Pollution Spread in the Stagnant River, Ansys Fluent Training
$160.00 Student Discount
- The problem numerically simulates the Pollution Spread in the Stagnant River using ANSYS Fluent software.
- We design the 3-D model with the Design Modeler software.
- We mesh the model with ANSYS Meshing software, and the element number equals 161562.
- We perform this simulation as unsteady (Transient).
- We use the VOF Multiphase model to define the phases of water and pollutant.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Description
The present study investigates the pollution entry into a stagnant river by ANSYS Fluent software. One of the environmentalists’ concerns is the water pollution caused by factories. If the chemical waste products from industrial processes discharge into rivers, It would be perilous for aquatic animals. Furthermore, these pollutions enter the human food chain and cause disease.
The present model is designed in three dimensions using Design Modeler software. The river’s width at the inlet is 11.05 m. The meshing of the model has been done using ANSYS Meshing software. The element number is 161562.
Also, due to the nature of the problem, the transient solver is enabled.
Pollution Methodology
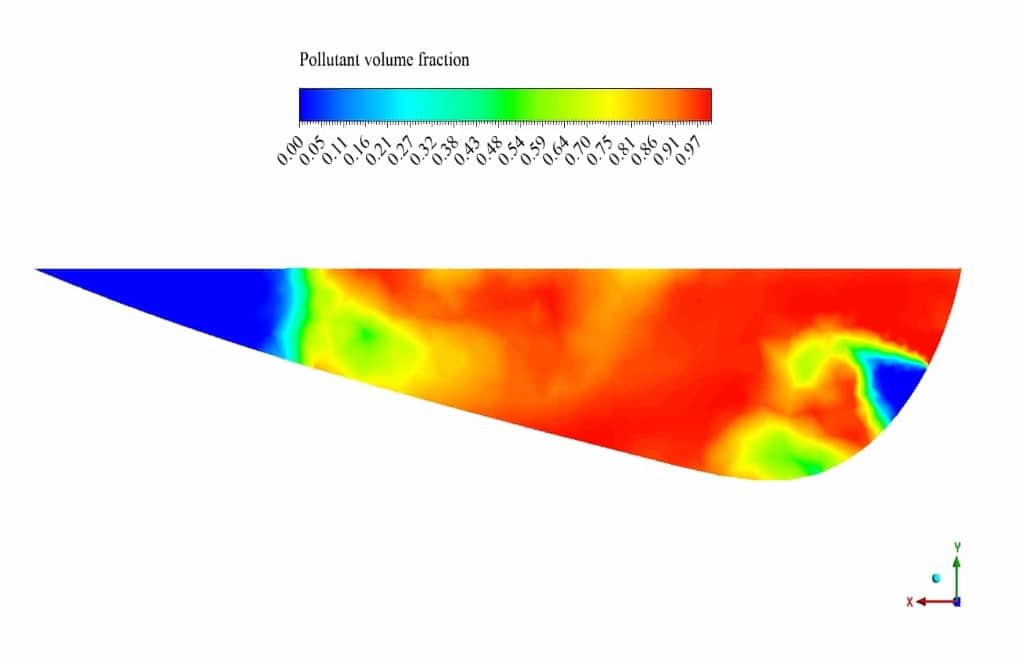
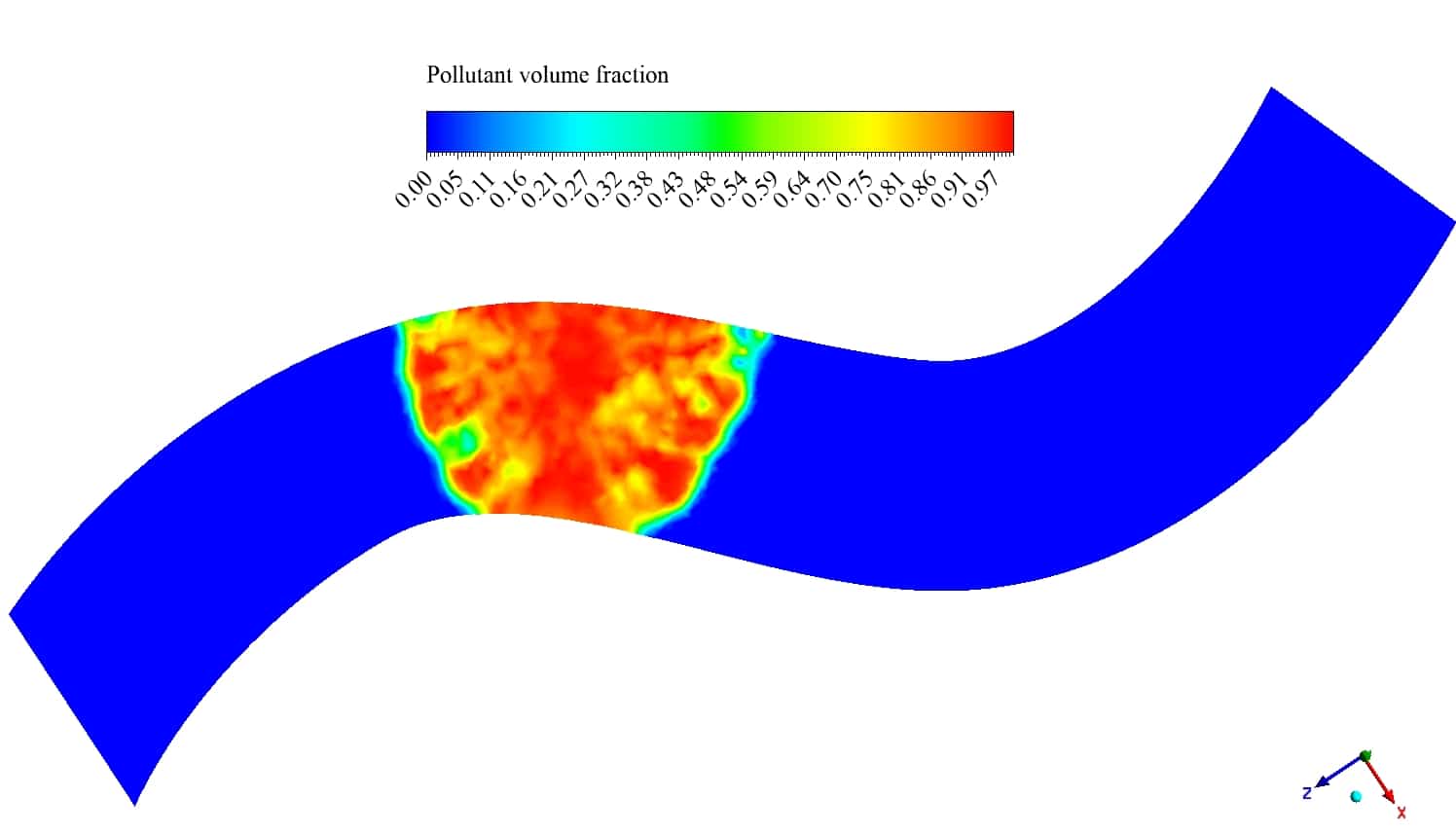
The VOF multiphase model is used to simulate the phases of water and pollutant. Pollutant enters the river from a nonuniform profile somewhere in the middle of the river and diffuses into the water.
Due to its density which is lower than water density, it floats on the free surface of the river. The K-epsilon Realizable viscous model with scalable wall function has been used to solve the turbulent flow equations.
The pressure-velocity coupling scheme is SIMPLE, and the second-order upwind discretization method has been used. As mentioned, the water inside the river is stagnant, and pollution enters the river with a velocity of 8m/s.
