Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation by ANSYS Fluent
$140.00 Student Discount
- The problem numerically simulates Darrieus Wind Turbine using ANSYS Fluent software.
- We design the 3-D model by the Design Modeler software.
- We Mesh the model by ANSYS Meshing software, and the element number equals 2289621.
- We perform this simulation as unsteady (Transient).
- We use the Mesh Motion method to define a rotational zone.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Darrieus Wind Turbine Evaluation, ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Training
This project is about the Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation via ANSYS Fluent software. We perform this CFD project and investigate it by CFD analysis.
Vertical Axis Wind Turbine (VAWT) is becoming ever more important in wind power generation thanks to its adaptability for domestic installations. However, it is known that VAWTs have lower efficiency, above all, if compared to HAWTs.
To improve VAWTs performance, industries and researchers are trying to optimize the design of the rotors. In this regard, CFD has been employed to evaluate this type of turbine in this study.
This project will simulate an airflow close to a vertical axis Darrieus wind turbine. The inlet is considered to wind at 1 m/s, and the turbine zone rotates with 120 RPM. This project investigates the behavior of airflow and pressure distribution, and studies drag force.
The geometry of the present model is drawn by Design Modeler software. The geometry included a rotary zone for the turbine walls and a stationary zone for the rest of the domain.
The model is then meshed by ANSYS Meshing software. The model mesh is unstructured, and 2289621 cells have been created.
Darrieus Method
In this simulation, the rotational motion of the turbine blades must be defined. But instead of applying rotational motion to the blades, rotational