SpaceClaim Course, Session 5: 3D Modeling
Free
- Introduction to 2D Constraints: Coincident, Parallel, Perpendicular, Equal
- Basics of 3D modeling with the Pull command
- Key Pull features: Pull, Revolve, Sweep
- Practical exercise: Creating simple 3D shapes (cube, cylinder, hollow curved pipe)
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Overview
In this session of SpaceClaim training, we will first provide a comprehensive introduction to the tools of the Constraint environment. After that, we will introduce the basic and important tools of the 3D environment, among which the “Pull” command is one of the most important and serves as the gateway from the 2D world to the 3D world. In this session, we will also teach the practical commands of the “Pull” environment, including Pull, Direction, Revolve, and Sweep.
1. Constraints
The Constraints environment in SpaceClaim is used to apply geometric constraints in 2D design. When creating sketches, you can use the Constraints tools to define geometric relationships between lines, arcs, points, and other sketch elements. With this environment, you can achieve precise control over the dimensions and positions of your drawn elements. In this session, we explained all tools of this section such as Dimension, Coincident Constraint, Parallel Constraint, Perpendicular Constraint and Equal Constraint.
2. 3D Modeling
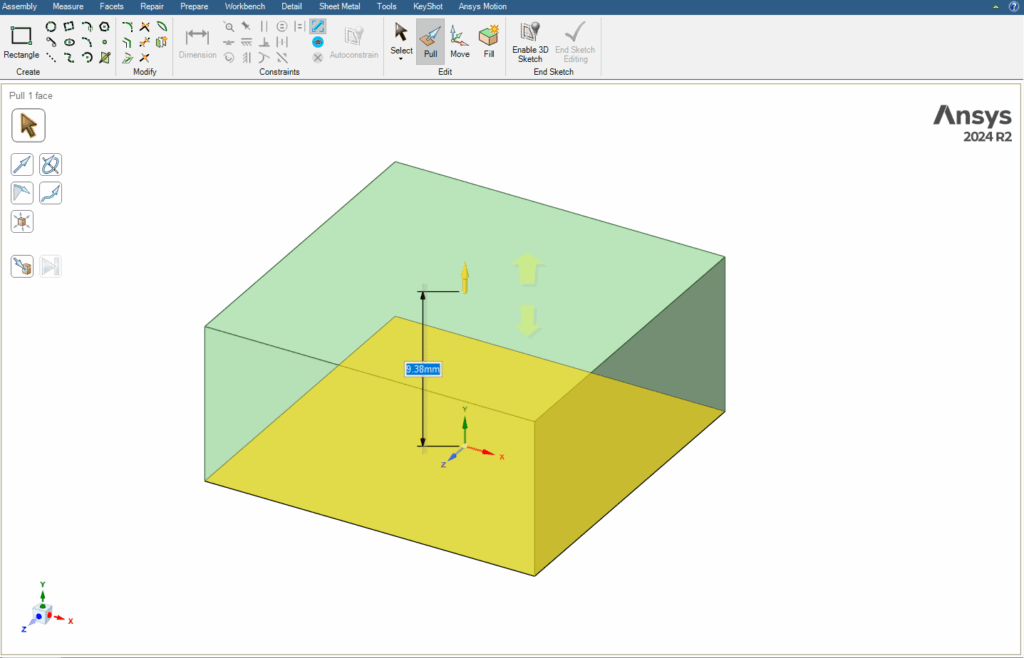
2.1. Pull
One of the most important 3D design tools in SpaceClaim is the Pull command, which allows us to create 3D shapes from a 2D geometry. This tool has diverse and extensive capabilities. In this session, we will focus on some of the most practical and fundamental features of this command, which include Revolve, and Sweep.
