DDPM, Proppant Transport among Multicluster Hydraulic Fractures, Paper Numerical Validation
$320.00 Student Discount
- The current CFD Analysis Validates the Paper ‘Field-Scale Numerical Investigation of Proppant Transport among Multicluster Hydraulic Fractures’ via ANSYS Fluent software.
- We have designed the geometry using ANSYS Design Modeler software and generated the mesh on this geometry using ANSYS Meshing software. The mesh type is structured.
- The Eulerian multiphase model is used to simulate the proppant.
- The Dense Discrete phase model (DDPM) is used in the simulation.
- The Saffman lift force, virtual mass force, and two-way turbulence coupling models are taken into account.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Proppant Transport among Multicluster Hydraulic Fractures, Paper Numerical Validation
Description
In this project, proppant transport among multicluster hydraulic fractures is simulated using ANSYS Fluent software. The study aims to validate a paper entitled “Field-Scale Numerical Investigation of Proppant Transport among Multicluster Hydraulic Fractures.” Hydraulic fracturing is a process used in the oil and gas industry to stimulate production from reservoirs.
It involves injecting a fluid, typically water mixed with sand and chemicals, under high pressure into a wellbore to create cracks in the deep-rock formations. The sand or similar particulate material, known as proppant, is used to keep these fractures open, allowing oil or gas to flow more freely.
