Solar Shading Double Glazing façade, Radiation
$120.00 Student Discount
The present problem simulates the radiation of solar rays into the room’s interior considering the effects of a wooden partition as a solar shading, and a double glazing glass of façade, using ANSYS Fluent software.
Click on Add To Cart and obtain the Geometry file, Mesh file, and a Comprehensive ANSYS Fluent Training Video.To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Solar Shading Double Glazing façade, Solar Radiation, ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial
The present problem simulates the radiation of solar rays into the room’s interior considering the effects of a wooden partition as a solar shading, and a double glazing glass of façade, using ANSYS Fluent software. Argon gas has accumulated in the space between the two glasses of the double glazing; Because argon gas has low thermal conductivity. Therefore, as an insulating layer, it reduces heat from the outside environment to the room. The Radiation model is used to define the radiant heat transfer due to solar radiation; So the selected radiation model is of type P1. Also, solar ray tracing mode has been activated to define solar radiation.
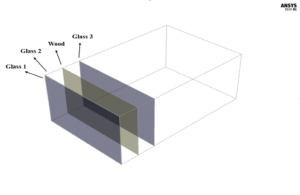
The room belongs to a region with a latitude and longitude of 24 degrees and 26 degrees and 1 pm, on the 30th day of June. The directions of the sun’s rays are obtained based on the longitude and east geographical location of the desired room. The glass walls adjacent to the room are defined as semi-transparent; That is, the sun’s rays relative to these walls have all three modes of absorption, diffusion, or reflection. However, the solar shading of this space acts as an opaque body and only allows the sun’s rays to be absorbed and reflected and does not allow the rays to pass.
Geometry & Mesh
The present model is designed in three dimensions using Design Modeler software. The present model belongs to a room connected to space with a wooden partition as solar shading and a double glazing façade. The desired room has a depth of 6 m, a width of 5 m, and a height of 3 m. Also, the space between the glasses of the double glazing is equal to 2 mm.
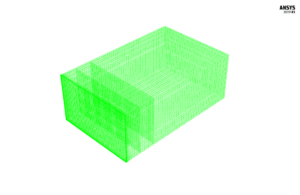
We carry out the model’s meshing using ANSYS Meshing software. The mesh type is structured. The element number is 239760. The following figure shows the mesh.
CFD Simulation
We consider several assumptions to simulate the present model:
- We perform a pressure-based solver.
- The simulation is steady.
- The gravity effect on the fluid is ignored.
The following table represents a summary of the defining steps of the problem and its solution:
| Models | ||
| Viscous | k-epsilon | |
| k-epsilon model | standard | |
| near-wall treatment | standard wall function | |
| Radiation Model | P1 | |
| solar load model | solar ray tracing | |
| Energy | On | |
| Boundary conditions | ||
| Glass 1 | Wall | |
| wall motion | stationary wall | |
| thermal condition | convection | |
| heat transfer coefficient | 20 W.m-2.K-1 | |
| free stream temperature | 310 K | |
| BC type | semi-transparent | |
| Glass 2 & Glass 3 | Wall | |
| wall motion | stationary wall | |
| thermal condition | coupled | |
| BC type | semi-transparent | |
| Wood | Wall | |
| wall motion | stationary wall | |
| thermal condition | coupled | |
| BC type | opaque | |
| Room & Argon Wall | Wall | |
| wall motion | stationary wall | |
| thermal condition | convection | |
| heat transfer coefficient | 20 W.m-2.K-1 | |
| free stream temperature | 310 K | |
| BC type | opaque | |
| Methods | ||
| Pressure-Velocity Coupling | SIMPLE | |
| pressure | second order | |
| density | second-order upwind | |
| momentum | second-order upwind | |
| turbulent kinetic energy | first-order upwind | |
| energy dissipation rate | first-order upwind | |
| energy | second-order upwind | |
| Initialization | ||
| Initialization methods | Standard | |
| gauge pressure | 0 pascal | |
| velocity (x,y,z) | 0 m.s-1 | |
| temperature | 310 K | |
Results
At the end of the solution process, two-dimensional and three-dimensional contours related to temperature, pressure, and velocity are obtained. Also, velocity vectors are obtained in two dimensions from the passing screen in the middle of the model. The results show that airflow circulation inside the model’s interior spaces and the temperature increase inside the domain due to solar radiation is quite evident.