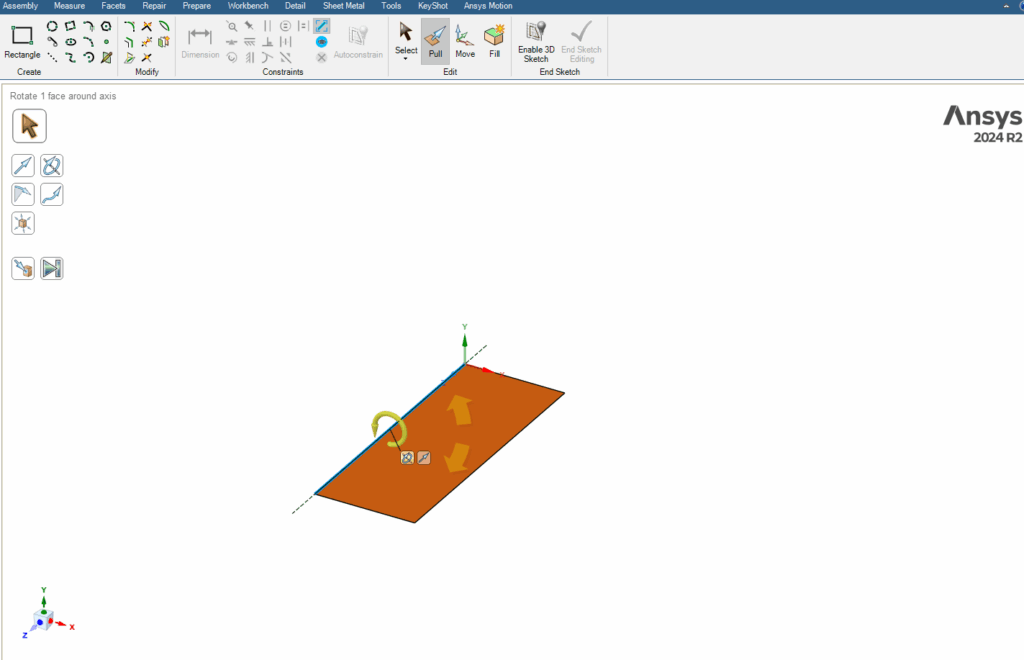
 2.1.1. Revolve
2.1.1. Revolve
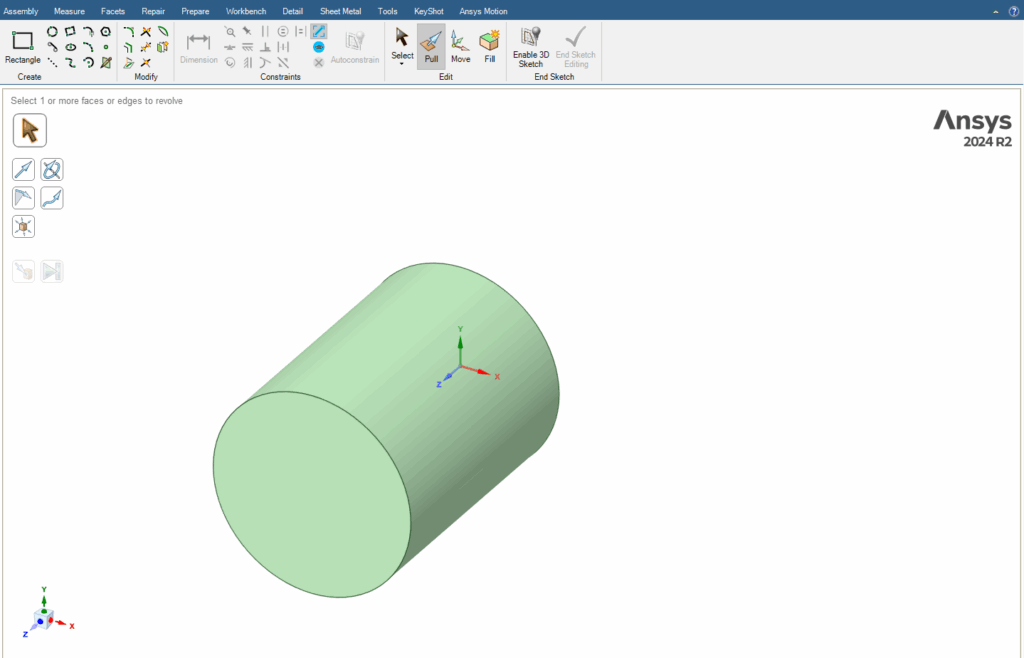
The Revolve option is one of the most efficient tools within the Pull command. This option works by selecting an axis of rotation for the desired geometry and then revolving it by the desired angle around that axis. For example, by revolving a rectangular geometry 360 degrees around one of its sides, we can create a cylinder.
