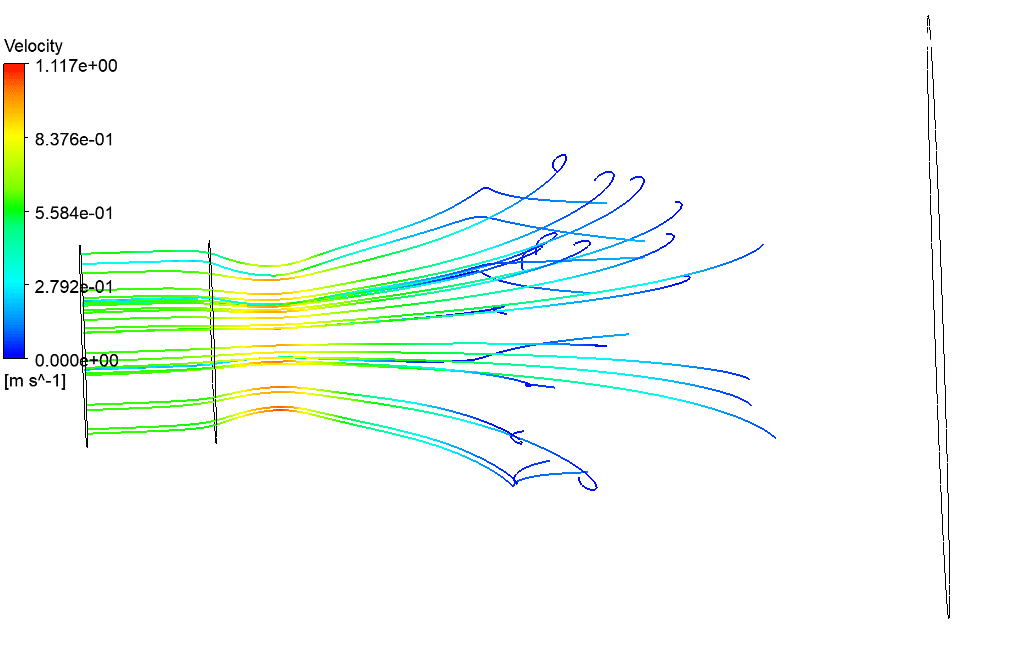
This simulation is modeling gas-particle movement through the convergence-divergence nozzle by a Two-way DPM model in Ansys fluent software. The nozzle is in grossly overexpanded condition. These kinds of nozzles are used in the gas and petrochemical industry.
Geometry & Mesh
The 3-D geometry of the present model is carried out using Design Modeler software.
The meshing of this present model has been generated by ANSYS Meshing software. The mesh grid is unstructured, and the total cell number is 16245216.
Gas Particles Movement CFD Simulation
To simulate the present model, several assumptions are considered, which are:
- The solver is pressure-based.
- Simulation has only examined fluid behavior; in other words, heat transfer simulation has not been performed.
- The gravity effect is ignored.
The following is a summary of the steps for defining the problem and its solution
| Models | |||
| K-epsilon | Viscous model | ||
| Realizable | k-epsilon model | ||
| Scalable wall function | k-epsilon options | ||
| air | primary phase | ||
| Gas | Particle | ||
| explicit | formulation | ||
| Boundary conditions | |||
| Velocity-inlet | inlet | ||
| Discrete phase pressure | escape | ||
| 448000 | initial gauge pressure | ||
| 5 m/s | velocity magnitude | water | |
| Pressure outlet | outlet | ||
| Discrete phase condition | Escape | ||
| 0 | Supersonic gage pressure | water | |
| wall | wall | ||
| stationary wall | wall motion | ||
| Solution Methods | |||
| Phase coupled | pressure-velocity coupling | ||
| PRESTO! | pressure | ||
| first-order upwind | momentum | ||
| first-order upwind | specific dissipation rate | ||
| first-order upwind | volume fraction | ||
| Initialization | |||
| hybrid | initialization method | ||
| 52 m/s | water velocity (0,y,0) | ||
| 0 m/s | particle velocity (x,y,z) | ||
Results
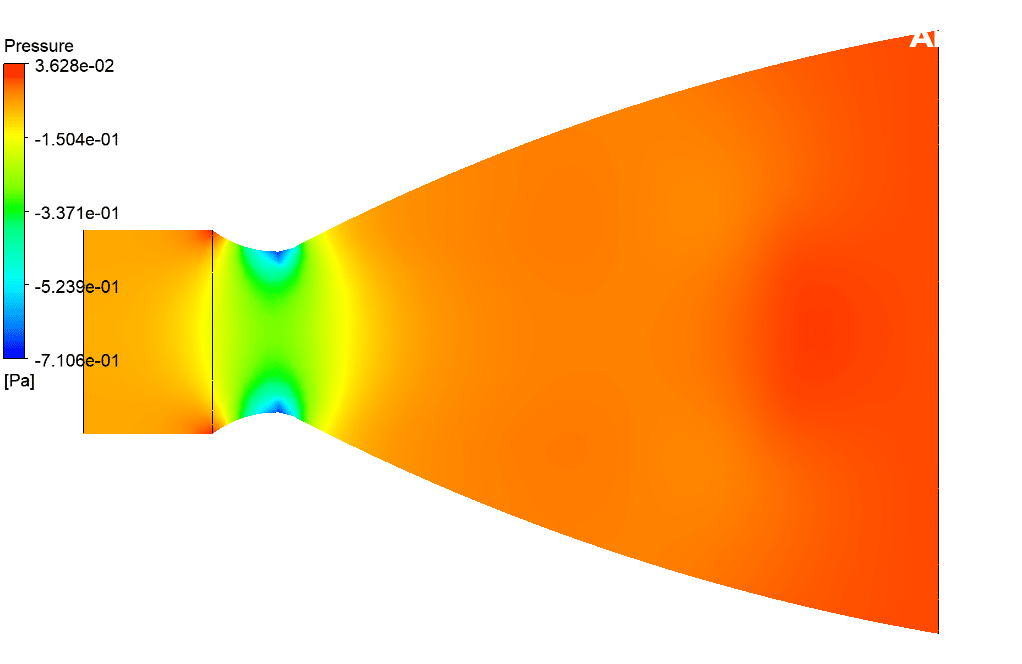
