PBM with CFD Simulation of FeNi Nanoparticle Synthesis
$410.00 $246.00 HPC
- PBM with CFD Simulation of FeNi Nanoparticle Synthesis is performed using ANSYS Fluent .
- A Multiphase Eulerian approach is applied with FeNi alloy represented in the secondary phase.
- Powder precursors (FeCl₂ and NiCl₂) are injected into the domain using the Discrete Phase Model (DPM).
- The Species Transport Model with finite-rate Arrhenius kinetics is used to simulate the reduction reactions.
- User-Defined Functions (UDFs) implement nucleation, growth, and agglomeration phenomena for nanoparticle prediction.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
PBM with CFD Simulation of FeNi Nanoparticle Synthesis Using ANSYS Fluent
Project Description
The PBM project focuses on the numerical modeling and simulation of FeNi nanoparticle production using PBM (Population Balance Modeling). In this simulation, the aim is to learn about flow behavior.ANSYS Fluent accomplished the simulation. The multiphase, disecet phase, and species models simulate the flow and reaction between them.
Geometry and mesh
The geometry of PBM project was modified using ANSYS Design Modeler, in which 856887 high-quality unstructured tetrahedral cells were created in the flow domain by ANSYS Meshing with a maximum skewness of 0.63.
Setup
A pressure-based and transient solver was used for PBM project. Powder composed of FeCl2 and NiCl2 is injected into the domain using DPM. Then the discrete particles evaporated and devolatilized to FeCl2 and NiCl2 species in the primary phase. The following three reactions were simulated using two two-phase, Eulerian phase reactions:
- FeCl2 + H2 → Fe + 2HCl
- NiCl2 + H2 → Ni + 2HCl
- FeCl2+NiCl2+2H2 → FeNi + 4HCl