Pollution Conclusion
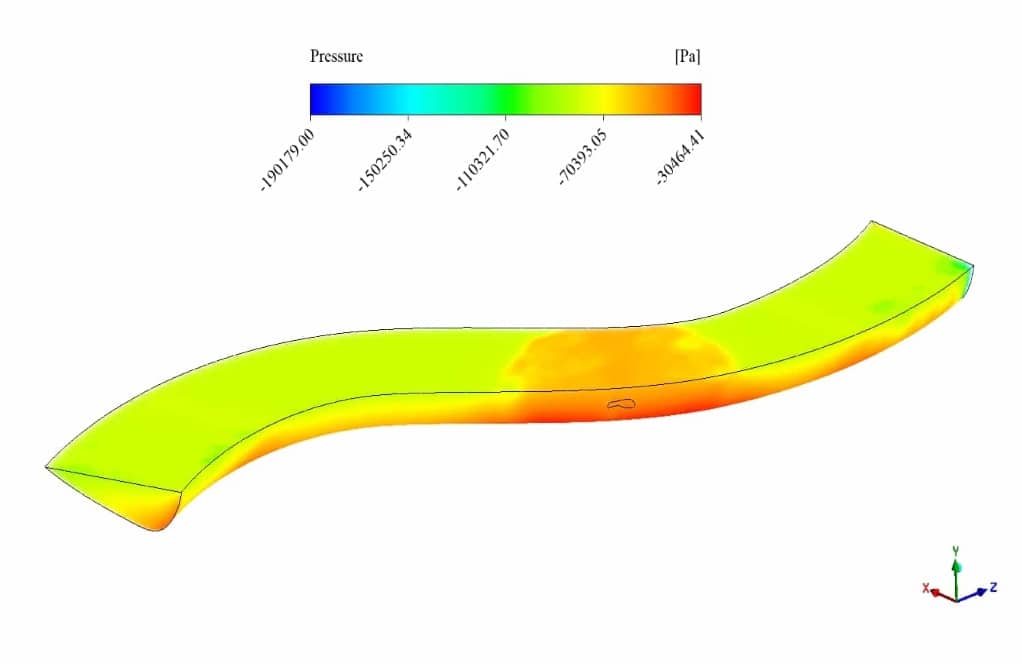
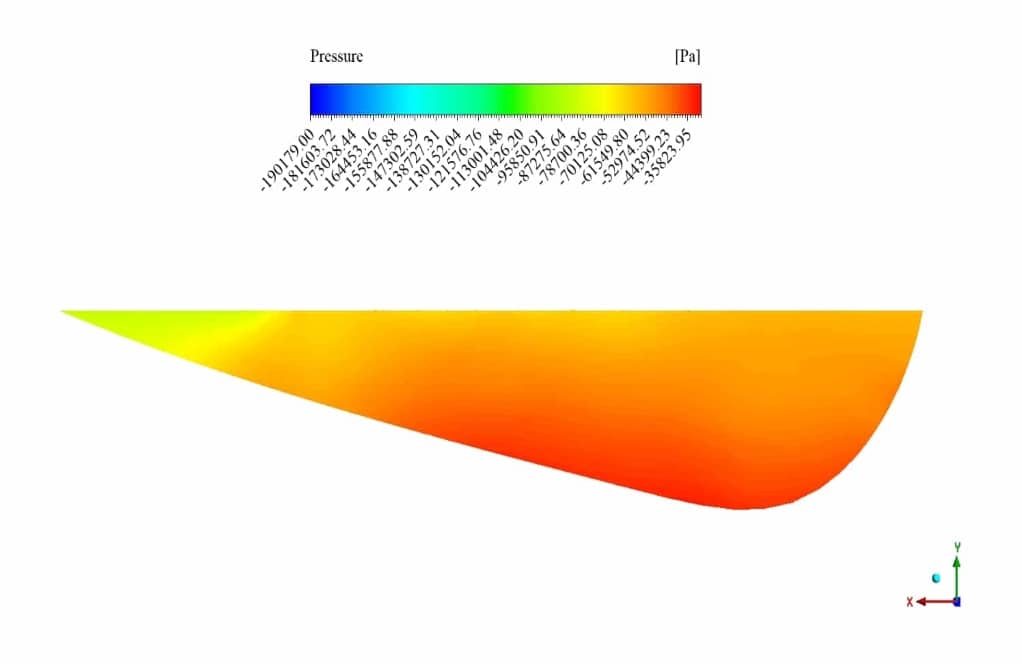
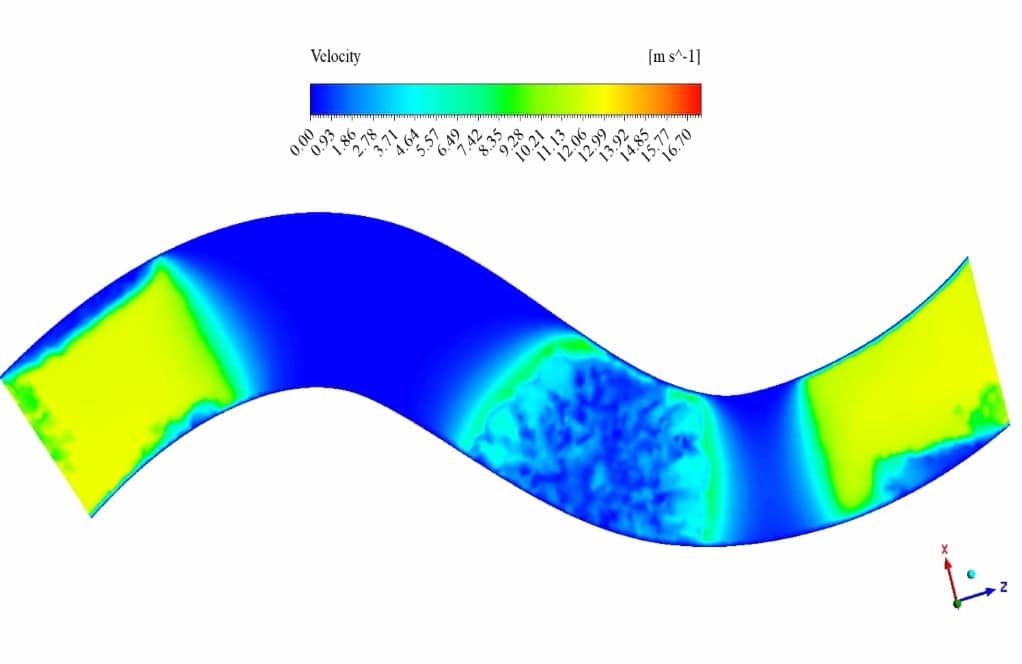
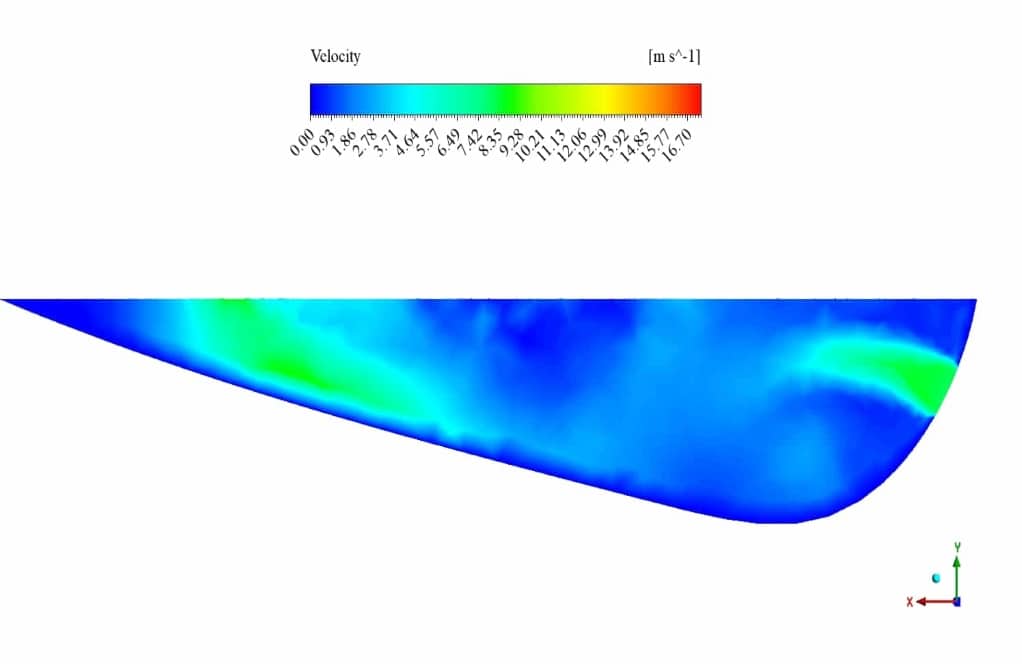
After the solution process is completed, contours of velocity, pressure and pollutant volume fraction are extracted and presented below. As observed, the pollutant diffuses through time into the river’s water, and the pressure near the pollutant inlet is higher than in other areas.