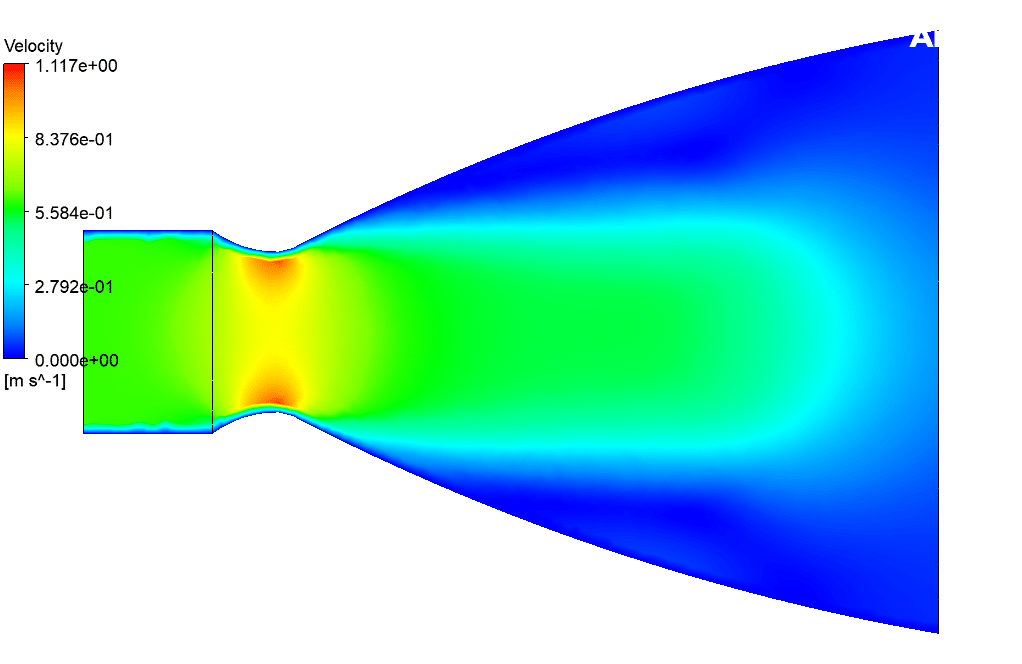
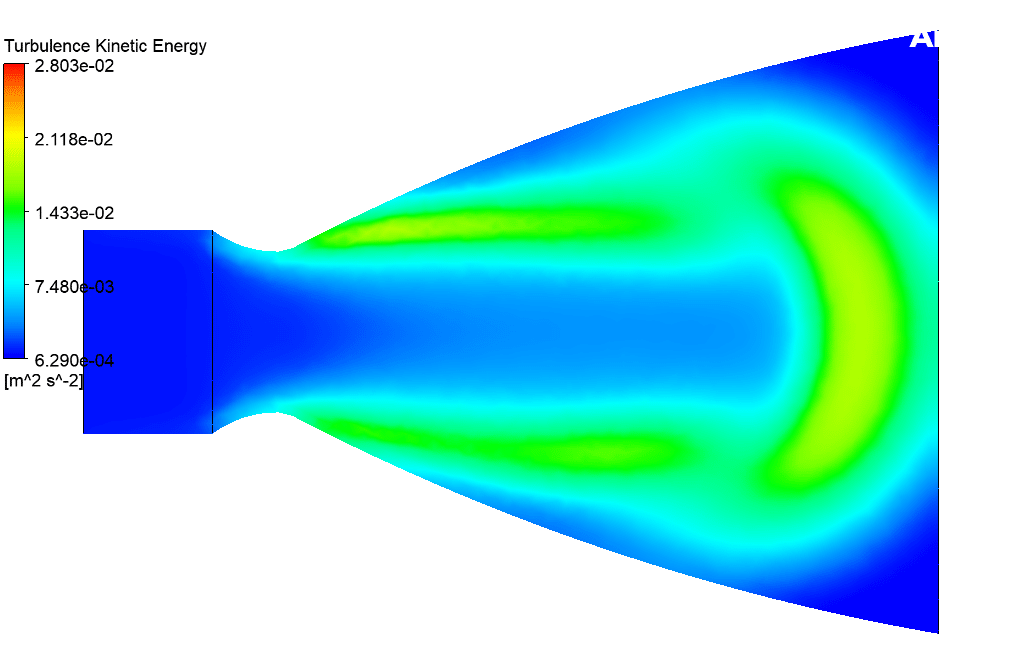
At the end of the solution process, two-dimensional and three-dimensional velocity and static enthalpy and turbulence kinetic energy are obtained. This 3-D simulation shows how gas particles enter the nozzle from the inlet and travel through a nozzle and how the nozzle effect particle velocity in other simulation conditions.



Mrs. Leanne Bergnaum V –
The configuration and methodology of the gas particle movement simulation are quite impressive! The attention to detail in setting up the nozzle’s geometry and the precision in defining the boundary conditions for an overexpanded state reflect a well-thought-out process, well done on this insightful tutorial!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback! We are really glad you found our tutorial on Gas Particle Movement Through the Nozzle insightful and helpful. We always strive to offer detailed and precise simulations to assist in understanding complex concepts. Should you have any more questions or need further clarifications, we’re here to help!
Garland Pouros PhD –
I followed the simulation tutorial and noticed a significant effect of the nozzle on the particle velocity. Could you clarify if secondary phases were considered in the two-way DPM simulation, or was air the only primary phase considered?
MR CFD Support –
The tutorial for the gas particle movement through the nozzle simulates with air as the primary phase and particles as the secondary phase. In the two-way Discrete Phase Model (DPM), interactions between the gas (primary phase) and particles (secondary phase) are considered, meaning that the particles can affect the flow of the gas and vice versa.
Prof. Cleora Heathcote –
I’ve noticed that the heat transfer simulation has not been performed in this study. Can you explain why thermal effects were neglected?
MR CFD Support –