All the above species were considered in the primary phase, except FeNi, which was created in the secondary phase. The reactions were simulated using a finite rate reaction using the Arrhenius reaction rate. The plasma effect was considered using a fixed temperature zone for the two plasma areas with temperatures of 2500 and 3000. The nucleation and growth rate were modeled using the equations exhibited in the following paper, with a bit of modification:
Körmer, R., H-J. Schmid, and W. Peukert. “Aerosol synthesis of silicon nanoparticles with narrow size distribution Part 2: Theoretical analysis of the formation mechanism.” Journal of aerosol science 41, no. 11 (2010): 1008-1019.
The related equations were developed in a UDF and implemented in the ANSYS Fluent, while the agglomeration was modeled using the Leu model.
Results
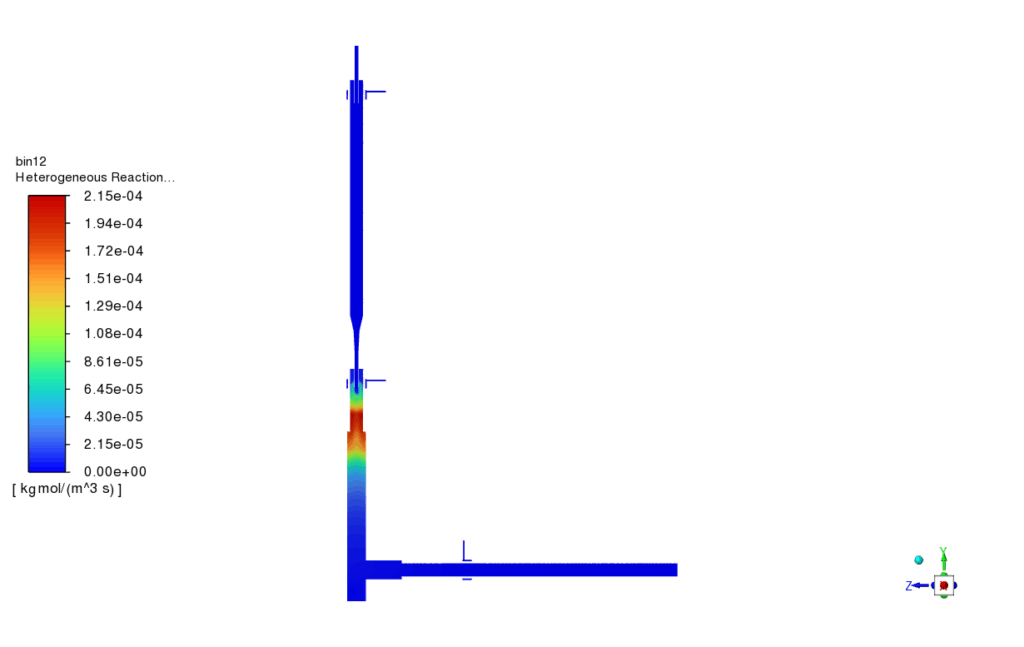
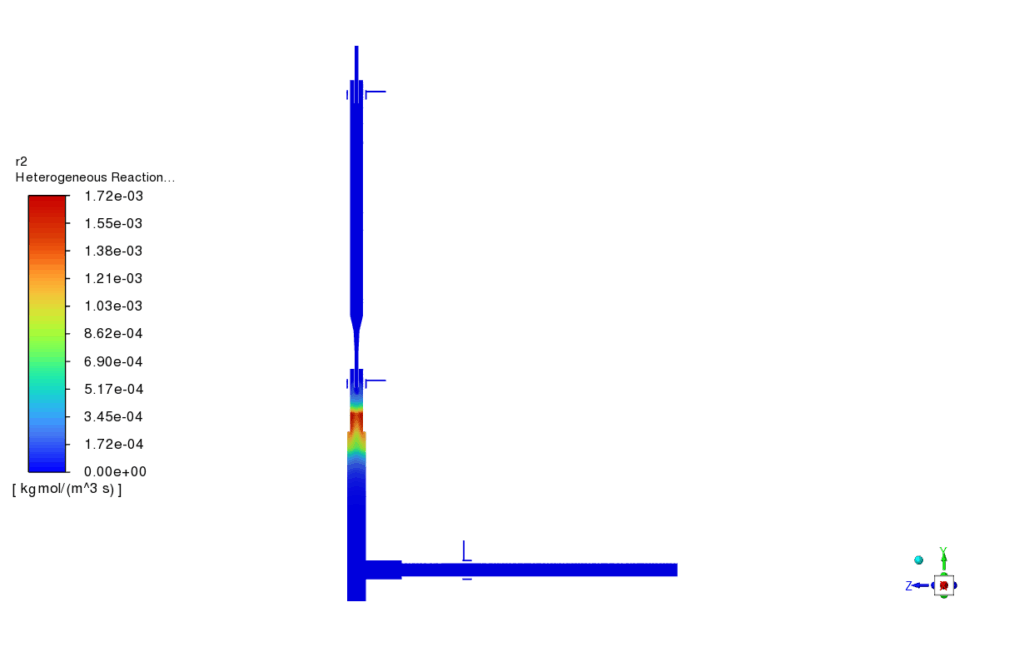
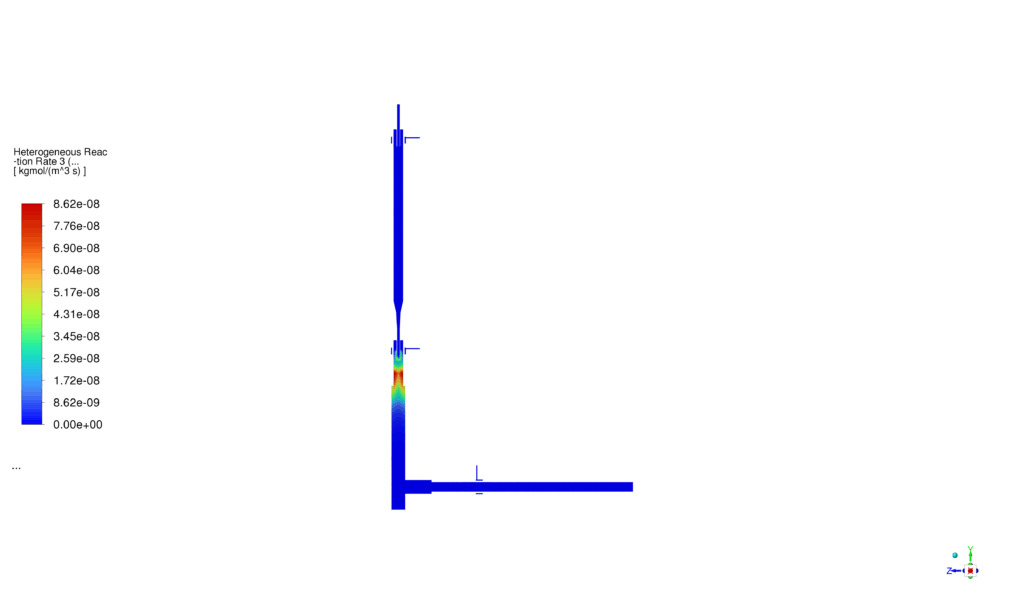
The simulation results of PBM project, provided a comprehensive view of the thermal, chemical, and particle behavior inside the flow domain. The fluid temperature contours showed the influence of the two high-temperature plasma zones (2500 K and 3000 K), which created strong thermal gradients and promoted particle reaction and transformation. The pathlines of the injected powder particles demonstrated how FeCl₂ and NiCl₂ dispersed within the reactor before undergoing evaporation and reduction. Species distribution contours confirmed that both chlorides were effectively consumed through reactions with hydrogen gas, with noticeable decreases in their concentrations across the domain. This correlated well with the zones of high reaction rate observed for the first two reactions, indicating active conversion of FeCl₂ and NiCl₂ into elemental Fe and Ni.