motion is applied to the field around the blades. So, it is necessary to separate a distinct zone as the moving zone from the total computing zone.
Since this turbine is one of the vertical axis turbines, the behavior of the fluid is dependent on time; because the position of the turbine blades varies over time. Then the Mesh Motion is used in cell zone conditions. In this method, the rotation axis and rotation speed must be determined.
Darrieus Conclusion
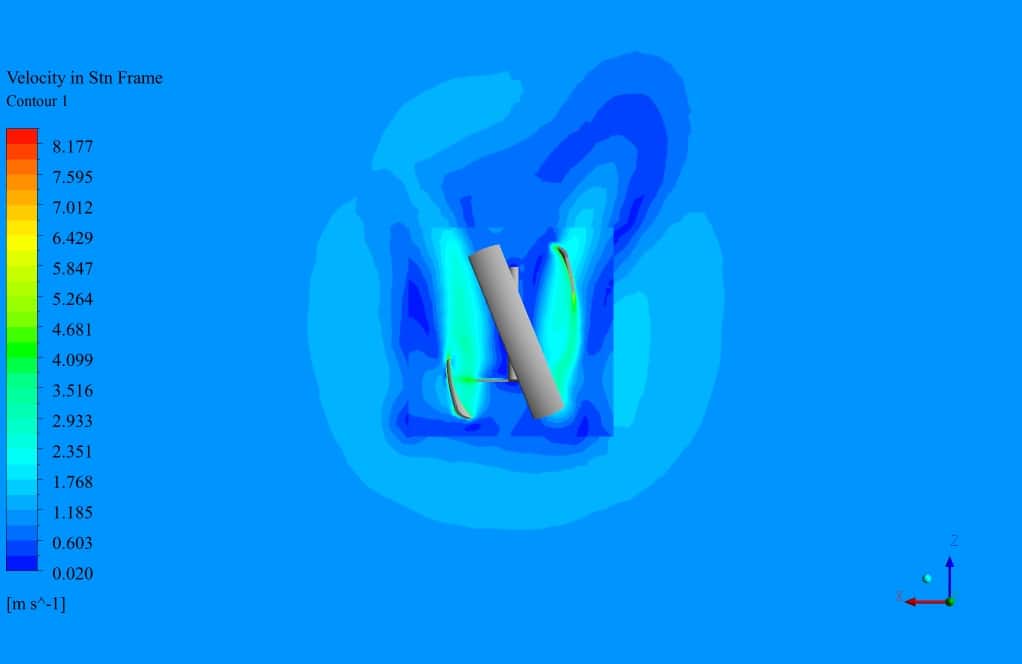
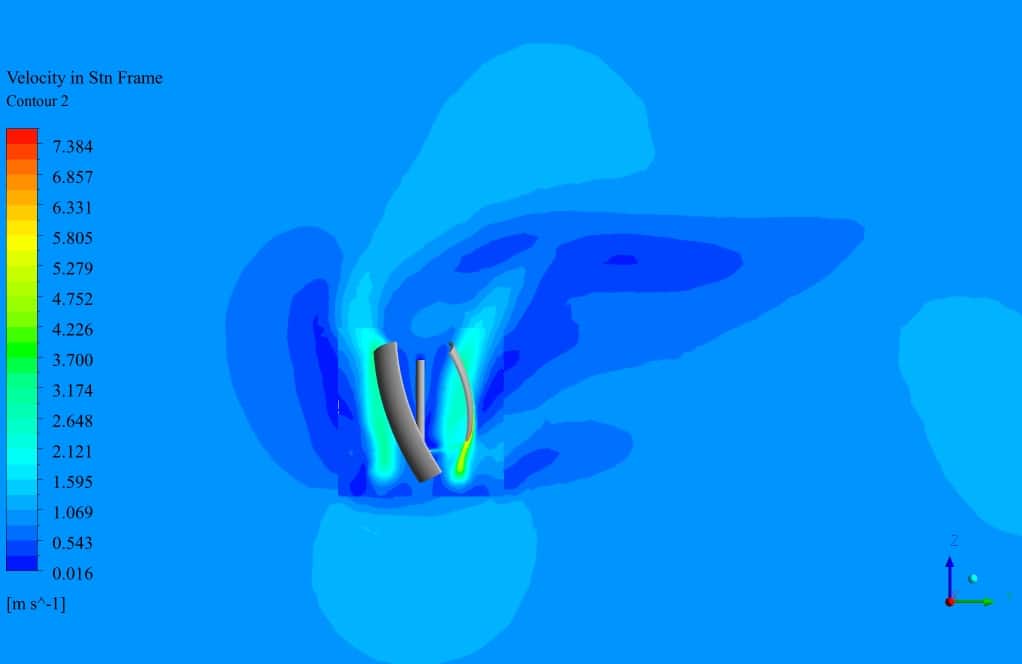
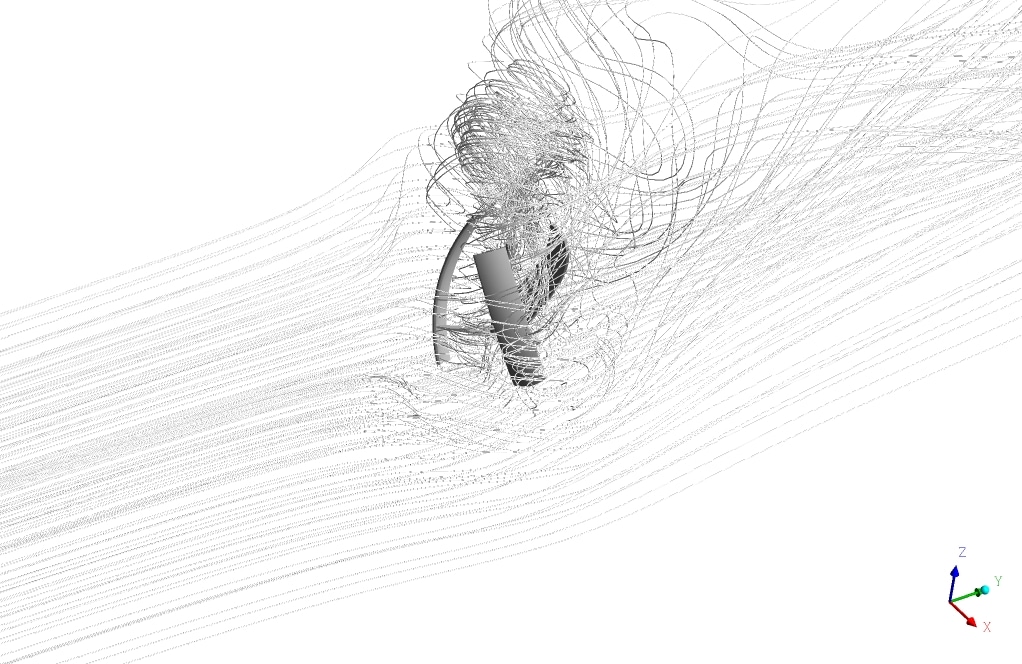
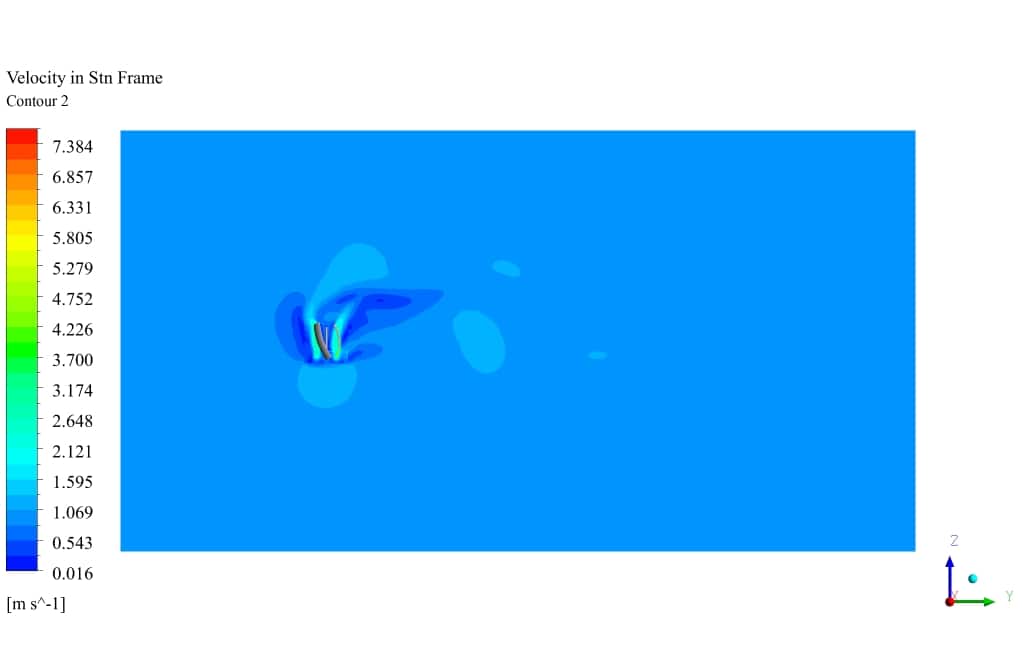
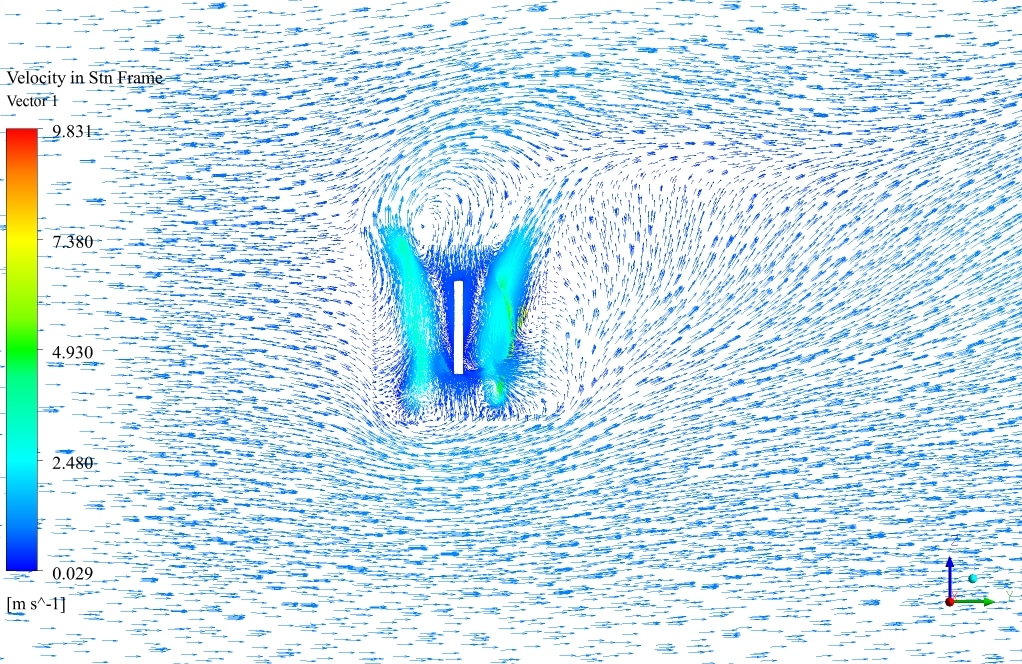
After simulation, the contours of velocity and pressure are obtained. Also, velocity vectors around the turbine blades are obtained. The results show that the wind flow around the turbine blades has a rotational movement. The velocity field adjacent to the wall of the turbine has the highest gradient.