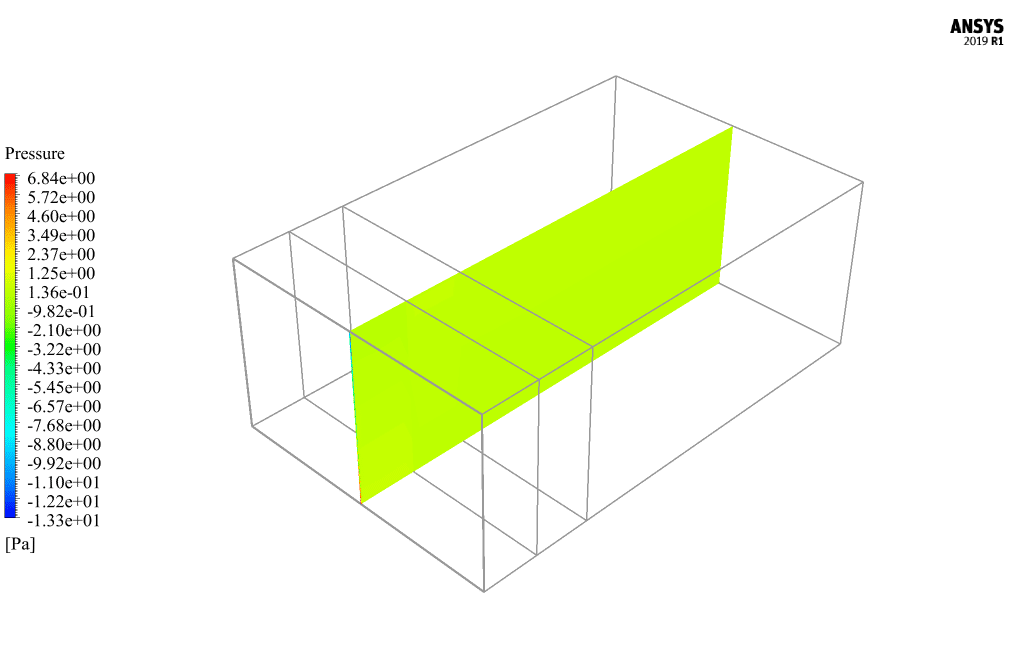
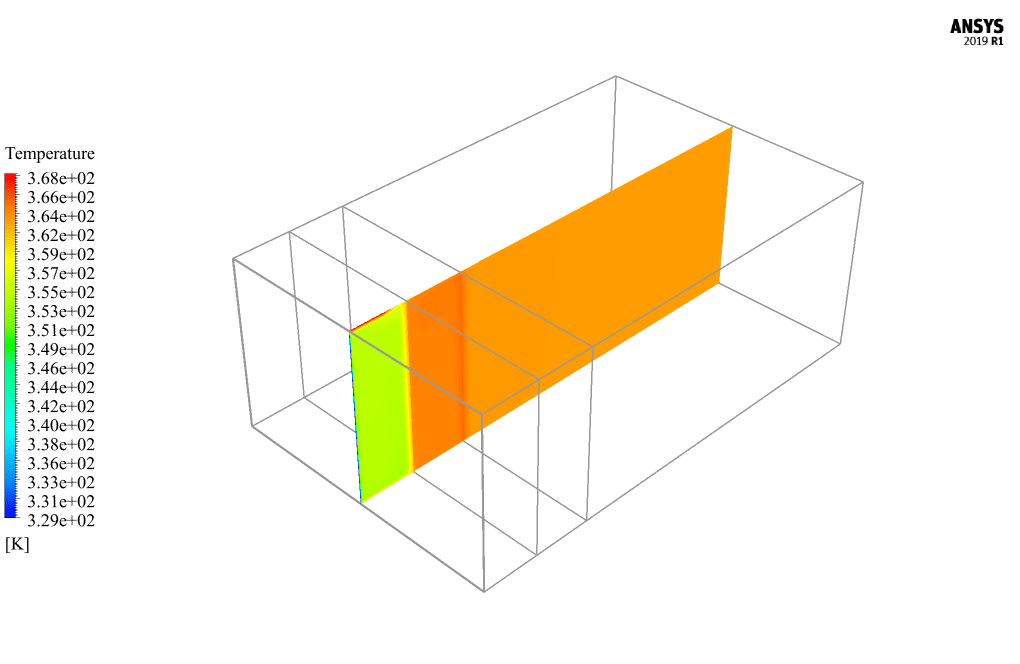
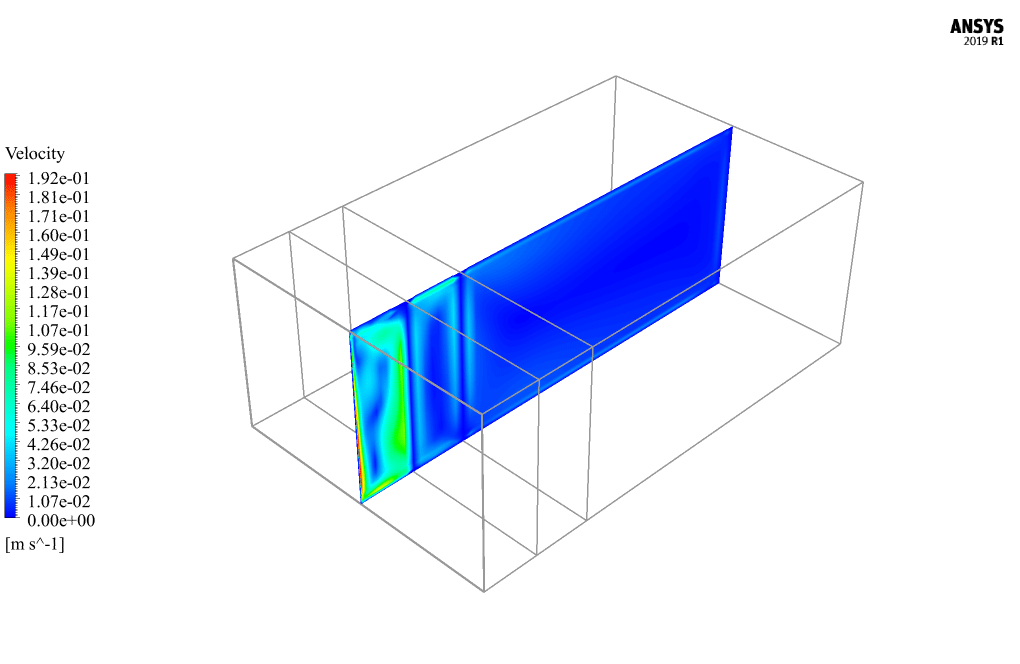
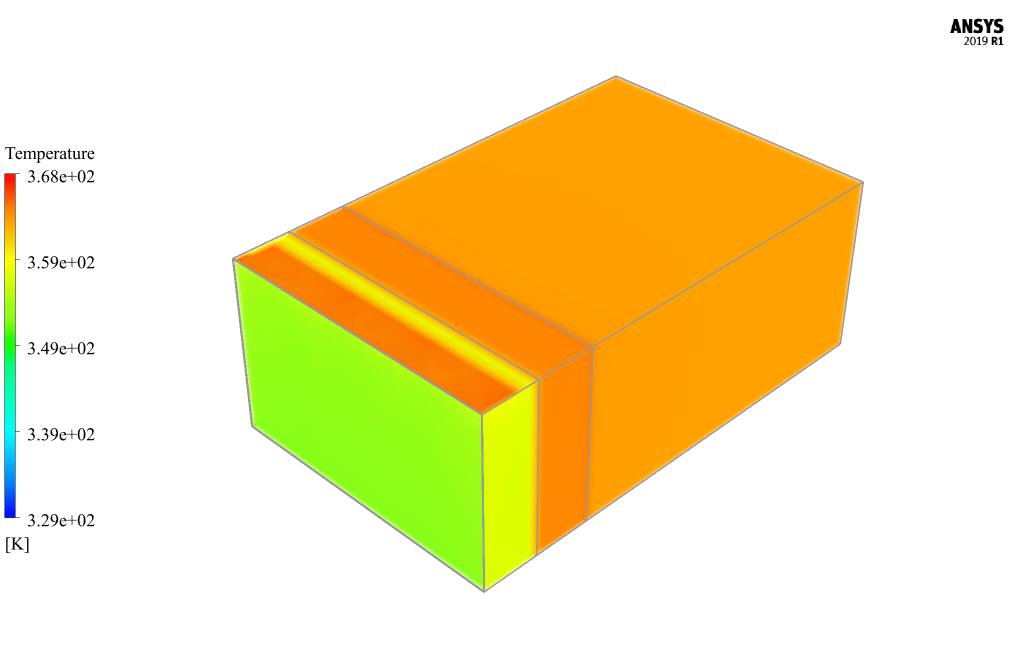

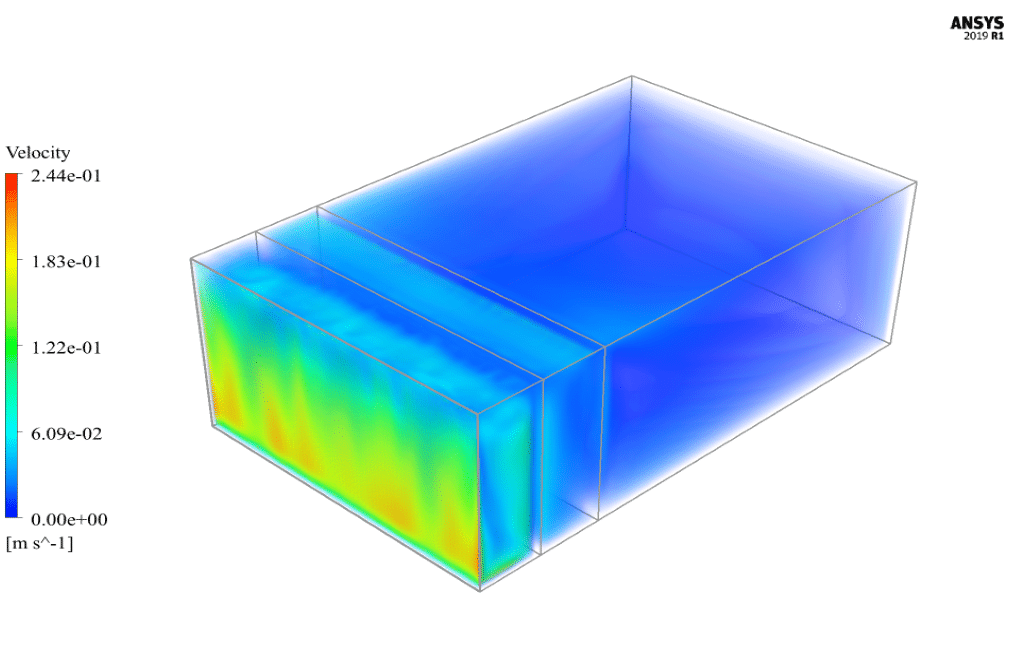

Brown Cummerata –
This tutorial was very thorough and educational. The structured approach helped me understand the complexities of solar radiation within a double glazed facade system. Well done on the clear explanations and quality mesh presentation!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are thrilled to hear that you found the tutorial educational and that the explanations met your expectations. If you ever have any more questions or need further clarification on any step, don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
Joanne Fahey –
The tutorial was super helpful! The inclusion of the step-by-step setup, especially for the boundary conditions and solar ray tracing, elucidated complex concepts. Also, the use of argon gas as insulation was smart.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you very much for your kind words! We’re so glad to hear that our tutorial on simulating solar radiation effects through a double glazing façade was helpful and informative for you. If you have any more questions or need further tutorials on similar or different topics, feel free to ask. We’re always here to help!
Elias Howe –
