Battery Thermal Management CFD Simulation Training Package: 4 Projects by ANSYS Fluent
$1,497.00 $898.20 HPC
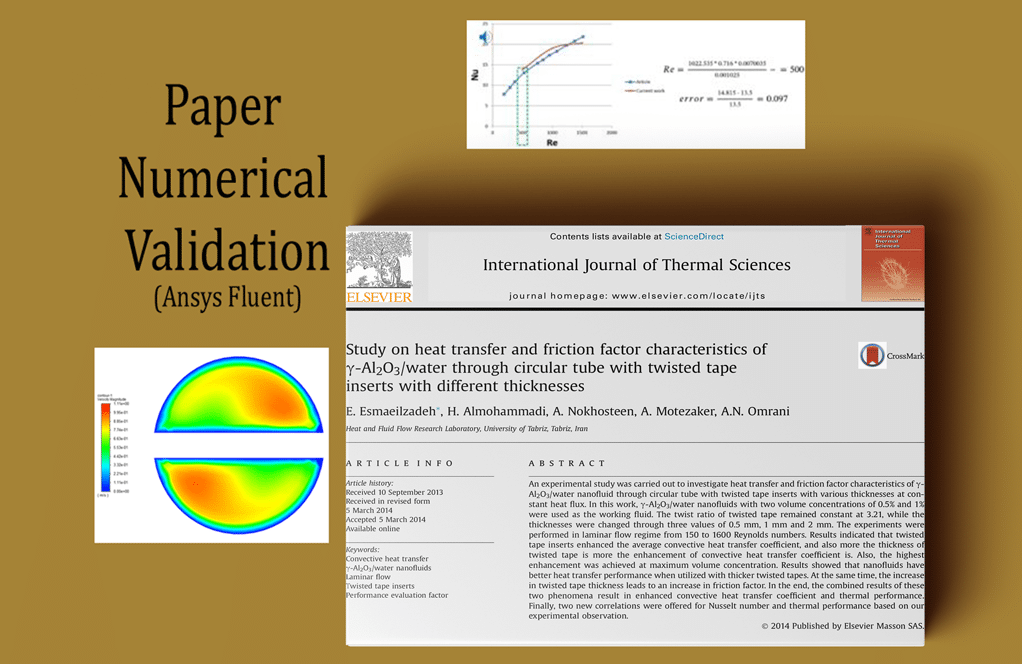
- Lithium-Ion Battery Thermal Management with PCM, Paper Numerical Validation: Foundation project establishing PCM modeling fundamentals and validation methodologies against published research, providing benchmark results for cross-validation in advanced studies
- Battery Cooling by PCM, ANSYS Fluent Training: Advanced PCM optimization directly building on validation techniques from Project 1, enabling comparative analysis with active cooling systems while applying proven modeling methods to complex scenarios
- Thermal Management of Battery Using Nano Fluid: Enhanced single-phase active cooling introducing nanofluid properties, building on heat transfer principles from PCM projects while establishing foundation for complex fluid dynamics in vapor cooling
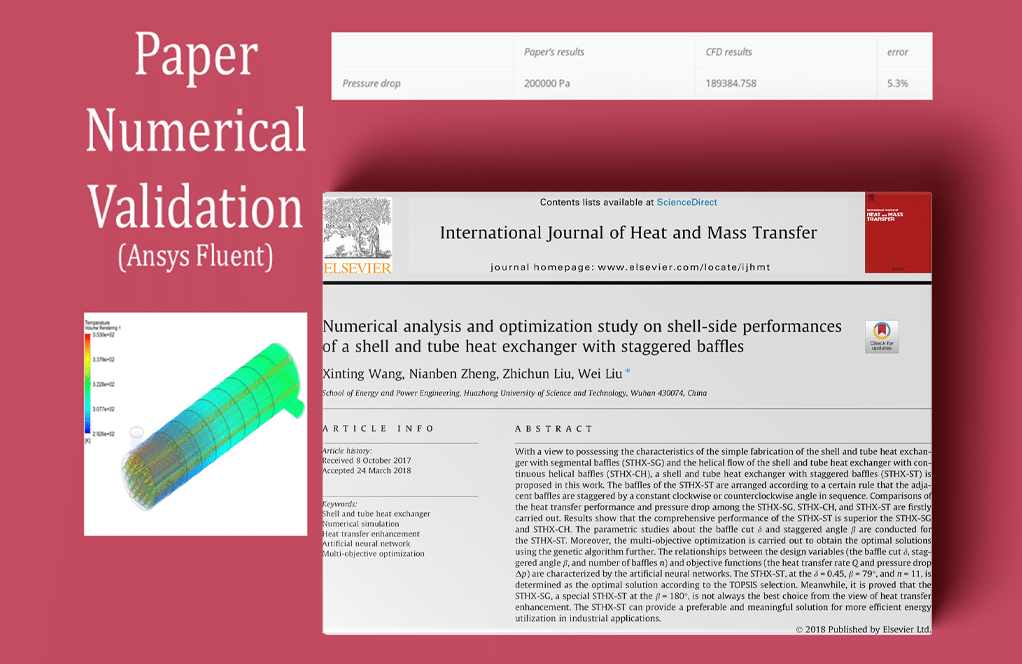
- Battery Thermal Management with Water Vapor Cooling: Cutting-edge two-phase system integrating validation methods, optimization techniques, and fluid modeling from all previous projects, culminating in comprehensive comparative analysis across all thermal management technologies
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email (info@mr-cfd.com), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via info@mr-cfd.com after you buy the product.