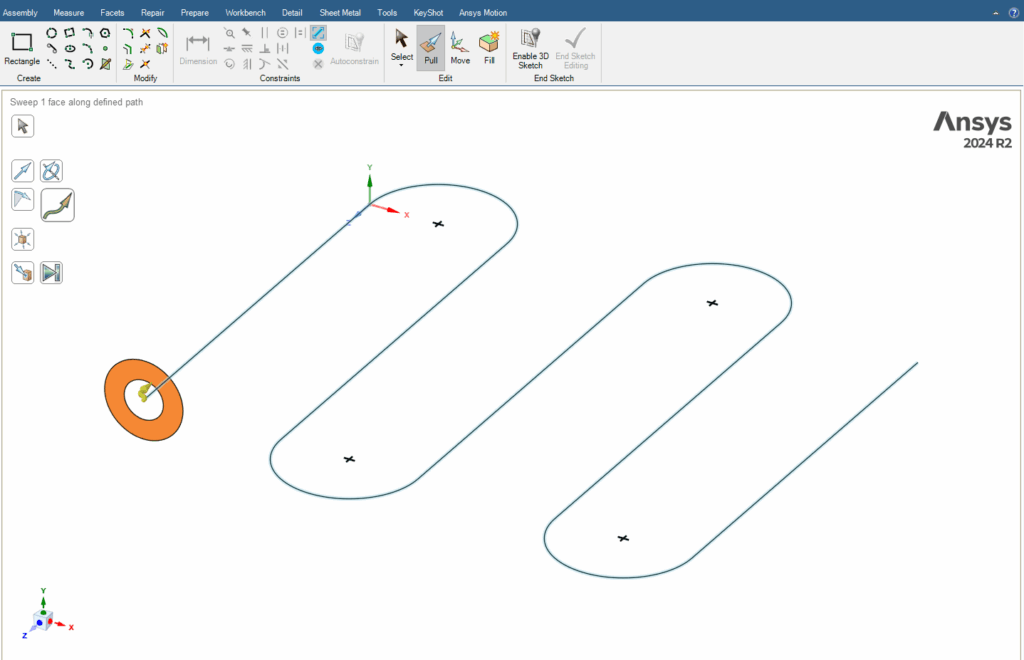
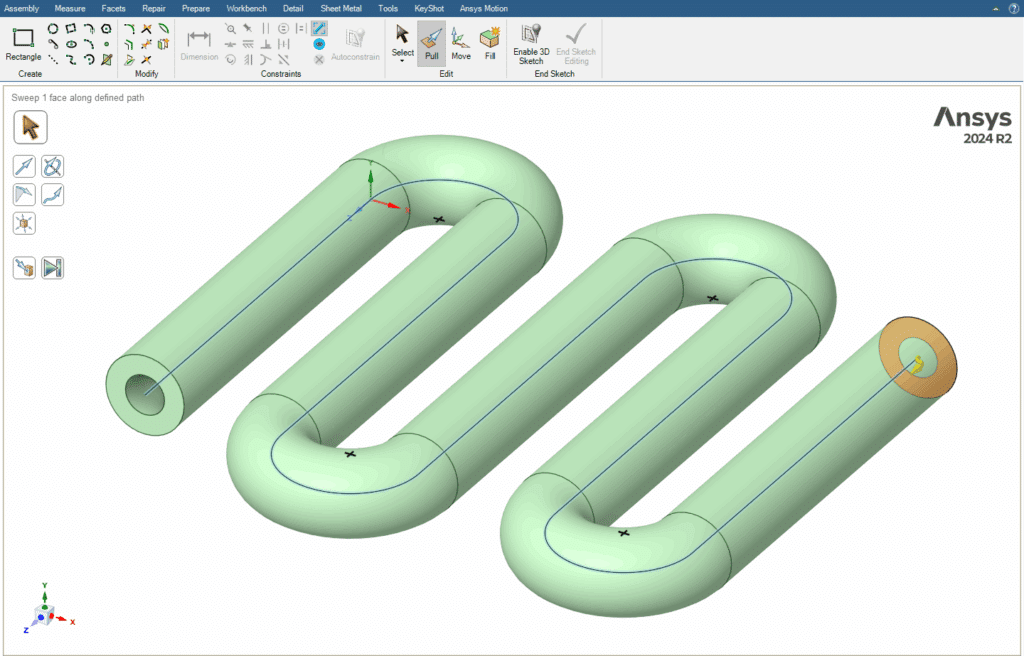
2.1.2. Sweep
The Sweep option in the Pull toolset is one of the most practical and important tools in this section. This command allows us to move a 2D geometry (profile) along a drawn 2D path, thereby creating a 3D solid. Simply put, in the Sweep command, we define a profile and a path, and the software extrudes the profile along the selected path to produce the desired 3D shape. For example, by using a circle as the profile and a line or curve as the path, we can create three-dimensional pipes or coils.
Summary
The purpose of this session was to complete some practical points in the 2D environment, including working with the tools in the Constraint section. In addition, we introduced the basics of creating 3D objects.
By the end of this session, you should be able to draw simple 3D shapes such as a cube, a cylinder, and also a hollow curved pipe. Each of these models can be created using different tools available in the Pull command.
You must be logged in to post a review.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.