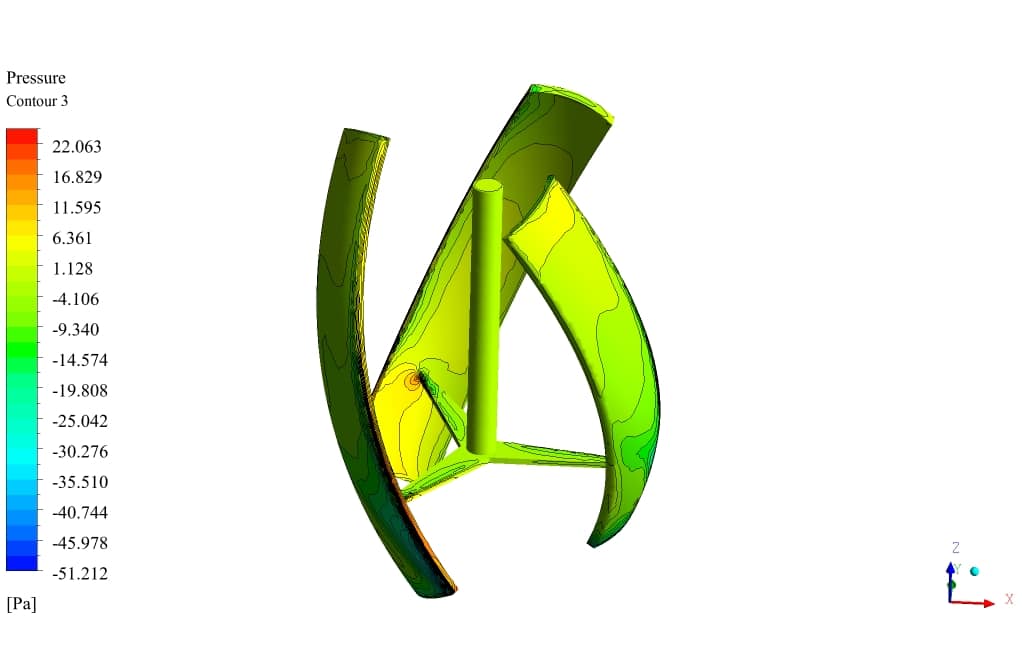
Also, The leading edge of the turbine wall suffers from the highest-pressure gradient, which is logical since the velocity has just met zero. Additionally, the streamlined vectors illustrate the quality of the flow streams resolved in the wake section, which is the core challenge of aerodynamic simulation.
Finally, the drag force is 0.1826 (N), which is accurate for a turbine with the noted specifications.






Alfred Bauch I –
The level of detail in this simulation is truly impressive.
Lesly Abbott –
This simulation is a testament to the power of computational fluid dynamics!
Hipolito Labadie –
I’m really impressed by how realistic the simulation seems to handle airflow and pressure distribution around the Darrieus Wind Turbine. It’s encouraging to see such a detailed CFD analysis which would greatly assist in optimizing the efficiency of these turbines.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to hear that our CFD simulation of the Darrieus Wind Turbine was able to vividly present the intricacies of airflow and pressure distributions. Our aim is indeed to offer a detailed and realistic analysis to aid in the optimization process for VAWTs. We appreciate your recognition of the effort put into this project.