The transport of proppant in these fractures is a critical aspect that affects the efficiency and success of hydraulic fracturing. ANSYS Design modeler designs the model. The computational domain is divided by a structured grid using ANSYS Meshing software.
Methodology of Proppant Transport among Multicluster Hydraulic Fractures
The standard k-epsilon turbulence model is used to predict turbulence effects. In this multiphase project, the secondary phase is considered to be a dense phase. Thus, the Dense Discrete phase model (DDPM) is used along with the Eulerian multiphase model to simulate the proppant. Actually, the carrier, which is the continuous phase, is water liquid.
It’s worth mentioning that the discrete phase is solved regarding the 2-way approach. The Saffman lift force, virtual mass force, and two-way turbulence coupling models are taken into account.
Conclusion
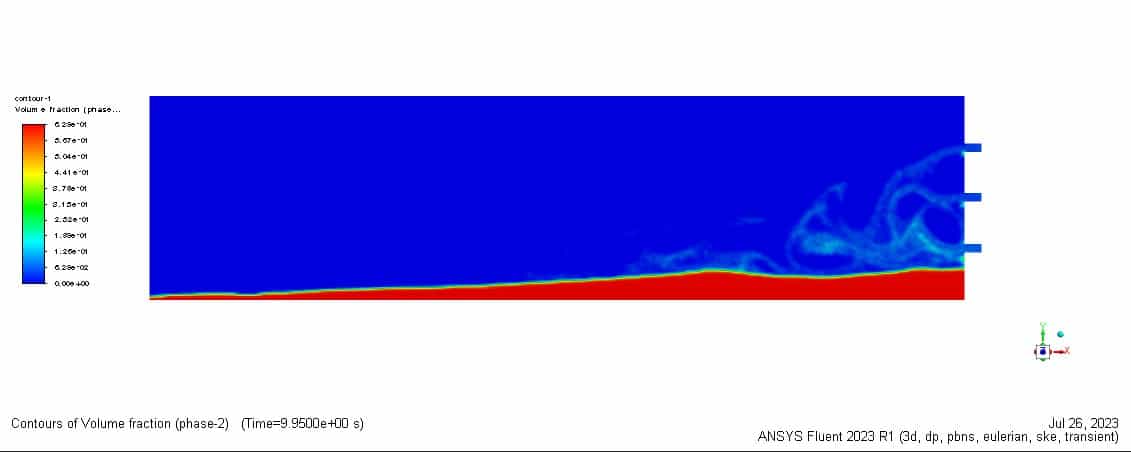
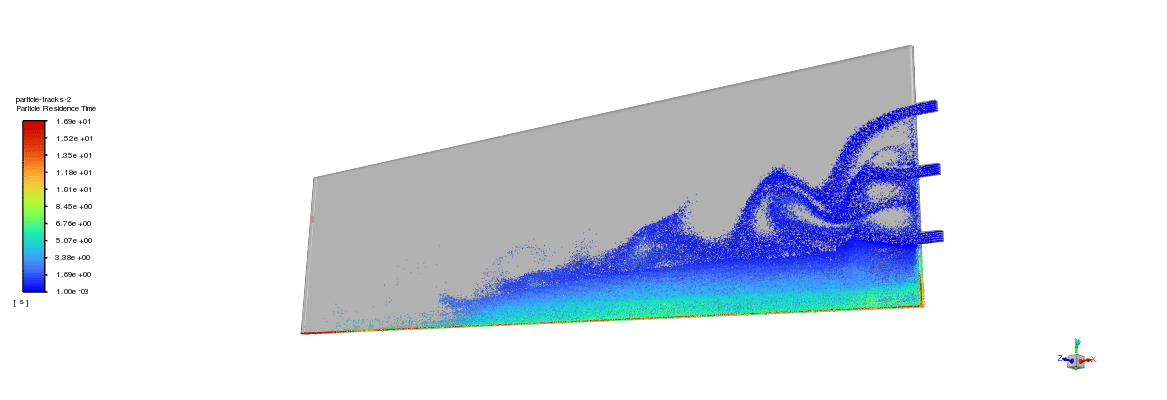
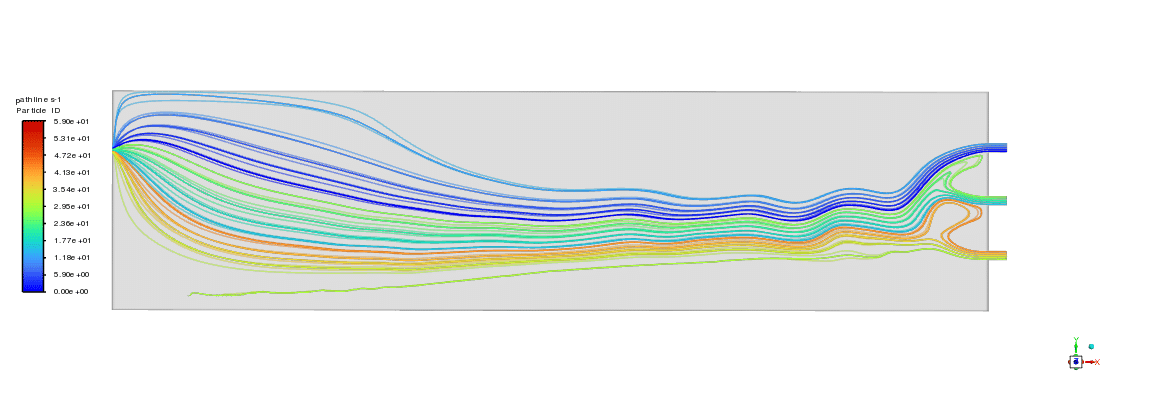
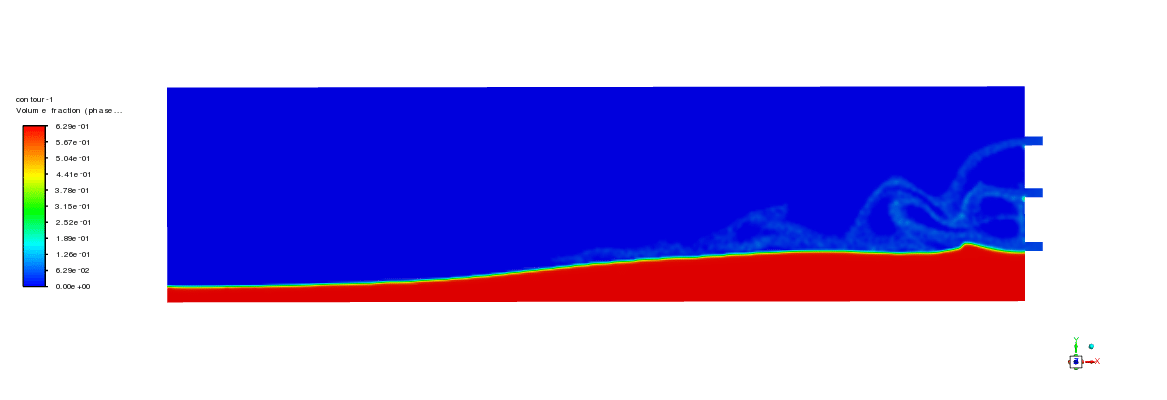
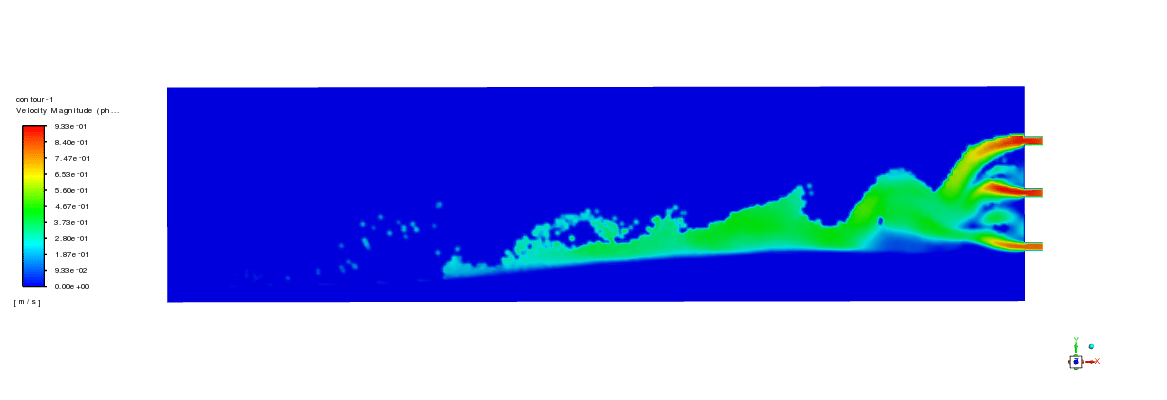
As can be seen in the animation, the proppants directly settled down after injection, forming a dune at the bottom of the slot. As shown in contours, proppants were transported to the other end of the slot at 10 seconds of injection. The dune grew quickly in the height dimension.
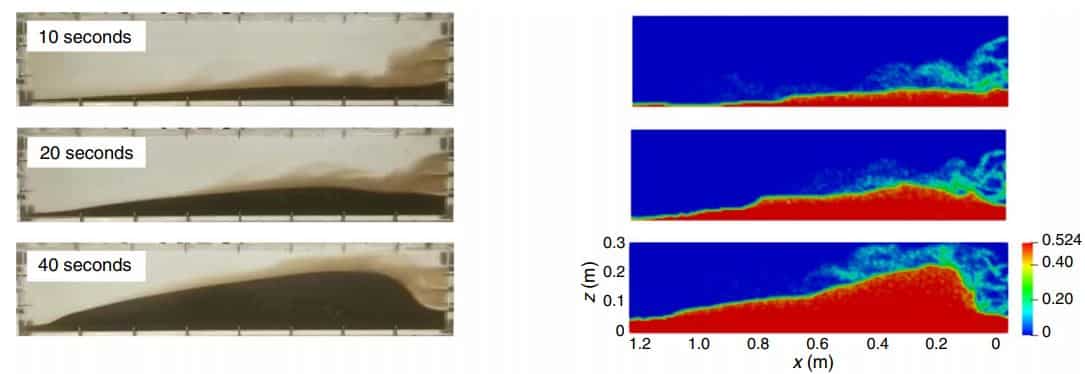
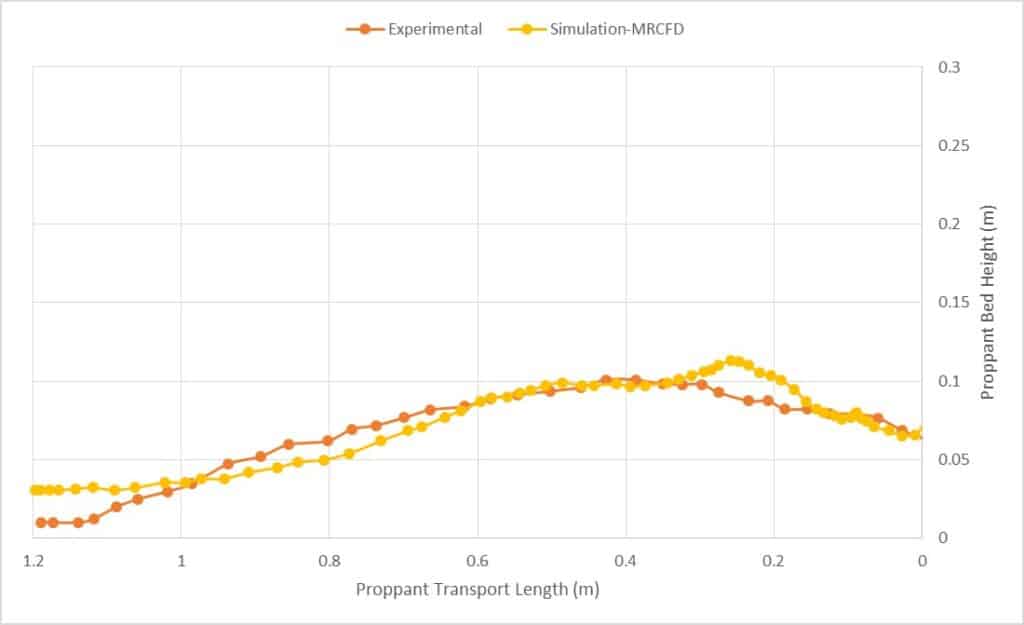