I was deeply impressed by how well the Solar Shading Double Glazing façade simulation managed to demonstrate the insulation effects. The part where you detailed the wood partition acting both as a solar shading and absorbing reflected rays was particularly informative!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for sharing your positive experience with the Solar Shading Double Glazing façade simulation. We’re delighted to hear that the detailed aspects of the simulation, such as the role of the wooden partition, provided you with clear insights. If there’s anything else you’d like to learn more about or have another CFD topic you’re interested in, please let us know!
Miss Karli Kreiger –
I’m thrilled with how the simulation demonstrates airflow and temperature variations caused by solar radiation. The application of the P1 model and precise boundary conditions clearly depict the sun’s influence through the façade. Fantastic educational tool!
MR CFD Support –
Hello! We appreciate your positive feedback. It’s wonderful to know that our CFD simulation tutorial met your expectations and that you were able to gain valuable insights into the effects of solar radiation. Thank you for acknowledging the detailed setup and calculations that went into this simulation. If you have any further queries or require additional learning materials, feel free to reach out to us!
Mrs. Ludie Satterfield DVM –
The provided explanation of the solar shading double glazing façade CFD simulation was quite thorough. It detailed the model’s geometry, boundary conditions, meshing, various models used, and the simulation’s assumptions. The ability to use a semi-transparent setting for the glass to mimic absorption, diffusion, and reflection of solar rays adds a realistic touch that is impressive. I’m particularly appreciative of the detail regarding the use of argon gas for its insulative properties and the specific geographical details that add to the authenticity of the simulation settings. It’s wonderful to see how the results convey realistic airflow circulation and the thermal effects inside the room due to solar radiation.
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to receive your positive feedback about the Solar Shading Double Glazing facade simulation tutorial. It is gratifying to know that the balance between comprehensive detail and realistic simulation settings fulfilled expectations. User satisfaction with the authenticity and practical application of our instructions is integral to our aims at MR CFD Company. Thank you for taking the time to complement the in-depth nature of the simulation’s representation and the care taken to ensure accuracy in depicting thermal effects — your acknowledgment means a lot to us.
Laurine Ledner –
Excellent tutorial – the detail and explanation of how solar radiation is simulated, especially considering the impacts of argon gas in double glazing and wooden partitions for solar shading, was incredibly helpful in understanding radiation within architectural contexts.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that our tutorial was helpful and provided a clear understanding of the radiation effects involved in architectural designs using ANSYS Fluent. We strive to provide detailed and thorough instructions, so it’s great to know that we’ve achieved this. If there are any more questions or further assistance needed, please don’t hesitate to reach out!