Julien Stokes MD –
I truly appreciate the detailed simulation of the Darrieus Wind Turbine conducted using ANSYS Fluent. The insights on aerodynamic performance and the ability to capture the flow characteristics around the rotating blades provided significant learning in terms of computational fluid dynamics principles applied to renewable energy devices.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! It’s fantastic to hear that the simulation helped enhance your understanding of CFD applications in renewable energy. We’re glad the project was insightful for you.
Muhammad Yousef –
This is so great. I was exactly looking for sth like this!!
Mr CFD Support –
Thanks for purchasing our products. Hope you enjoyed it!!
Duncan Braun –
The learning module provided by MR CFD was superb! It meticulously explained the CFD Simulation of the Darrieus Wind Turbine, including meshing details and how to define the rotatory zone for the moving parts. Plus, the aerodynamics insights like high-pressure gradients at the leading edge were quite interesting.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the positive feedback! We’re pleased to hear that our Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD simulation training was helpful and informative. Understanding aerodynamics is crucial for optimizing wind turbine design, and we’re glad our module could shed light on these important aspects. If you have any further questions or need more assistance in the future, feel free to reach out!
Eloy Gleason I –
The project helped me understand the aerodynamics at play quite effectively. The visualization of flow streams and their resolution in the wake section was particularly impressive. I was also appreciative of the concise explanation on the drag force result for the turbine. Excellent work on the CFD simulation training regarding the intricate aspects of Darrieus Wind Turbine aerodynamics!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our CFD simulation could effectively aid your understanding of the Darrieus Wind Turbine’s aerodynamics. Our goal is to provide comprehensive insight through detailed visualizations and accurate data analysis. Your appreciation motivates us to continue delivering high-quality training and simulations. If you have any further questions or need more information, please feel free to reach out.
Dr. Nicholas Champlin –
Fantastic resource! I found ‘Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation by ANSYS Fluent’ extremely helpful for understanding the aerodynamics of vertical wind turbines. The detailed explanation of mesh motion and the clear presentation of results such as velocity and pressure contours made the concepts easy to grasp!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are so pleased to hear that the ‘Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation by ANSYS Fluent’ was comprehensive and facilitated your understanding of vertical axis wind turbines. If you have any further inquiries or need more clarification on any other topics, please don’t hesitate to ask. Your positive feedback truly means a lot to us!
Rocky Parisian –
The Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation course seems to cover comprehensive subjects. However, I’m curious about how the rotating zone around the turbine blades affect the mesh. Could you elaborate on that?
MR CFD Support –
In the Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD simulation, a rotating zone is defined around the turbine blades to simulate rotational movement. This method simplifies the rotation handling by keeping the actual turbine blades stationary rather than physically rotating them. This means that during simulation, the mesh within the rotating zone moves following the prescribed angular velocity, effectively representing the turbine blades in motion. This method allows for a less complex mesh since it doesn’t need to constantly update the position of the turbine blades, which prevents issues like mesh distortion that can occur during physical mesh rotation.
Ms. Lavada Kling MD –
I’m impressed by how the Darrieus Wind Turbine simulation captures the complex airflow dynamics! The insight into pressure distribution and drag force is particularly helpful for optimizing turbine design.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind feedback! We are delighted to hear that our simulation was insightful and helpful in understanding the aerodynamics of Darrieus Wind Turbines. We continuously strive to provide accurate and useful simulations for design optimization and it’s great to know our efforts are appreciated.
Alfonzo Goyette –
The course content was engaging, and the practical applications for VAWT design were enlightening. The step-by-step CFD process demonstrated in ANSYS Fluent contributes significantly to understanding the complete workflow of simulating Darrieus Wind Turbines. The simulations’ results, particularly those visualizing airflow and pressure distribution around turbine blades, were informative and showcased the thoroughness of the study. Excellent resource for those interested in vertical axis wind energy technology!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our course content was informative and helpful in providing a deep understanding of the CFD process, especially as it relates to the Darrieus Wind Turbines simulations using ANSYS Fluent. It’s gratifying to know that our training could demonstrate the airflow and pressure distribution effectively. We appreciate your appreciation for the course, and it encourages us to keep providing high-value content. Thank you for choosing us as a resource in your learning journey!