After 17 seconds of simulation, the dune height was almost two times higher than that of 10 seconds. In order to test the accuracy of the simulation, the experimental results that show proppant volume fraction are selected to compare with simulation results. As the figure below shows, the results indicate a good agreement. Based on the measured data, the error is below 12%.

Prof. Darren Haley V –
Are the virtual mass force and two-way turbulence coupling essential for accurately predicting proppant transport, and can you explain their significance briefly?
MR CFD Support –
In the context of this simulation, yes, both the virtual mass force and two-way turbulence coupling are essential components for accurately predicting the proppant transport. Virtual mass force accounts for the added mass effect, which is the resistance faced by the dispersed phase (proppant) accelerating in a continuous phase (fluid). This is crucial for simulating the momentum exchange between the phases. Two-way turbulence coupling ensures that the presence of particles (proppant) is accounted for in the continuous phase flow field. This means the turbulence of the fluid is affected by and, in turn, affects the particles. Both effects are significant for capturing the detailed physics of proppant settling and transport in hydraulic fractures.
Precious Gleason –
Is the DDPM approach more beneficial for simulating proppant transport when compared to other multiphase models? Why was this chosen in particular for this simulation?
MR CFD Support –
The Dense Discrete Phase Model (DDPM) is particularly effective for simulating proppant transport in hydraulic fracturing because it accounts for the dense particle phase dynamics. This model is capable of simulating a large amount of particulates with consideration for the interactions between them and the carrier fluid, which is crucial for accurately capturing the behavior of proppants in the fractures. The DDPM was likely chosen for its ability to manage dense particulate flows and maintain a balance between accuracy and computational efficiency in this context.
Dr. Riley Blanda Sr. –
Great job capturing the complexities of proppant transport! It seems your model successfully matched the experimental data. What specific features of ANSYS Fluent’s DDPM did you find most advantageous for this simulation?
MR CFD Support –
We’re glad you found the simulation results satisfactory! The ANSYS Fluent’s Dense Discrete Phase Model (DDPM) provided advanced capabilities for handling dense particle loadings which was critical for this simulation. The DDPM’s ability to simulate interactions between particles and continuous fluid phase through a two-way coupling and including forces like Saffman lift force and virtual mass, certainly offered a more accurate representation of proppant dynamics under turbulent conditions.
Alessandra Schmidt –
I’m highly impressed by the proppant transport simulation work carried out. Modern fracturing techniques demand accurate models like this.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for such a positive review! We’re thrilled to hear that our simulation on proppant transport among multicluster hydraulic fractures delivered valuable insights. If you have more questions or need assistance with similar simulations, feel free to reach out to us.