Description
Strategically Organized into Two Specialized Learning Sequences with Optimized Progression
Overview
This comprehensive Battery Thermal Management CFD Simulation Training Package has been strategically organized into two specialized learning sequences with an optimized project sequence that follows pedagogical best practices. The reordered structure ensures a smooth learning curve from fundamental concepts to advanced applications, building complexity progressively within each specialization.
Phase Change Material (PCM) Thermal Management Systems
Progressive Mastery of Passive Thermal Management Solutions
PCM Projects (Ordered for Optimal Learning):
Foundation Project: Lithium-Ion Battery Thermal Management with PCM, Paper Numerical Validation, ANSYS Fluent
Validation and Fundamentals
Advanced Project: Battery Cooling (Thermal Management) by PCM, ANSYS Fluent Training
Optimization and Implementation
Pedagogical Rationale for This Order:
Learning Progression Logic: The PCM Validation Project establishes solid theoretical foundations with rigorous validation methodology, while the PCM Training Project progresses to practical implementation and optimization strategies. This sequence follows the classic “learn-then-apply” educational approach that ensures students master fundamental concepts before tackling complex optimization challenges.
Skill Development Journey: The foundation phase focuses on mastering basic PCM modeling principles, developing validation skills against published research, understanding fundamental enthalpy-porosity methods, and building confidence through verified results. The application phase then applies foundational knowledge to complex design scenarios, develops optimization and troubleshooting skills, explores advanced PCM configurations, and focuses on practical implementation challenges.
Active Fluid-Based Thermal Management Systems
Progressive Mastery of Advanced Active Cooling Technologies
Active Fluid Projects (Ordered for Optimal Learning):
Foundation Project: Thermal Management of Battery Using Nano Fluid
Enhanced Single-Phase Systems
Advanced Project: Battery Thermal Management with Water Vapor Cooling Using CFD in ANSYS
Complex Two-Phase Systems
Pedagogical Rationale for This Order:
Learning Progression Logic: The Nanofluid Project introduces enhanced fluid properties in familiar single-phase flow, while the Vapor Cooling Project progresses to complex two-phase vapor systems with multiple transport phenomena. This sequence builds from simpler to more complex fluid dynamics, ensuring students develop a solid foundation in enhanced fluid modeling before tackling the challenges of multiphase systems.
Skill Development Journey: The foundation phase emphasizes mastering enhanced single-phase fluid modeling, understanding nanofluid property implementation, developing skills in enhanced heat transfer analysis, and building familiarity with active cooling system concepts. The advanced phase then applies fluid dynamics knowledge to two-phase systems, masters complex vapor generation and condensation modeling, develops expertise in advanced multiphase phenomena, and tackles cutting-edge cooling technology challenges.
Enhanced Learning Benefits of This Optimized Structure
The curriculum progression moves systematically from simple to complex concepts, validated methodologies to innovative applications, single-phase to multi-phase systems, passive to active cooling approaches, and established techniques to cutting-edge technologies. This structured approach ensures that each project builds upon the knowledge and skills acquired in previous studies.
PCM Systems Progression:
PCM Validation → PCM Training
Starting with validation provides students with proven methodologies and published validation references, building confidence through successful replication of established results. The subsequent implementation phase applies these validated techniques to practical design challenges, with advanced PCM training reinforcing and extending foundational concepts through optimization and real-world application scenarios.
Active Fluid Systems Progression:
Nanofluid → Vapor Cooling
Beginning with enhanced single-phase flow builds on conventional CFD knowledge that students likely already possess, creating a comfortable learning environment. The progression to two-phase vapor systems represents advanced CFD challenges that leverage the solid foundation established through nanofluid expertise, providing a natural stepping stone to vapor cooling mastery.