Jerald Kuhn –
Fantastic resource for understanding Darrieus Wind Turbines. The application of CFD in analyzing the aerodynamics and efficiency of different rotor designs is clearly demonstrated in the course. It’s great to see real-world applications of CFD, which can lead to more efficient and optimized turbine designs. The detailed explanation of simulation setup and results interpretation is particularly beneficial!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are thrilled to hear that you found the Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation course using ANSYS Fluent helpful and informative. Our goal is to provide comprehensive learning resources that enable our customers to apply CFD in real-world scenarios effectively. We appreciate your recognition of the course’s practical applications and detailed instructions. If you have any further questions or need additional resources in your future studies, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
Edgardo Reichel –
I’m absolutely thrilled with the capabilities showcased in the Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation training. The intricacy of airflow behaviour and the details in pressure distribution analysis were beyond impressive. It’s clear that this training is a valuable resource for anyone interested in optimizing VAWTs. The use of rotational motion within a separated moving zone seemed like an effective approach to tackle the time-dependent behaviour of the turbine blades. Well done!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that our Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation training met your expectations and impressed you with its detailed approach to the study of VAWT aerodynamics. It’s always our goal to provide thorough and effective training material that adds value to our customers. We appreciate your recognition of the effectiveness of the moving zone and time-dependent blade behavior simulation technique. Your satisfaction is a great motivation for us to keep improving our services.
Leopold Deckow DDS –
I recently completed a course using the MR CFD Company’s Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation training product, and the detail in airflow analysis overwhelmed me. The 3D graphical representations helped me visualize the difficult concepts of rotational flows and pressure distribution. Truly an exemplary tool for understanding the complexities of vertical axis wind turbines!
MR CFD Support –
We are thrilled to hear that our Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation course has been beneficial to your learning experience and that the 3D graphics were helpful in your understanding of this complex subject. We strive to provide detailed and high-quality learning tools for our clients. Thank you for choosing our training product, and we appreciate you taking the time to leave such a positive review!
Lori Ziemann –
What differences should be expected in the simulation outcome if the wind speed is increased from 1 m/s to 5 m/s?
MR CFD Support –
Increasing the wind speed in the simulation from 1 m/s to 5 m/s would result in a proportional increase in the dynamic forces acting on the turbine blades. You can expect to observe a greater wind force transferred to the turbine, which could potentially lead to increased power output. Higher velocities would also affect the pressure distribution and flow patterns around the blades, as well as possibly cause greater turbine wake effects.
Ms. Jeanette Nitzsche –
I was impressed by the level of detail in the airflow analysis around the turbine blades. The use of CFD to visualize these intricate patterns must be incredibly helpful for optimizing turbine design. Thanks for a thorough and insightful product!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re thrilled to know that you found the CFD simulation insights valuable for understanding the airflow patterns around the Darrieus Wind Turbine blades. We always aim to provide detailed and accurate analyses in our products. Your appreciation is greatly motivating for us!
Icie Aufderhar –
What is the main objective of the Helical Wind Turbine CFD Simulation?
MR CFD Support –
The main objective of this simulation is to analyze the airflow around a helical wind turbine and understand its aerodynamic behavior. This includes studying the effects of wind speed on the turbine’s performance.
Danielle Rowe –
The explanation of the Darrieus Wind Turbine simulation was eye-opening, particularly the innovative way that the rotational motion is applied to the fluid field instead of the blades themselves. Your project has illuminated some complex concepts in a digestible format. A job well done!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for appreciating our Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation training. We are glad to hear that we were able to present the concepts in a way that is both informative and understandable. Your encouraging feedback motivates us to continue producing high-quality educational materials. If you have any further questions or need more information, feel free to reach out.
Joshua Hodkiewicz –
The Darrieus wind turbine simulation sounds very detailed. I was especially interested in the way the airflow and pressure distribution are handled. Does the simulation model account for turbulence and if so, how is it modeled?