In the analysis of gas particle movement through the nozzle, thermal effects are neglected to simplify the model and focus on the dynamics of the particulate flow. This assumption is common when the primary interest is in analyzing the mechanical behavior of particles under conditions where thermal influences on particle movement and the interaction with the flow are considered negligible.
Dr. Hugh Hodkiewicz Jr. –
I’m thrilled with how detailed the Gas Particle Movement Through the Nozzle Simulation is! The granularity of the gas-particle interactions and the precision of the mesh are particularly impressive, leading to insightful predictions about gas dynamics in industrial applications.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to hear that you’re impressed by the level of detail in the simulation. Our team always strives to provide high-quality and precise CFD simulations to aid in understanding complex fluid dynamics. Your appreciation truly means a lot to us!
Ora Gutmann –
The tutorial seems very comprehensive. Was the erosion of the nozzle due to particle impact also studied in this simulation, or was it strictly gas particle dynamics?
MR CFD Support –
In the given simulation, the primary focus is on gas particle dynamics through the nozzle using the Two-way DPM model. The erosion study of the nozzle due to particle impact, which entails assessing the nozzle’s material wear, is not covered in this simulation.
Mr. Mateo Gibson II –
The tutorial sounds very detailed. Was there any part of the simulation process that was particularly challenging or needed extra attention?
MR CFD Support –
Additionally, all technical and service simulations have unique complexities; however, special care was assessed focusing on accurately setting up the Two-Way Discrete Phase Model (DPM) to ensure realistic tracking and interaction of particles within the gaseous flow through the nozzle.