Moreover, as we know, water pressure increases with depth shown in the cross-sectional pressure contour.

Maddison Herzog Sr. –
This Pollution Spread simulation really shows the spread of pollutants in a detailed way. Great work!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that the Pollution Spread in the Stagnant River training was able to effectively illustrate the pollution dynamics. Your appreciation means a lot to us!
Whitney VonRueden –
The project on pollution spread in the stagnant river is fantastic. It wonderfully captures the complex dynamics of environmental pollutants in water bodies. So impressed with the visualization that clearly depicted the diffusion process and the pressure variation. It’s a very helpful tool for understanding pollution dispersion.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you! We’re thrilled to hear that our Ansys Fluent training for the pollution spread in a stagnant river was not only informative but also provided clear visualization to enhance understanding. We strive to produce high-quality learning material that makes complex topics accessible to our users. Your feedback is greatly appreciated.
Dr. Concepcion Mraz –
This training helped me understand the environmental impact of industrial pollution on rivers. Could you explain how you determined the appropriate mesh size for such a complex flow?
MR CFD Support –
In the simulation, we determined the appropriate mesh size by considering the balance between accuracy and computational efficiency. A finer mesh was likely used at the areas where high gradients occur, like the pollutant inlet, to capture the details of the pollution diffusion while still maintaining a manageable number of elements overall at 161562 to ensure reasonable computation times.
Andrew Hoeger –
I’m amazed by the realistic simulation of the pollution dispersion in a stagnant river. The use of the VOF multiphase model to track the pollutant effectively and the choice of the k-epsilon Realizable model, along with a transient solver, are superb for catching the complex behaviors over time. Hats off to the team for crafting such a detailed and thorough process!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you very much for your kind review and for recognizing the details of our simulation work. We are delighted to hear that you appreciate the complexity and the accuracy of our approach to modeling pollution spread in stagnant water. Our team strives for excellence in every project and we’re pleased that it shows in our simulations. If there is anything else we can help you with, feel free to reach out.
Valentina Daniel –
I found the training on pollution spread in a stagnant river incredibly informative. The methodology gave me a clear understanding of how pollutants behave in a water body, and the application of different software functions, like VOF multiphase modeling and the K-epsilon Realizable model, was well explained. The step-by-step approach to tackling such a complex environmental issue offers excellent learning for both students and professionals in the field.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re delighted to hear that you found the training course on pollution spread in the stagnant river insightful and easy to follow. Our goal is to provide comprehensive and practical education on CFD and environmental simulations, using tools like ANSYS Fluent, and we’re glad it’s making a difference in your learning journey. If you have more feedback or need further information, feel free to reach out!
Eladio Olson –
I just completed the ‘Pollution Spread in the Stagnant River’ training, and the case study was illustrative and well-presented. It’s remarkable seeing the pollutant’s behavior and diffusion over time captured so vividly. The instructions were clear, and I now better understand pollution dynamics in stagnant waterways.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind feedback! We’re delighted that the training gave you valuable insights into pollution spread and that the case study was effectively communicated. If you have any more questions or need further clarification in future studies, don’t hesitate to ask. We appreciate you choosing MR CFD Company’s learning products for your educational needs!
Leon –
It reminded me of oil spread in the sea.
Gianni –
Nice job.
I hope that pollutant dispersion doesn’t happen anywhere in the entire world because it hurts the environment deeply.
Roslyn S. –
I am so thankful for this project.
Max M. –
It would be more interesting if the pollutant moves with the river flow.
Kadin Quigley –
I found the explanation of pollutant behavior and the pressure variation details very insightful. The 3D model seems to accurately represent what happens with pollution in real rivers and helps understand the environmental impacts meaningfully.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re pleased to hear that you found the simulation insightful and accurate. Our goal is to create realistic models that can help in understanding and solving environmental issues. We’re glad you appreciate our efforts and learned from the simulation!