MR CFD Support –
Indeed, the simulation includes turbulence modeling to accurately predict the airflow behavior around the turbine blades. In ANSYS Fluent, a suitable turbulence model, such as the k-epsilon or k-omega model, is generally used to capture the turbulent nature of the wind flow. The specific turbulence model selection would be based on the requisites of the simulation to resolve the flow streams within the wake of the turbine effectively.
Miss Hulda Cronin DVM –
The simulation details were great! Understanding the airflow movement around the turbine blades and determining drag force was extremely insightful.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad that you found the simulation details helpful and insightful. The understanding of fluid dynamics around turbine blades is crucial for optimizing wind turbine performance, and we pride ourselves on providing detailed and accurate simulations. We appreciate your review and are happy that you appreciated the effort put into this project.
Dr. Florencio Reichert –
The Darrieus Wind Turbine simulation sounds insightful! The in-depth analysis of airflow, pressure distribution, and drag force using CFD techniques to optimize VAWT design is fantastic. Great work on leveraging the advanced capabilities of ANSYS Fluent to obtain detailed insights on turbine behavior under operational conditions.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback on the Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation! We’re glad that you found the analysis and insights provided in this simulation to be comprehensive and enlightening. It’s motivating to know that our dedication to using advanced simulation technology like ANSYS Fluent is appreciated by our customers. Your satisfaction reaffirms our commitment to delivering high-quality CFD learning material. If you ever have any more questions or need further information, we’re here to help!
Julio Blanda PhD –
Fantastic resource! The Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation training was incredibly helpful. Understanding the flow dynamics and force distributions on the turbine was instrumental for my research project on renewable energy systems. Well-structured and comprehensive training.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that our Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation training was instrumental for your research. It’s our pleasure to provide resources that help our clients succeed in their projects. If you need any further assistance or have questions in the future, remember that we’re here for you!
Alia Crona IV –
I was so impressed with the way the Darrieus Wind Turbine simulation is set up in ANSYS Fluent. It taught me a great deal about the simulation of vertical axis turbines and the importance of using CFD for performance optimization. The project explanation detailed the setup thoroughly, making it easy to follow the simulation process.
MR CFD Support –
We are thrilled to hear that you are satisfied with the Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation training and its clear setup instructions. Our aim is to provide in-depth understanding and high-quality learning materials. Thank you for taking the time to share your positive experience!
Mrs. Pamela Pagac II –
I’m really impressed with the detailed airflow and pressure distribution analysis. Amazing to see how CFD can be applied to optimize a wind turbine’s performance!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind review! We are thrilled to hear that our CFD simulation of the Darrieus Wind Turbine gave you a clearer insight into the aerodynamics involved. Our goal is to harness the power of simulation to better understand and improve such renewable energy technologies.
Prof. Leanne Jast –
The project provided an insightful understanding of the Darrieus Wind Turbine operation. The detailed mesh with over 2 million cells ensured precision in capturing the complex flow patterns. Excellent work on representing both the pressure gradients and wake section, which are critical aspects of VAWT simulations. The use of an unstructured mesh is apt for the curved geometries. Additionally, the extraction of aerodynamic forces like the drag force adds significant value to design optimization. Keep up the compelling analytical work!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your thoughtful feedback and appreciation of our CFD simulation for the Darrieus Wind Turbine. We are glad to hear that the level of precision and detail in our analysis met your expectations and that you find value in the aerodynamic data provided. We aim to deliver high-quality simulations that can aid in efficient design optimizations for our clients. Your words of encouragement motivate us to keep producing quality work. Thank you once again for your review.
Tatum Yundt –
The simulation captures the intricate behavior of air around the wind turbine perfectly! The detailed breakdown and visualization of velocity and pressure distributions alongside the consideration of drag on the blades are especially impressive.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the kind words! We are glad to hear that you are impressed with the simulation details and the quality of the results obtained for the Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD simulation.
Prof. Lorenzo Bartoletti –
The training for the Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulations sounds thorough. Just wondering, how easy is it to follow and replicate the simulation steps for someone new to CFD?
MR CFD Support –
The training material provided for the Darrieus Wind Turbine CFD Simulation is tailored to be comprehensive and user-friendly. For someone new to CFD, following the provided step-by-step guidance in the software should make it straightforward to replicate the steps and understand the simulation process.