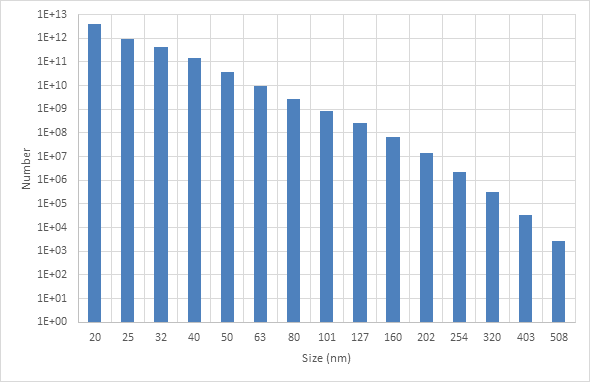
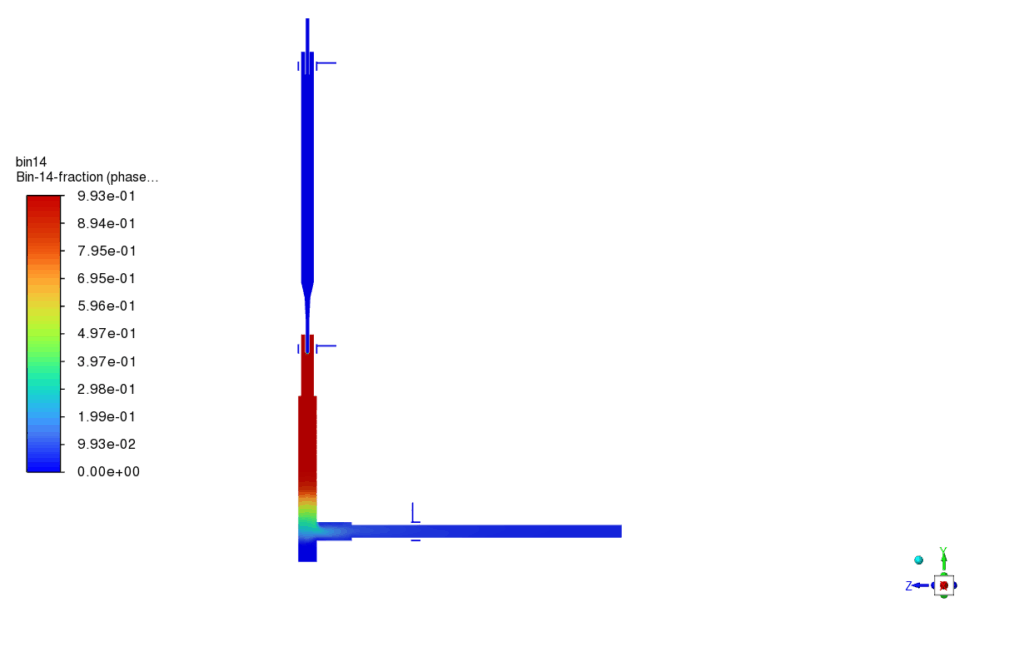
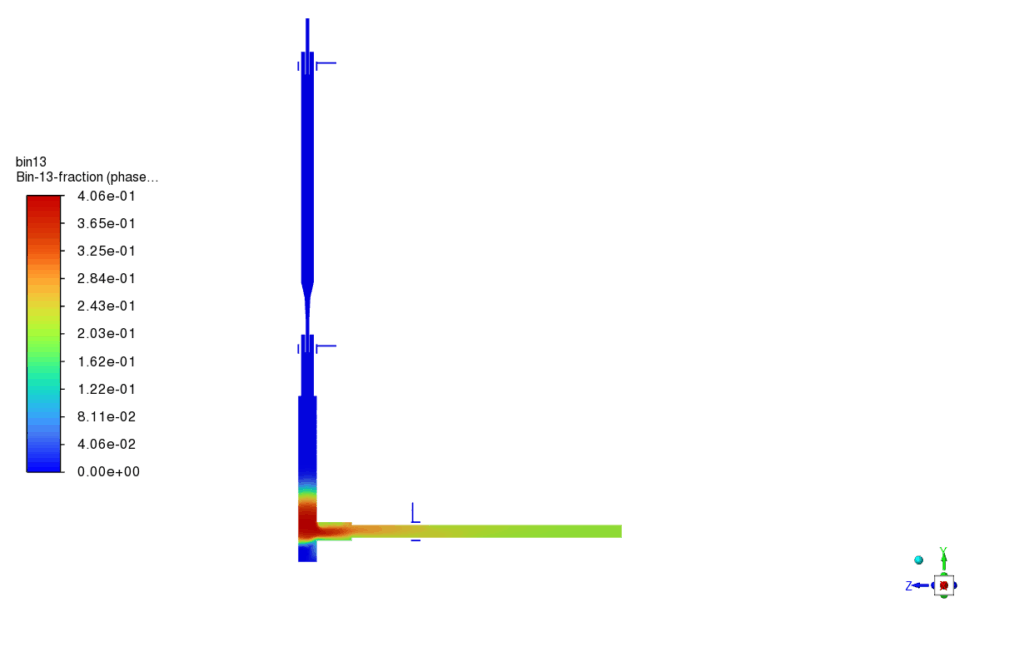
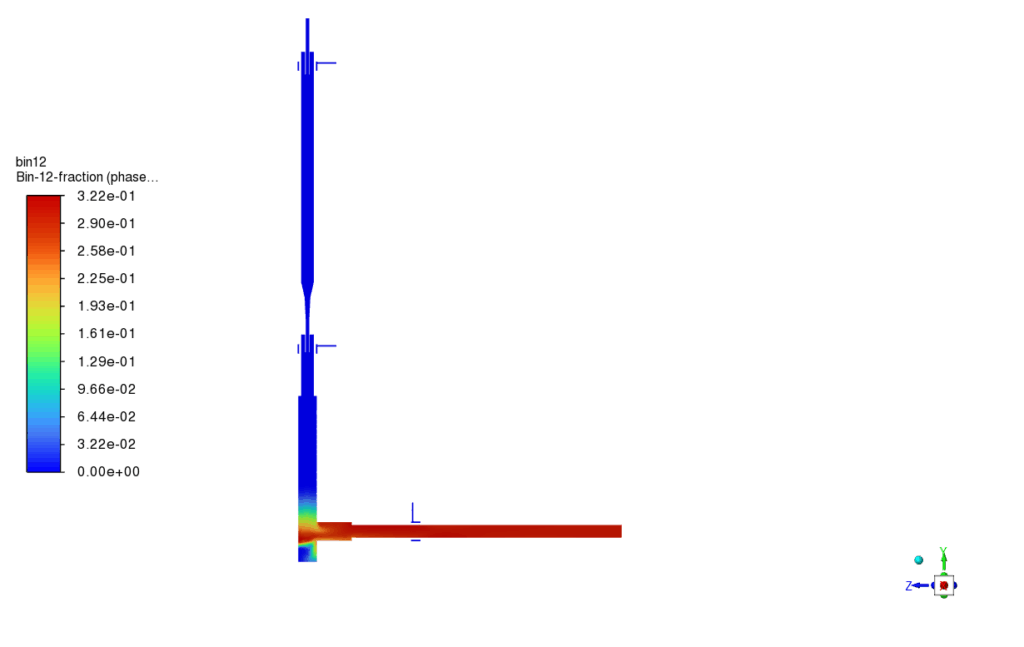
The third reaction, responsible for FeNi alloy formation, showed promising results in selected high-temperature regions, with FeNi concentrations clearly visible in the secondary phase contours. The nucleation rate and growth rate distributions confirmed successful initiation and development of nanoparticles, producing a range of particle sizes throughout the domain. Specifically, the particle size fractions for diameters of 20 nm, 25 nm, and 32 nm indicated a relatively narrow size distribution, consistent with the theoretical predictions from the implemented PBM model. The simulation results validated the chosen modeling approach and showed that FeNi nanoparticles can be effectively synthesized under the defined plasma and reaction conditions.
Reaction rates contour
2nd reaction:
You must be logged in to post a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.