Cross-Technology Learning Synergies:
Technical Skill Building: Foundation projects in both PCM Validation and Nanofluid modeling establish fundamental modeling and validation skills that are essential for advanced work. Advanced projects in PCM Training and Vapor Cooling then apply optimization and cutting-edge design techniques, with progressive complexity ensuring that each project builds upon previous CFD and thermal management knowledge.
Professional Development Routes:
For beginners progressing to intermediate level, the recommended sequence starts with PCM Validation as the most accessible entry point, progresses to Nanofluid modeling with familiar single-phase physics, advances to PCM Training for optimization skills development, and culminates with Vapor Cooling as the most challenging concepts. Intermediate to advanced professionals can focus on PCM Training and Vapor Cooling for optimization and cutting-edge technology while using PCM Validation and Nanofluid modeling as reference and validation foundations.
Learning Outcome Optimization:
After PCM Systems Completion: Students develop a solid foundation in passive thermal management with proven validation and verification skills. This builds confidence in PCM modeling and optimization while preparing them for advanced active cooling challenges. The progression ensures thorough understanding of passive systems before moving to more complex active technologies.
After Active Fluid Systems Completion: Students achieve mastery of enhanced fluid properties and modeling with expertise in complex two-phase systems. This develops advanced CFD skills for cutting-edge applications and comprehensive active cooling system design capabilities. The knowledge gained represents the current state-of-the-art in battery thermal management technology.
After Complete Package: The comprehensive curriculum provides full spectrum thermal management expertise with progressive skill development from basic to advanced levels. Students gain validated modeling capabilities across all major cooling technologies and develop industry-ready skills for next-generation battery thermal management applications.
Flexible Implementation Options:
Sequential Learning (Recommended): The optimal progression follows PCM Validation → PCM Training → Nanofluid → Vapor Cooling for comprehensive skill development. This sequence ensures maximum learning efficiency and knowledge retention.
Technology-Focused Learning: Students can complete PCM systems first, then Active fluid systems (or vice versa), which is ideal for specialized professional development in specific technology areas.
Alternating Approach: The sequence PCM Validation → Nanofluid → PCM Training → Vapor Cooling provides excellent comparative technology understanding and prevents learning fatigue from focusing too long on a single technology type.
Professional Applications by Learning Stage:
Foundation Stage Professionals: This level serves new CFD users entering thermal management, engineers transitioning from other thermal applications, graduate students beginning battery thermal research, and validation and verification specialists who need proven methodologies.
Advanced Stage Professionals: This level targets experienced thermal engineers seeking specialization, R&D professionals developing next-generation solutions, senior designers working on cutting-edge applications, and optimization and performance enhancement specialists.
Technology-Specific Professional Focus:
PCM Systems Professionals: This specialization serves battery pack thermal designers, passive cooling system engineers, cost-sensitive application developers, and thermal energy storage specialists. The focus is on reliable, maintenance-free solutions that provide consistent thermal management over extended periods.
Active Fluid Systems Professionals: This specialization targets high-performance thermal system designers, advanced CFD specialists, next-generation cooling technology developers, and research and development engineers. The emphasis is on achieving maximum thermal performance and precise temperature control.
Industry Relevance by Technology:
PCM Applications: These technologies find primary application in electric vehicle battery pack design, energy storage system development, cost-effective thermal management solutions, and passive safety systems. The focus is on applications where reliability, cost-effectiveness, and maintenance-free operation are paramount.
Active Fluid Applications: These systems are essential for high-performance electric vehicle applications, advanced thermal management research, next-generation cooling technology development, and cutting-edge battery thermal solutions. The emphasis is on applications requiring maximum thermal performance and precise control.
Technology Comparison and Selection:
When to Choose PCM Systems: PCM technologies are optimal for cost-sensitive applications, passive safety requirements, long-term thermal stability needs, and maintenance-free operation requirements. These systems provide reliable thermal management without external power or control systems.
When to Choose Active Fluid Systems: Active fluid systems excel in high heat flux applications, precise temperature control needs, rapid thermal response requirements, and advanced performance optimization scenarios. These systems provide maximum thermal performance but require more complex control and maintenance.
This optimized project ordering ensures maximum learning efficiency while maintaining the flexibility to accommodate different learning styles and professional objectives. The progression from validated fundamentals to cutting-edge applications provides a solid foundation for professional success in battery thermal management across both passive and active cooling technologies. Students completing this curriculum will possess the comprehensive knowledge and practical skills necessary to address current and future challenges in battery thermal management system design and optimization.
You must be logged in to post a review.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.