Mrs. Pamela Davis PhD –
I found the study fascinating! I am curious about how the proppant particles interact with the hydraulic fractures. Is there more detailed interaction data available for me to understand better how the DDPM accounts for particle collisions and settling within the fractures?
MR CFD Support –
Absolutely! The DDPM accounts for particle-particle and particle-wall interactions using a combination of forces, such as frictional and collision models. As particles enter the fractures, they collide with each other and the fracture walls. These interactions are modeled to capture the physics involved in settling, packing, and distributing the proppant within the fractures. The comprehensive data on these interactions provide insights into behavior like dune formation and growth that you observed.
Elyssa Kling –
This simulation perfectly exhibits the proppant behavior in multicluster hydraulic fractures. Superb and thorough application of the DDPM method. The visualization elements provided, including the dune formation and growth animation, really enhanced my comprehension of proppant transport dynamics.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that the visualization and application of the Dense Discrete Phase Model (DDPM) in this simulation have enhanced your understanding of proppant behavior in hydraulic fracturing. It is our goal to provide clear and informative content, and we appreciate you taking the time to complement our efforts.
Misael Wiegand PhD –
I am impressed by the accuracy of your simulation compared to the experimental results within 12% error margin. Can you share what specific challenges you faced in achieving such a close match between the simulation and experimental data?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words about our simulation results. One key challenge we faced was ensuring that the computational mesh was refined enough to accurately capture the complex dynamics of proppant transport. We also had to carefully select and apply turbulence models and multiphase flow conditions to reflect the physical phenomena involved in the dense discrete phase model effectively. Achieving two-way turbulence coupling and managing the interactions between the fluid and the proppants required detailed attention to the physical properties and forces in the system. Thanks for your review, and if you have more questions, we’re here to answer!
Orlando Hartmann DDS –
I found the DDPM modeling explanation very thorough! It’s impressive how the simulation captures the realistic movement and settling of the proppants.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind feedback! We’re delighted to hear that you found our explanation informative and that the simulation results provided a realistic representation of proppant behavior in hydraulic fractures. We always strive to deliver accurate and valuable insights through our simulations.
Thaddeus Toy –
I enjoyed learning about proppant transport in hydraulic fractures. Can you tell me if you have plans to expand this study to other fluids or proppant types for a broader scope of applications?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the wonderful feedback on our proppant transport project. Currently, we don’t have specific information on future expansions regarding different fluids or proppant types. Our team is constantly working on enhancing our products, and customer suggestions like yours are valuable for guiding our research scope. Stay tuned for updates to our learning materials!
Jeromy Runte –
Your team has managed to capture the complexities of proppant transport with great precision. I’m particularly impressed by the low margin of error in comparison to experimental results, which instills confidence in the numerical model’s reliability.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We strive to provide accurate simulations that can reliably replicate real-world scenarios. Your feedback encourages us to continue improving our models and services.
Andy Lynch –
The detail on the proppant dune formation was fascinating, especially how it evolved over time in the simulation. Can the MR CFD product also simulate different proppant sizes and their respective transport behavior within the hydraulic fractures or is there a limitation on that aspect?
MR CFD Support –
Yes, the MR CFD product can simulate different proppant sizes and their transport behavior within hydraulic fractures. The Dense Discrete Phase Model (DDPM) allows for the inclusion of various particle sizes and properties, which can help you assess the impact of different-sized proppants on the fracture conduits’ efficiency.
Gloria Haley –
I’m pleased with the validation results mentioned in your description! Showing an error of below 12% means the simulation accurately reflects the complexity of proppant transport in hydraulic fracturing which is critical for the development of oil and gas extraction technology. Excellent work on this simulation and validation.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you very much for your positive feedback! We are delighted to hear that the accuracy of our simulation met your expectations. Our team strives to provide precise and reliable CFD simulations, and it is always rewarding to know when our efforts contribute to the successful application in such important industrial processes as oil and gas extraction. We appreciate your acknowledgment and look forward to serving you with more high-quality simulations in the future.
Clara Bernhard II –
Fantastic real-world applications replicated accurately through simulation; I’m curious, how does the DDPM approach enhance the prediction of proppant transport compared to other models?