Dr. Kamryn Nikolaus Jr. –
I am thrilled with how comprehensive the training was on simulating pollution spread in a stagnant river using ANSYS Fluent. It provides a very crucial perspective on environmental impacts, which is exceptionally educational. Well done on such an engaging piece of training material.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind feedback! We’re really glad to hear you found our training on pollution spread simulation using ANSYS Fluent comprehensive and educational. Understanding environmental impacts is crucial, and we strive to create training that is both informative and engaging. We appreciate your comments!
Kacie Kautzer –
I was amazed at how the simulation captured the pollution diffusion. Can you tell me the overall time span covered by the transient simulation to observe the pollution spread?
MR CFD Support –
I’m glad to hear you found the simulation results impressive! The transient simulation was run long enough to capture the complete process of the pollutant diffusion into the river. Typically, these simulations run for several seconds to hours of simulated time, depending on the scale of the problem and how quickly the pollution spreads. Unfortunately, the specific overall time span has not been stated explicitly in the provided description.
Hailie Brown –
I’m impressed by the study on pollution spread! Has this model been validated with experimental or real-life data to ensure its accuracy?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your compliment! Validation against experimental or real-life data is an essential step in any simulation process to ensure the model’s reliability and accuracy. MR CFD provides comprehensive training with a focus on accuracy, but for specifics on validation for this particular project, it would be best to refer directly to the study documentation or approach our team for detailed information.
Dandre Gleichner –
I’m impressed with the depth of analysis on the pollution spreading in stagnant water. It clearly reflects how various factors like diffusion and water density impact the distribution of pollutants. Was seasonality or changing river flow rates over time part of the simulation, or was the water always considered stagnant throughout the study?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words and insightful question. In this particular study, the river was considered stagnant throughout the simulation. Seasonality or changes in water flow rates over time were not part of the analysis. The main focus was on the diffusion of pollutants from a stationary source into an undisturbed water body, thereby simplifying the modeling to gain a clearer understanding of pollutant behavior under static conditions.
Prof. Ray Krajcik –
This pollution simulation must be a powerful tool for environmental studies! Can it predict the impact on aquatic life over time as well?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your review! Yes, this simulation can provide critical insights into pollutant concentration profiles and dispersion patterns over time, which can help predict the potential dangers to aquatic life and their habitats. These predictions, combined with biological and environmental data, can facilitate a comprehensive impact assessment on aquatic ecosystems over time.
Bernard Russel –
I followed this CFD training on pollution spread and really appreciated the attention to environmental realities. The visuals helped me to understand the real-world consequences of pollution in an easy-to-follow way. Thanks to the MR CFD team for creating such an insightful course!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are delighted to hear that you found the course insightful and that the visuals were helpful in understanding the environmental impact of water pollution. It’s great that our efforts to incorporate real-world concerns into the training resonated with you. If you have any further feedback or need assistance with any other learning products, feel free to reach out. Your satisfaction motivates us to keep delivering high-quality courses.
Mrs. Isabella Quitzon –
I’m truly impressed by the thorough nature of the ‘Pollution Spread in the Stagnant River’ study using ANSYS Fluent. It’s a crucial piece of work given the extensive impact of industrial waste on aquatic ecosystems and human health. The detailed modeling and simulation do an excellent job of capturing the dispersion characteristic and can be an essential tool for environmental control. Great to see such sophisticated simulations providing clearer insights and empowering responsible actions!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your thoughtful review of our ‘Pollution Spread in the Stagnant River’ training material! We are committed to offering valuable insights and comprehensive simulation studies like this to support environmental research and advocate for sustainable practices. Reading that our efforts are having a positive impact and being well received truly makes our day!
Lora Jakubowski –
After completing this training, I could truly appreciate the real-world application of such simulations. Your training provided clear insights into pollution modeling, which is incredibly valuable for environmental impact studies.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback on our Pollution Spread in the Stagnant River training using ANSYS Fluent. We are thrilled to hear that our product could provide such valuable insights and contribute to your understanding of environmental simulations. We always strive to create impactful and practical learning experiences for our users.
