Two-stage Water Desalination Equipment CFD Simulation
$200.00 Student Discount
In this project, Surface Evaporation inside the Desalination System using the multiphase VOF model have been simulated, and the results of this simulation have been investigated.
Click on Add To Cart and obtain the Geometry file, Mesh file, and a Comprehensive ANSYS Fluent Training Video.To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Description
Water desalination or distillation is a widely used mechanism for purifying water by removing impurities such as salts, minerals, and other contaminants. This process involves heating water to its boiling point, which causes the water to vaporize and leave the impurities behind.
The water vapor is then condensed into a liquid, resulting in pure water. Distillation is a highly effective method for removing impurities from water, as it can remove the smallest contaminants that other methods may not eliminate.
Distillation/desalination can be performed using various equipment, ranging from simple pot stills to more complex industrial-scale distillation systems. The process has numerous applications, including producing drinking water, pharmaceuticals, and industrial chemicals.
Two-stage Water Desalination Equipment Methodology
The VOF multiphase model was used in this project to simulate the surface evaporation occurring inside the desalination system. A user-defined function (UDF) was hooked to the Fluent source code to model the mass transfer through surface evaporation, as this mechanism is not included in the base code.
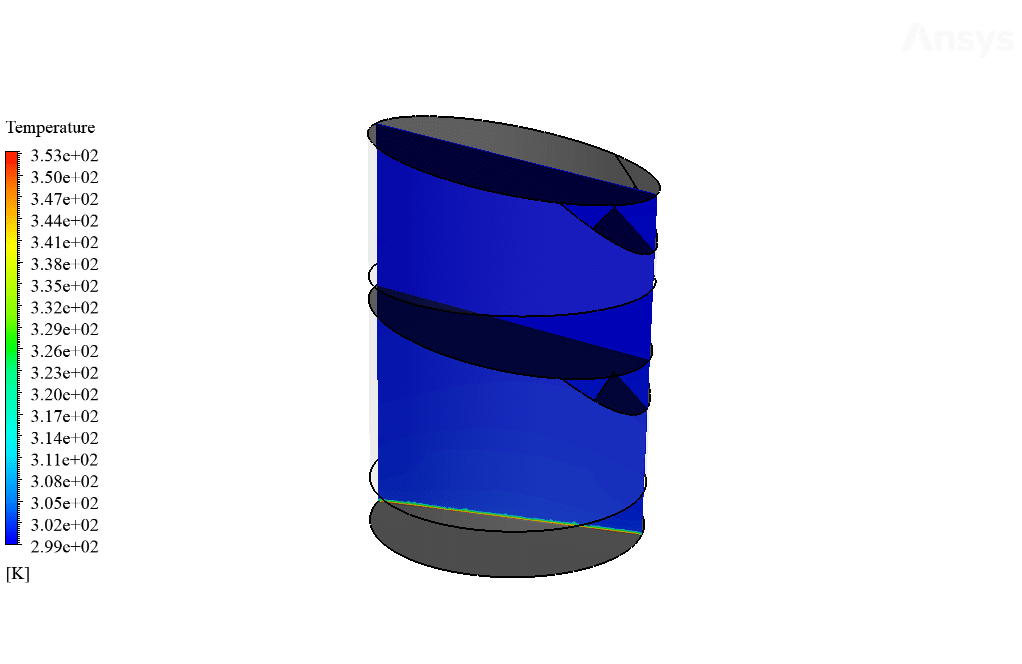
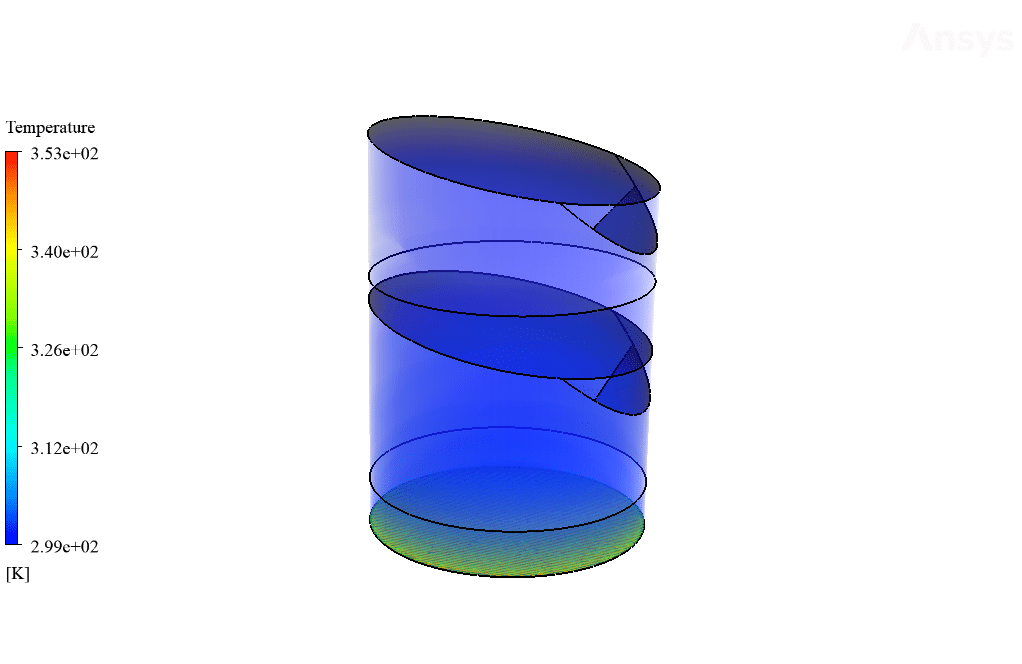
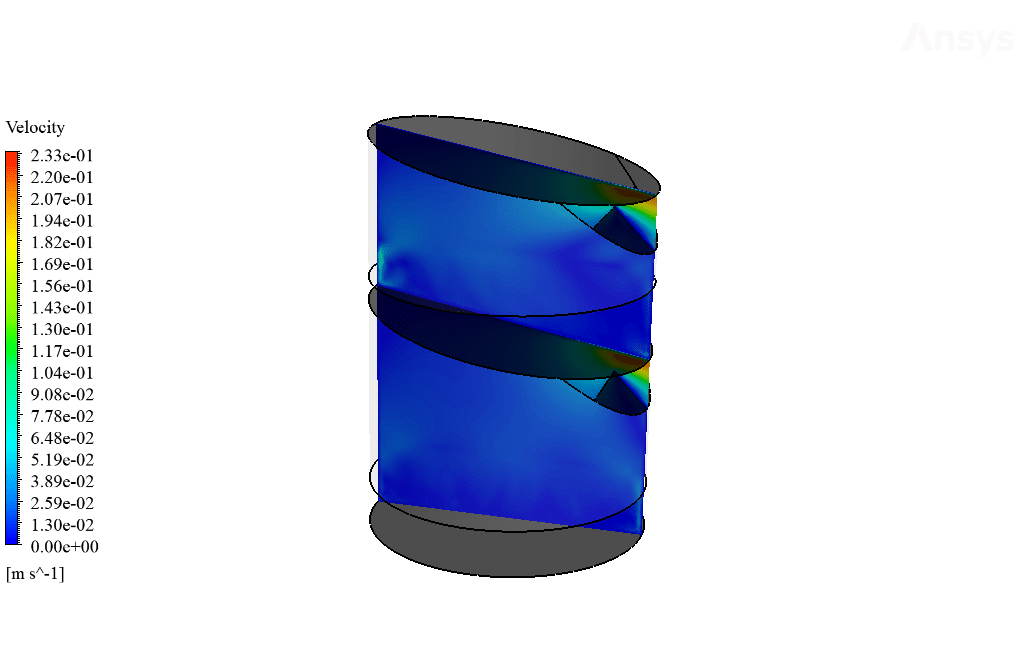
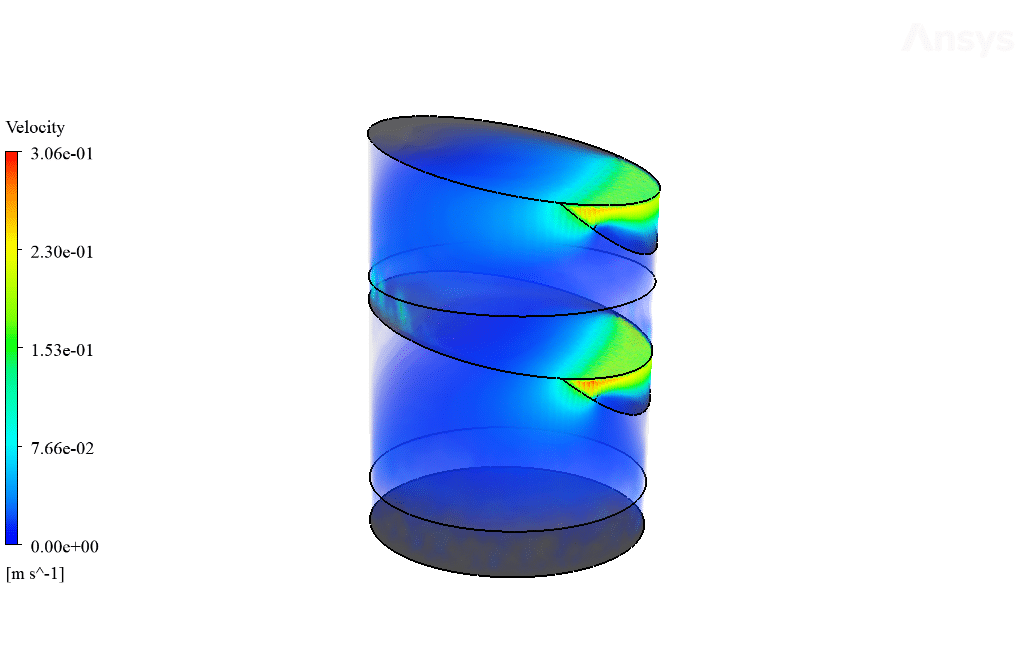
The device’s bottom surface increases the bulk temperature of water to around 353 K, resulting in increased molecular energy of water, which helps with the surface evaporation process occurring faster. The vaporized water will then hit cool sloped surfaces where it will condense into water liquid and be directed to the system outlet.