MR CFD Support –
The DDPM (Dense Discrete Phase Model) greatly enhances the simulation of dense particle flows like proppant transport by accounting for volume fraction effects and offering improved interphase force predictions. This results in more accurate tracking of particles and predictions of their effect on the continuous phase (such as water in this case), which is critical for optimizing hydraulic fracturing operations.
Prof. Rafael Schuster –
This course material regarding the DDPM approach and simulation of proppant transport sounds incredibly thorough. The practical application of concepts to validate professional research papers gives invaluable experience.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to hear you found our course material on DDPM and proppant transport simulation to be detailed and practical. It is our goal to provide simulations that are not only instructive but also closely aligned with real-world applications and current research. Your appreciation means a lot to us!
Aron Thiel –
The video and contours made it really easy to understand the behavior of proppant in hydraulic fractures. Great job on the clear presentation of complex fluid dynamics!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re delighted to hear that our visual aids and detailed results helped make the complex concepts in proppant transport more comprehensible. We take pride in our commitment to clarity and educational quality in our simulation materials.
Prof. Breana Bruen DVM –
The animation and contour representation in the proppant transport simulation was incredibly helpful for visualizing the process. It was especially interesting to see the dune formation over time. Great validation work!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to hear that the visual aids provided in the simulation were effective in illustrating the complex proppant transport phenomena. It’s always rewarding to know our efforts in simulating and validating experimental results contribute meaningfully to our users’ understanding.
Prof. Dina Kuhlman II –
I’ve read about the Dense Discrete Phase Model (DDPM) but can’t find a simple explanation of what it is exactly. Can you please explain?
MR CFD Support –
Dear customer, I’m glad you’re interested in learning more. The Dense Discrete Phase Model (DDPM) is a numerical approach used in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to simulate the behavior of a dense collection of particles, like sand in a proppant, as they interact with a fluid flow. It blends the discrete phase model, typically used for sparse particle concentrations, with the volume of fluid (VOF) or Eulerian multiphase models, comfy for dense slurry flows. In effect, it allows you to predict how particles distribute and move collectively, as well as their effect on, and reactions to, the carrying fluid flow.
Dr. Jaiden Howell I –
I’m really impressed by these results. Could you tell me if using the DDPM added significant complexity to the modeling process?
MR CFD Support –
Using the Dense Discrete Phase Model (DDPM) within ANSYS Fluent does add a level of complexity to the modeling process, as it requires careful consideration of the particulate phase properties and interactions, such as collision, coalescence, and transport mechanisms. However, for simulating dense particulate flows like proppant transport in hydraulic fractures, the DDPM provides more accurate, physically-representative insights into proppant behavior and interactions, which are crucial for the process’s effectiveness.
Melvin White –
I was particularly impressed by the level of accuracy achieved in the simulation. Could you highlight how the error measurement of below 12% was determined and how it aligns with industry standards for numerical validation?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback on the accuracy of the simulation. Error measurements typically involve comparing the simulation results with the experimental or published data. The 12% error reported was likely calculated using standard statistical methods like the root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute percentage error (MAPE). Such an error margin for complex multiphase flows simulations is commonly acceptable in the industry, although the aim is always to reduce it as much as possible to ensure greater fidelity to real-world scenarios.
Dr. Dean Conn –
The simulated proppant transport in your product seems impressively detailed. Great work on maintaining a low error rate. It’s interesting to see how the dune formation was captured over time.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive review! We are very pleased to hear that you found the simulation details comprehensive and accurate. We strive hard to ensure our simulations closely reflect real-world scenarios, and it is gratifying to know that our efforts have been successful in the project you mentioned. If there’s more you’d like to explore or discuss, feel free to let us know!
Caesar Turner DVM –
I appreciate the thorough analysis presented! Could you share whether the effects of any chemical additives in the fluid were considered in the simulation alongside proppant transport?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the positive feedback on our analysis. In this simulation, focus is primarily given to the physical transport characteristics of proppants within hydraulic fractures. The effects of chemical additives on proppant transport are not considered. The fluid properties, such as viscosity and density, are aligned with the injected water liquid, disregarding the presence of chemical additives.