Florence Sanford –
Very impressed with how the Pollution Spread in Stagnant River training outlined the application of ANSYS Fluent’s VOF model for tracking pollutant diffusion. Super insightful!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are thrilled to know that our training product was insightful and met your expectations. If you have any further questions or need insight on another simulation, please feel free to reach out.
Jabari Osinski Sr. –
The product seems to cover important environmental aspects which I deeply care about. Does the training also provide insights on measures to mitigate pollution spread or is it limited to only simulating pollution dispersion?
MR CFD Support –
The training provided is focused primarily on simulating and understanding the dispersion patterns of pollution in stagnant river systems using ANSYS Fluent. While the primary goal is to model and analyze the spread of pollution, mitigation measures are not the central focus. However, understanding the dispersion can be instrumental in designing strategies for pollution control and mitigation. For detailed strategies on mitigation, specific environmental engineering or conservation measures might need to be studied in addition to the simulation knowledge acquired from this training.
Brock Wehner –
Just received the results of the ‘Pollution Spread in the Stagnant River’ project – truly incredible! It aids greatly in understanding the environmental impact and presents a clear visual interpretation of pollutant dispersion. What an essential tool for environmental engineers!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words! We are delighted to hear that our ‘Pollution Spread in the Stagnant River’ project exceeded your expectations and proved to be a useful tool for understanding environmental impacts. We’re committed to providing high-quality simulations that enable professionals to analyze and interpret complex systems clearly. Your feedback is greatly appreciated!
Carmine Kassulke –
The training materials provided a deep understanding of how chemical pollutants can spread in a suffused river context, which is invaluable information for any environmental impact studies. The dynamic visuals complemented the technical explanation superbly.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear the training materials on pollution spread in stagnant river scenarios were valuable and informative. We strive to provide clear and effective visual aids to support our in-depth explanations. If you have any further questions or need more information, please don’t hesitate to ask.
Iliana Olson –
The descriptions are very insightful. I’m amazed by the level of detail on the pollutant spread in the stagnant river, and how important factors like the volume fraction and pressure distribution were captured and analyzed using ANSYS Fluent. Well-explained methodology and conclusions provided a thorough understanding of the simulation process. Fantastic resource for environmental CFD analysis!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words. We’re delighted to hear that you found our training resource valuable and insightful. Understanding the complexities of environmental CFD analysis is crucial and we take pride in providing comprehensive simulations that can help address such concerns. Your appreciation motivates us to continue producing high-quality CFD training content. If you have any further questions or need assistance with similar projects, please do not hesitate to reach out.
Jensen Goldner –
The content is fascinating. I learned a lot about the dispersion of pollutants in water bodies through this training course. The methodology is explained well, and I appreciate the use of different software tools to conduct this important environmental study.
MR CFD Support –
We are so glad to hear that you found the course helpful and informative! Understanding the impact of pollutants on the environment is crucial, and we’re pleased that our training could assist you in this area. Thank you for your positive feedback!
Shanon Marks –
I am delighted with the detail and clarity of the results presentation for the Pollution Spread in the Stagnant River project. Great to see such comprehensive analysis of a critical environmental issue.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are pleased to hear that you found the analysis detailed and informative. Understanding the environmental impact of pollutants in water bodies is crucial, and we strive to provide the best possible analysis. Thank you for choosing our Ansys Fluent training for your studies.
Augusta Muller –
I was impressed with the details provided for pollution modeling. Do you provide any comparison with real-world data to validate the results of the simulation?
MR CFD Support –
In our product documentation, the methodologies employed are intended to demonstrate theoretical accuracy and robustness within the software framework. However, for specific real-world data comparison and validation, this might not always be included. We encourage users to undertake parallel studies or pursue validation exercises based on field data to substantiate the simulation results within the realms of their own projects for the utmost accuracy.
Marie Dooley –
This training seems incredibly insightful in modeling real-world pollution problems. Fantastic work on displaying the behavior of pollutants in a stagnant river environment. It’s great to see how the VOF multiphase model and the turbulence modeling scheme have been implemented to capture the intricacies of the scenario.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are glad that you found the training insightful and applicable to real-world environmental issues. Our goal is to provide comprehensive learning materials that help users understand complex phenomena like pollution spread. If you have any further questions or need more information on our products, feel free to reach out!