Furthermore, a realizable k-epsilon model is used to solve turbulent fluid equations. This model provides higher accuracy when simulating internal flows. The energy equation is also enabled due to the fact that we have heat transfer in this model. The present study is performed in transient format and 3D. Moreover, gravity is enabled to capture the upward motion of vapor due to its lesser density than water liquid.
The geometry of the present project is designed in Design Modeler and meshed in ANSYS Meshing software. The mesh type is unstructured, and the element number equals 1,936,581.
Conclusion
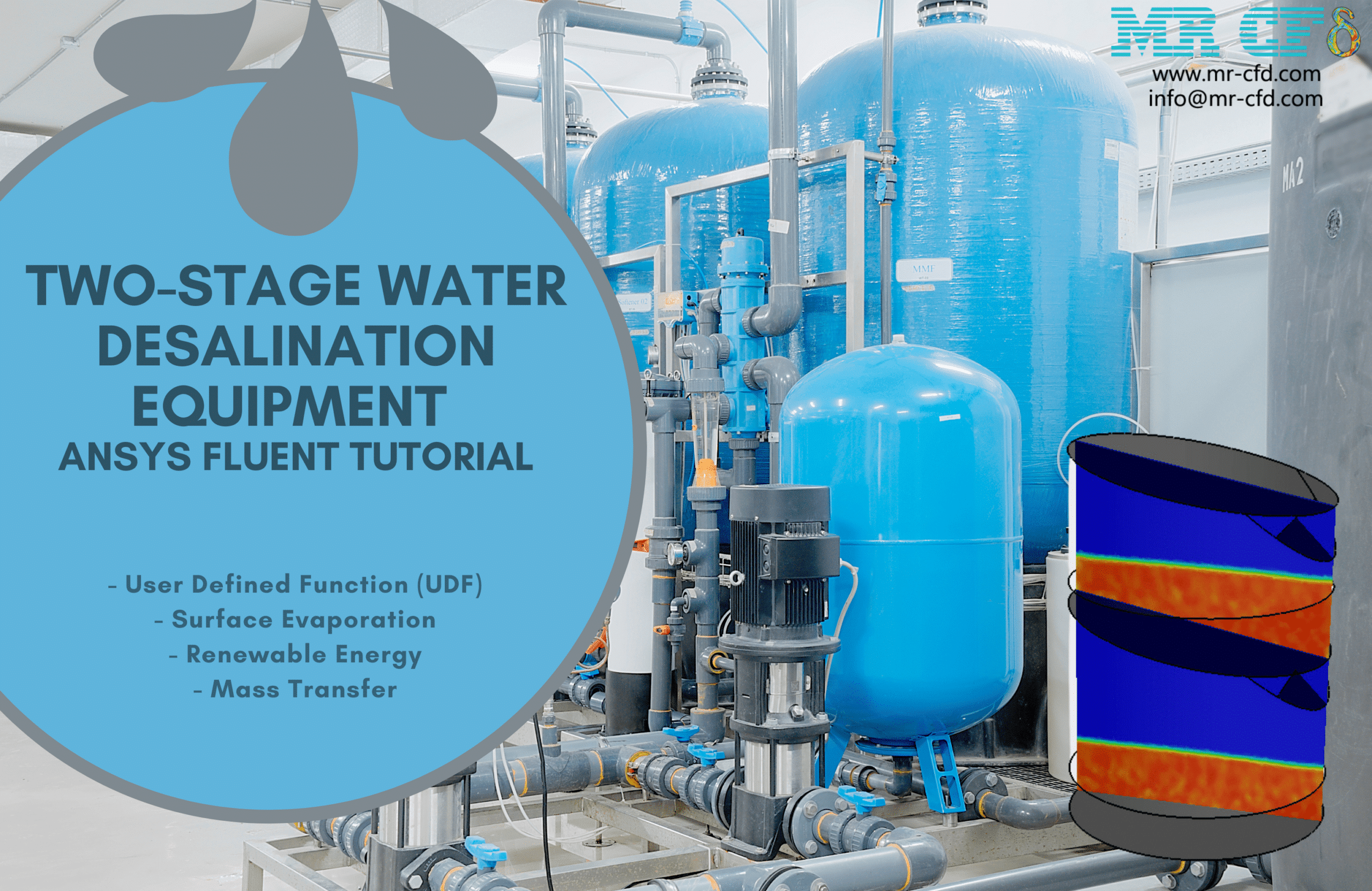
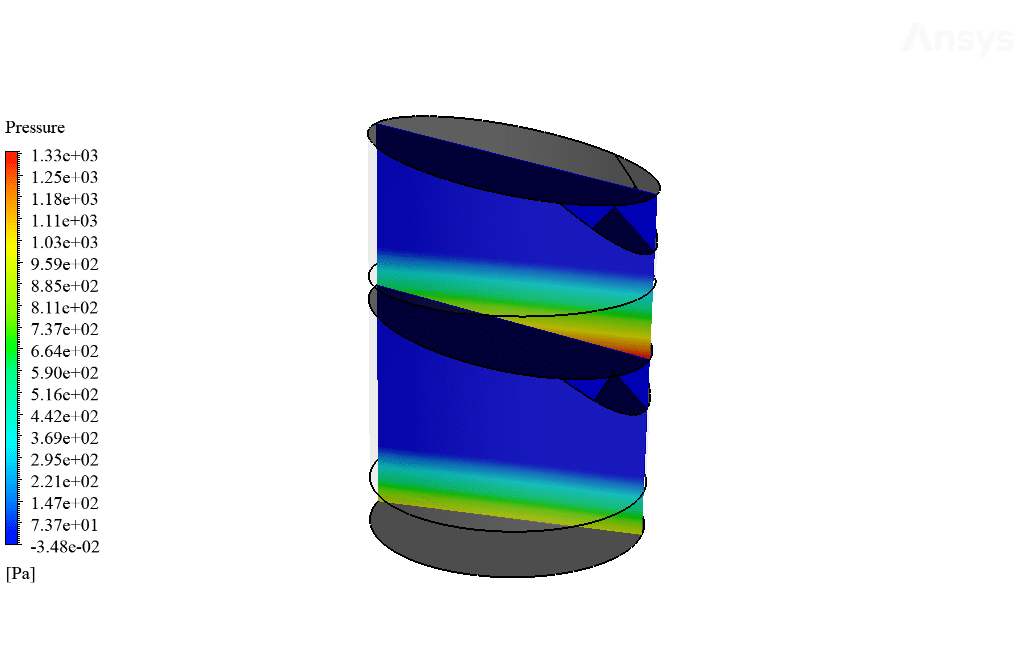
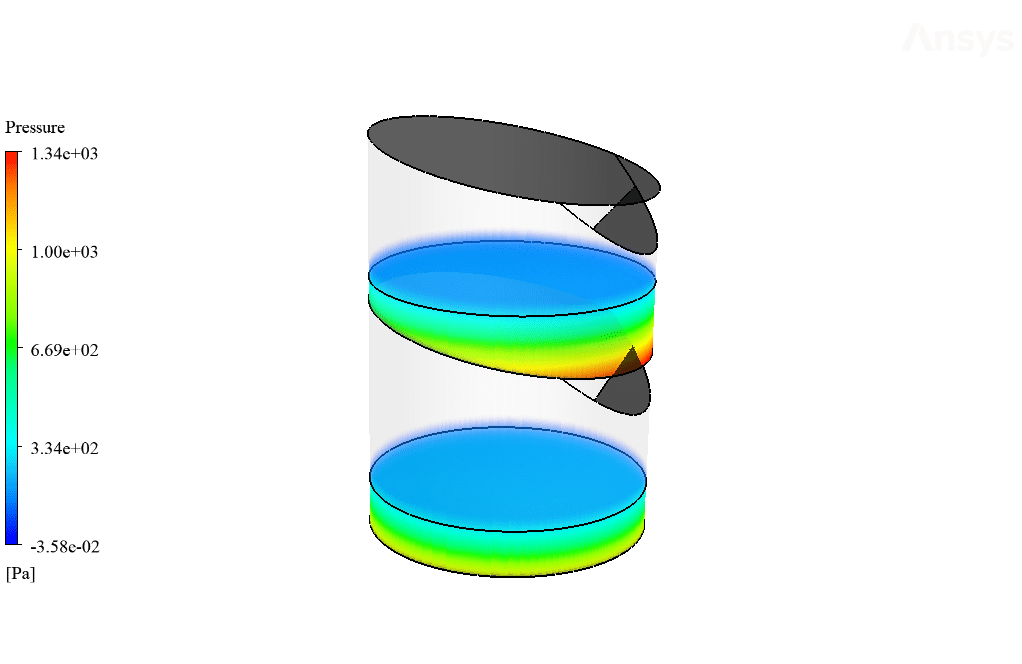
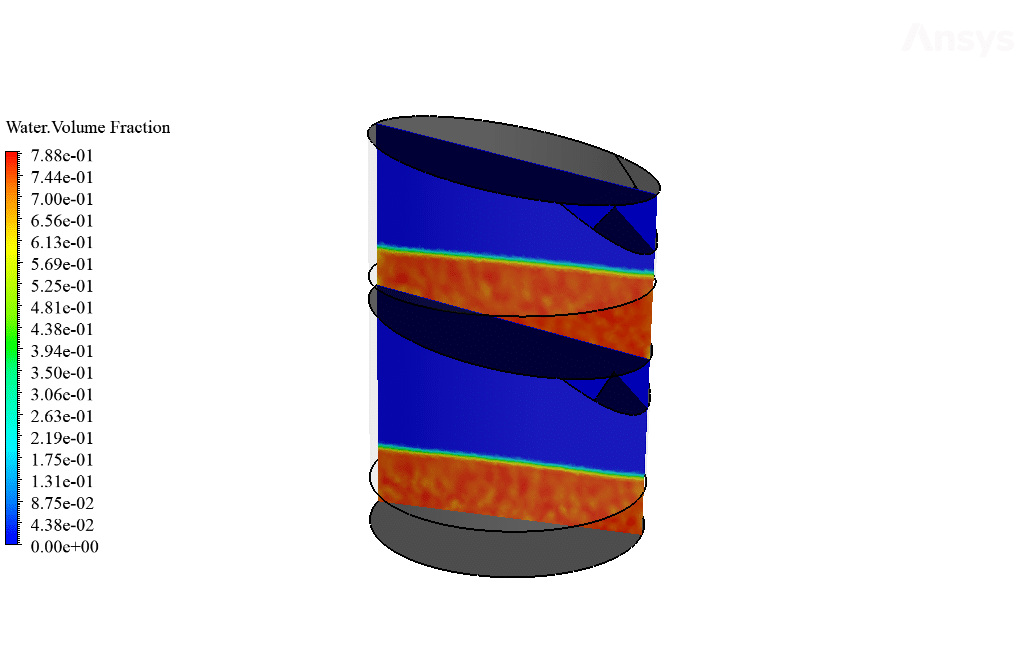
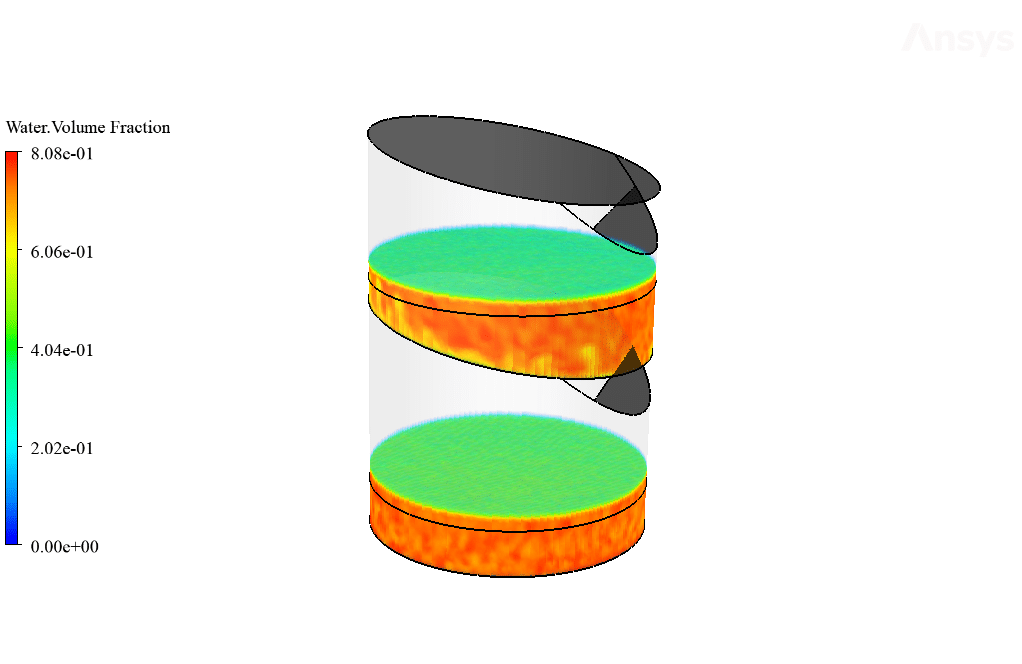
As observed in the obtained results and contours, stratified pressure distribution inside the system trays is clearly shown. This is due to the hydrostatic pressure of the water column inside the trays.
Also, as observed in the temperature contour, the bottom surface has an increased temperature which causes the water liquid’s molecular motion path to increase. This increase in molecular motion will lead to the increased kinetic energy of water molecules, which would, in turn, cause the surface evaporation process to occur faster.