Geraldine Harber –
The product review provides an outstanding explanation of the methodology and results of this simulation. Great work showcasing the software’s capabilities in simulating complex processes like proppant transport in hydraulic fracturing.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for taking the time to review our product. We’re thrilled to hear that our simulation met your expectations and provided a clear understanding of the proppant transport process. Your feedback is greatly appreciated!
Rashawn Pfeffer –
I’m really satisfied with how this CFD project turned out! The visualizations were extremely helpful in understanding the proppant dynamics. Fantastic work on the model validation against the experimental paper.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that the visualizations and the accuracy of the model validation met your expectations. Your satisfaction is our greatest reward, and we look forward to providing you with more quality simulations in the future.
Jennings Hudson –
This product was incredibly insightful! It helped me understand the complexities of proppant transport in hydraulic fracturing with great detail. The visual animations and the error comparison with experimental data made it a lot easier to grasp. Well done on a clear and comprehensive simulation case study!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are thrilled to hear about your positive experience with our simulation case study. It’s fantastic to know that the animations and data comparison enhanced your understanding of proppant transport in hydraulic fractures. We appreciate your feedback and look forward to providing you with more valuable learning products in the future.
Ms. Eryn Volkman III –
I was impressed with the focus on accuracy in your simulation of proppant transport. How do you ensure that the error remains below 12% across different scenarios?
MR CFD Support –
To ensure the error remains consistently low, rigorous methods and verification processes are applied. This includes refining the mesh to achieve a balance between computational cost and accuracy, calibrating the turbulence and multiphase models carefully to match the physics of proppant transport, and multiple validations against experimental data to ensure the reliability of the simulation outcomes.
Tia Johnston DVM –
This course helped me grasp the concepts of proppant transport in hydraulic fractures effectively. The animated visuals and the comparison with experimental results made the learning process engaging and comprehensive. Keep up the great work, MR CFD!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that our training material has enhanced your understanding of proppant transport in hydraulic fractures. We strive to create instructional content that is not only informative but also engaging. Your acknowledgment motivates us to continue providing high-quality educational resources.
Ahmed O’Connell PhD –
Very impressed with the accurate representation of proppant behavior. Could the team replicate studies for different proppant types or fluids?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for recognizing the efforts. Yes, the methodology employed in this project is flexible and can be modified to simulate different proppant types or fluid characteristics to understand their behaviors within hydraulic fractures under varying conditions.
Alfonzo Zemlak –
Can the methodology outlined in the project be applied to different fluid types and proppant materials, or is it specific to the conditions mentioned?
MR CFD Support –
The methodology described, which involves the use of the Eulerian multiphase model and Dense Discrete phase model (DDPM), can often be applied to various fluid types and proppant materials with the appropriate adjustments. The adjustments would involve modifying the material properties and possibly the force laws (like Saffman lift force, virtual mass force, and the turbulence coupling) to accurately reflect the behavior of different materials. However, it should be done with due consideration to ensure that the simulation accurately represents the new conditions.
Valentina Jacobs –
This ANSYS simulation seems complex. Can you explain the primary advantage of using DDPM in this context?
MR CFD Support –
The primary advantage of using DDPM (Dense Discrete Phase Model) in this context is to accurately account for the high particle concentration of proppants in hydraulic fracturing. DDPM enables the simulation of both the continuous fluid phase and the discrete solid phase while capturing the interactions between them, such as the proppant settling and forming dunes at the bottom. This model accurately represents the behavior of dense particulate flows, crucial for predicting proppant transport and deposition.
Opal Yost –
I’m impressed with the detailed methodologies and outcomes in your Proppant Transport simulation. Could you detail how the error rate was calculated and confirmed to be below 12%?
MR CFD Support –
The error rate in the simulation was determined through quantitative comparison between the simulation results and experimental data provided in the source paper. This involved comparing the spatial distribution and volume fraction of the proppant over time. The difference between the simulation predictions and the reported experimental results generated a percentage error that quantified accuracy. For this project, a careful examination confirmed the error did not exceed 12%, indicating a high level of precision in the simulation method for proppant transport.