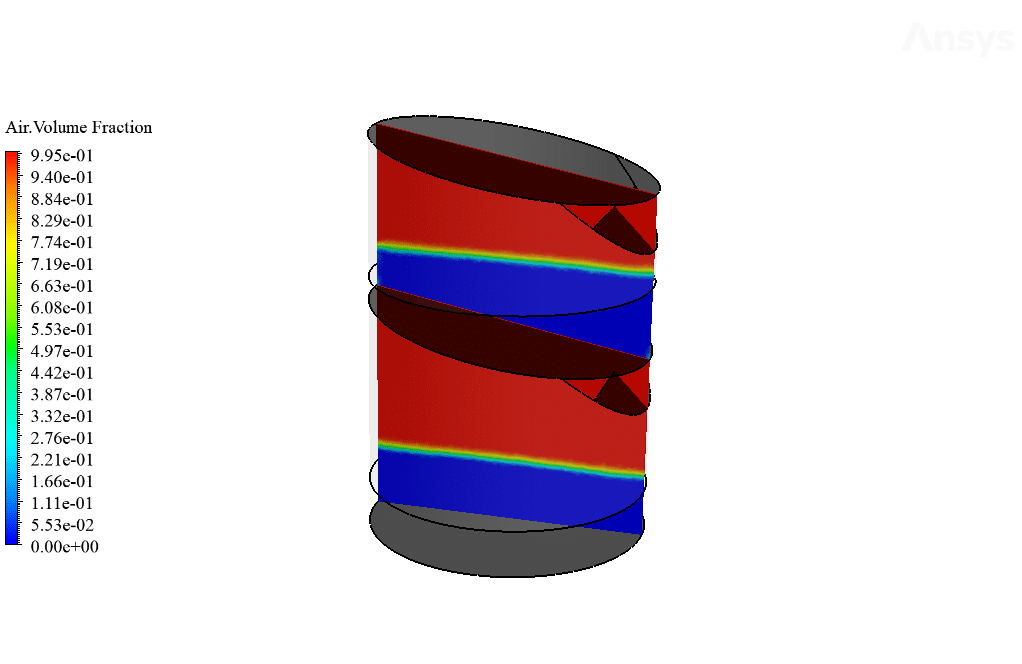
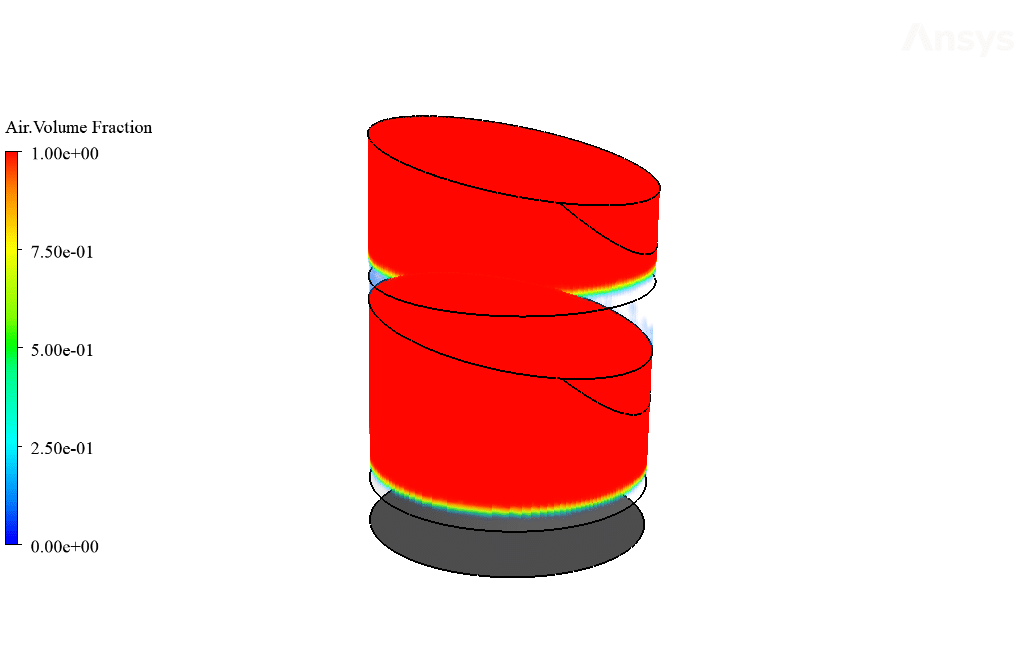
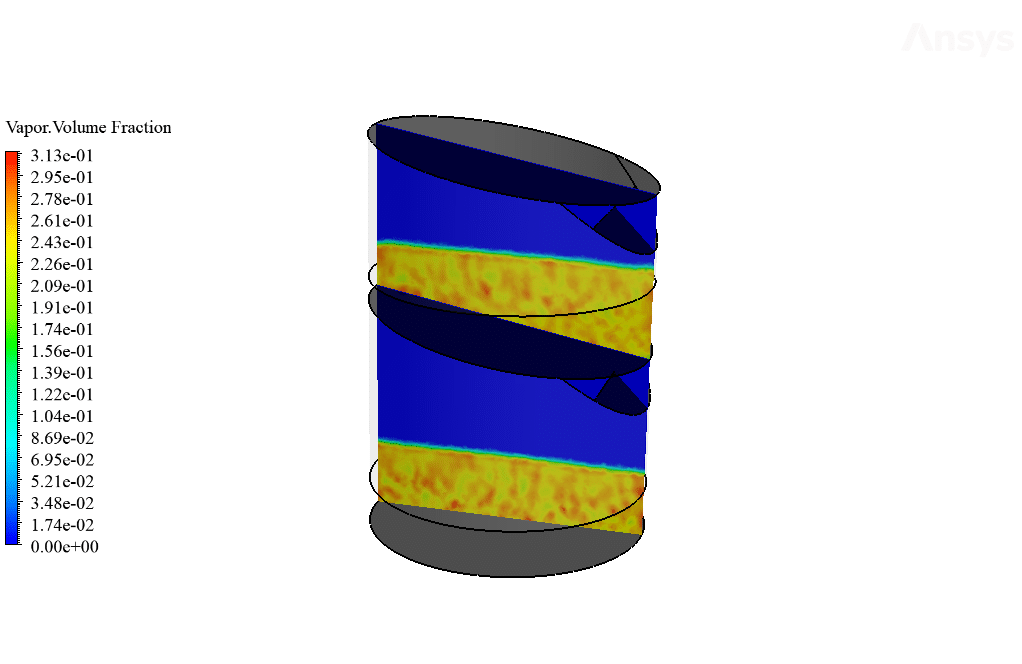
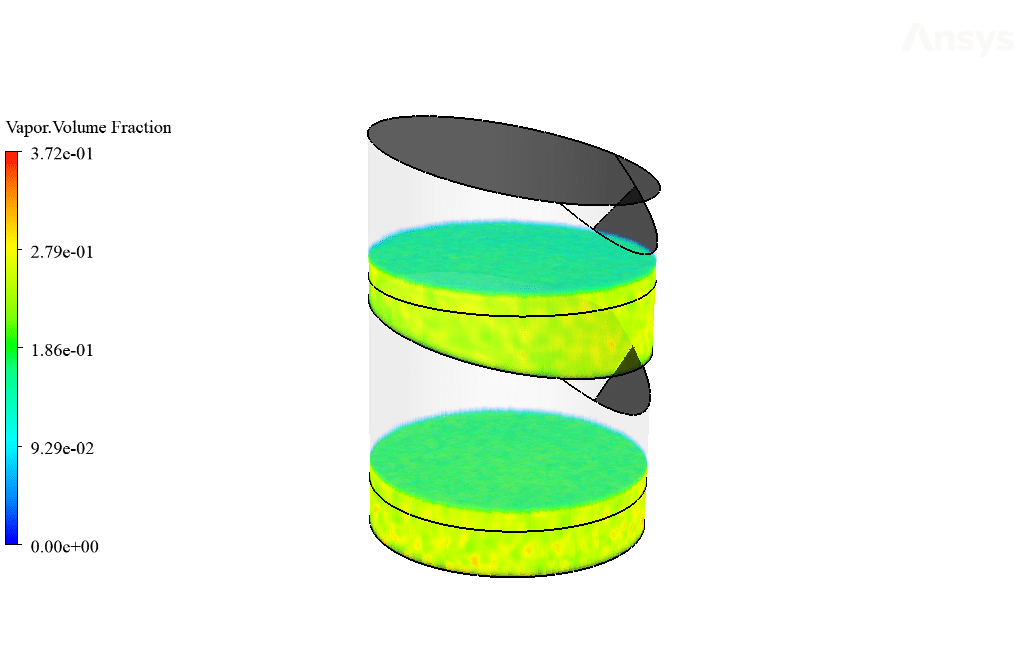
Moreover, the amount of the generated vapor can be obtained by viewing the mass transfer rate contour. The exact amount of the vaporized water will distill after it touches the cool sloped plates. Therefore, the amount of vaporized water within the trays equals the amount of distilled water leaving the system through outlet boundaries.

Karianne Erdman III –
This review is fascinating, but I’m curious about what measures were taken to ensure the accuracy of the user-defined function in simulating surface evaporation.
MR CFD Support –
In the simulation for two-stage water desalination, multiple calibration and validation tests have been run to fine-tune the user-defined function. This ensures that the modeled mass transfer matches experimental data or theoretical predictions before applying it to the distillation system simulation. The correctness of the UDF has been ascertained through compareación against known evapotransfer rates and other physical properties relevant in the distillation process.
Prof. Jaylin Roob III –
I’m thrilled with how comprehensive the two-stage water desalination equipment simulation is. It astonishingly captures the complexity of distillation processes and greatly contributes to the understanding of industrial-scale systems. The attention to detail, such as including gravity to account for the motion of vapor, and the use of a UDF for accurate surface evaporation modeling, is particularly impressive.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you! We appreciate your kind words and are glad to hear that you found the simulation insightful and beneficial for understanding the intricacies of water desalination equipment. We always strive to deliver detailed and accurate simulations that can be of value to our users. If you have any further feedback or need assistance with any other products, feel free to let us know.
Tevin Rowe DDS –
This method presents much efficiency in desalinating water, indeed. What measures are in place to ensure the pure water remains uncontaminated after condensation?
MR CFD Support –
In the water desalination equipment simulation, cleanliness of the condensed water is ensured by separating the vapor from impurities efficiently. The system’s design includes sloped surfaces which only allow condensed water vapor to collect and be directed out of the system. All contact surfaces are likely designed to minimize any potential for contamination. Additional filtration or purification processes may be utilized at outflow points to provide an extra layer of protection. It’s important to use materials resistant to corrosion and to implement stringent procedures for maintenance to further guarantee the purity of the distilled water.
Dr. Arlie Wunsch DVM –
The methodology for this simulation seems comprehensive, but I’m curious about how the mass transfer rate due to surface evaporation was quantified? Were specific experimental correlations or theoretical calculations used within the UDF to predict the evaporation rate?
MR CFD Support –
Inside the UDF, the mass transfer due to surface evaporation was quantified utilizing theoretical correlations for the phase change which depend on factors such as surface temperature, vapor pressure, and heat transfer coefficients. These correlations are based on well-accepted physical principles of thermodynamics and heat and mass transfer, providing a realistic prediction of evaporation rates under the simulation conditions.
Brando Watsica –
I’m very impressed by the results shown from the two-stage water desalination equipment simulation. The detailed visualization of pressure distribution and temperature contours greatly enhances the understanding of the desalination process.
MR CFD Support –
We’re glad to hear that our simulation results have impressed you and provided you with a clear understanding of the water desalination process. Thank you for your positive feedback!
Ali Dare II –
This simulation sounds quite useful. Can users customize the UDF to simulate different distillation conditions?
MR CFD Support –
Absolutely, users can customize the User-Defined Function (UDF) in this simulation to account for varying distillation conditions, such as different heat sources, environmental temperatures, or material properties of the distillation equipment. Doing so would allow the exploration of a wider range of scenarios and more tailored solutions in water desalination projects.
Rigoberto Adams –
I’m deeply impressed by the detailed analysis and how the complex phenomenon of water distillation is captured using CFD. The application of the VOF model alongside the realizable k-epsilon model shows a comprehensive approach to tackling multiphase and turbulent flows in the desalination process.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback on the Two-stage Water Desalination Equipment CFD Simulation. We are thrilled that you appreciate the thoroughness and complexity of the analysis. It’s encouraging to know that our efforts to model and simulate this important process have resonated well with you.
Dr. Clinton Rosenbaum I –
The explanation of the methodology in your product was very enlightening. I’ve always wondered how complex physical processes such as water distillation can be accurately simulated on a computer. Your use of the VOF multiphase model and UDF for accurate mass transfer representation is a stellar example of cutting-edge simulation technology in action.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that you found the simulation methodology elucidative. At MR CFD, we constantly strive to implement the latest computational techniques to deliver accurate and insightful results. If you have any more queries or if there’s anything else we can assist you with, we’re here to help!
Hailey Jacobson –
Did the VOF multiphase model successfully capture the dynamic interaction between the water vapor and liquid phases in your simulation?
MR CFD Support –
Yes, the VOF multiphase model was indeed capable of capturing the dynamic interaction between the water vapor and liquid phases effectively. The demonstration of this successful capture is evident through the observed results, which showcase a distinct stratification pattern and water vapor behavior within the desalination system.
Layne Nikolaus –
Here’s a review I think the team might appreciate: The 3D simulations present in the Two-stage Water Desalination Equipment provided deep insights into the thermodynamics and fluid behavior of the desalination process. The results were easy to visualize and interpret, demonstrating clear stratifications and temperature differentials critical for understanding the distillation efficiency. Great work on integrating the UDF for surface evaporation – it captured the essence of phase change physics beautifully! The utilization of the realistic k-epsilon turbulence model was a smart choice for accuracy in predicting the internal flow within those complex geometries.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your thoughtful review! We are pleased to hear that our simulation exceeded your expectations in detailing the water desalination process and that the visual representations aided in your comprehension of the thermodynamics involved. It’s always rewarding to know our efforts have provided value to our customers. Your acknowledgment of our choice of the UDF implementation and turbulence modeling is much appreciated. We look forward to providing you with more high-quality simulations.
Tyrese Berge –
I’m genuinely impressed by the level of detail MR CFD’s team has put into this two-stage water desalination simulation. The use of a UDF for surface evaporation shows deep understanding. Well done!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are happy to hear that you are impressed with the detail and depth of our two-stage water desalination simulation. We strive to provide the best possible CFD solutions, and it’s great to see that our efforts are acknowledged and appreciated by our customers.
Henderson Connelly PhD –
The methodology of the desalination simulation was sound and expertly carried out. The use of the VOF model for surface evaporation and UDF for mass transfer shows a detailed understanding of the physical phenomena and the capabilities of ANSYS Fluent. I was impressed with the in-depth analysis, particularly how the temperature distribution affects the process and the importance of including hydrostatic pressure in predicting equipment performance. The conclusion highlighting the pressure and temperature contours, as well as the evaporation rate, underscores the efficacy of the model in capturing the dynamics within this desalination system.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your thoughtful review and for recognizing the complexities of the two-stage water desalination equipment CFD simulation. It’s heartening to know that the detail of the analysis and our use of advanced features like UC User-Conducted Function (UDF) and VOF made a positive impression. We’re committed to delivering precise and practical simulations and are glad to hear when it benefits our customers. If there are further particulars or other projects you need assistance with, please feel free to reach out to us. We look forward to continuing to support your projects!