Vortex Tube CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent Training
$100.00 Student Discount
- This project numerically simulates the Vortex Tube using ANSYS Fluent software.
- The 3-D geometry is designed in Space Claim software.
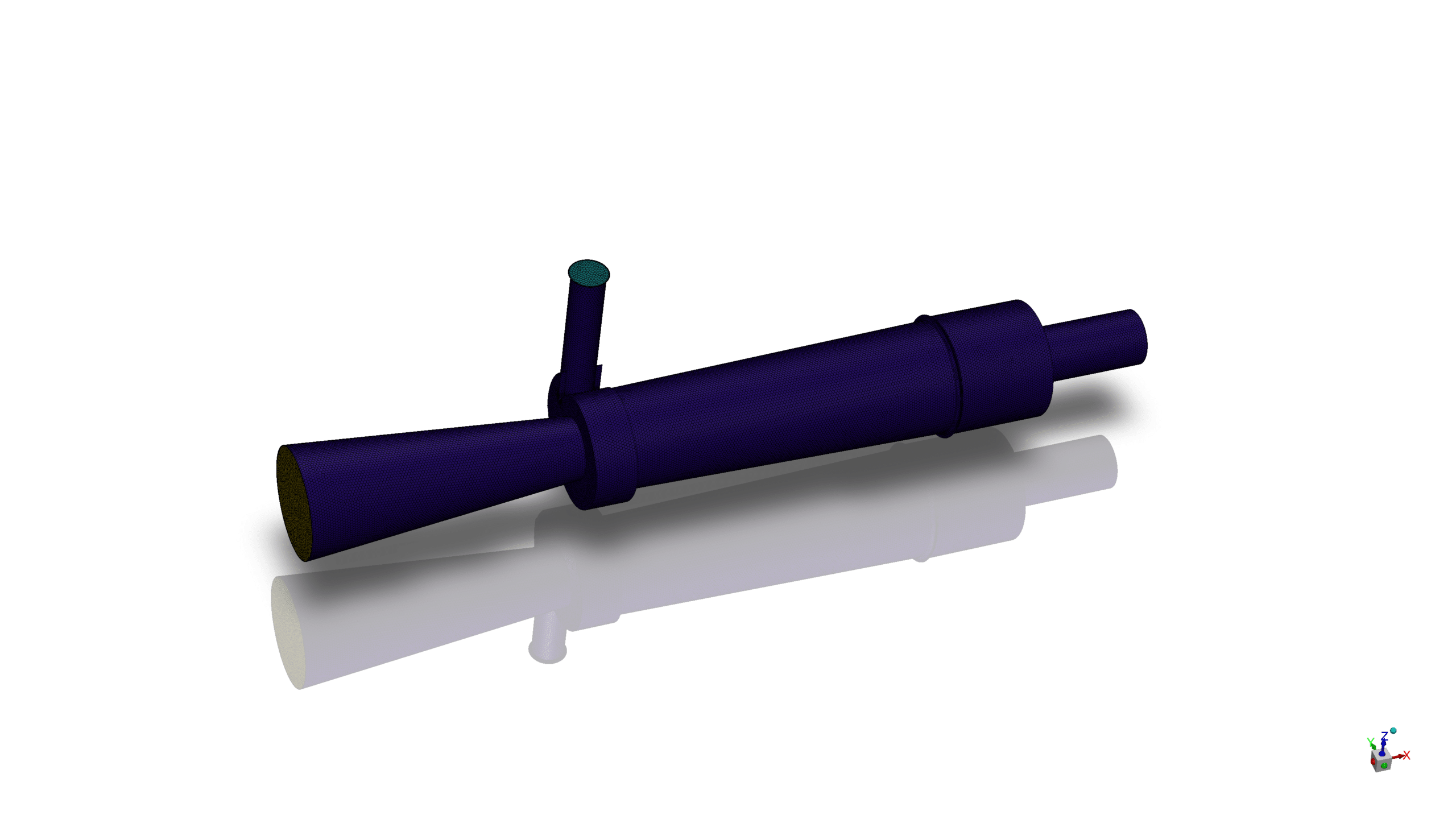
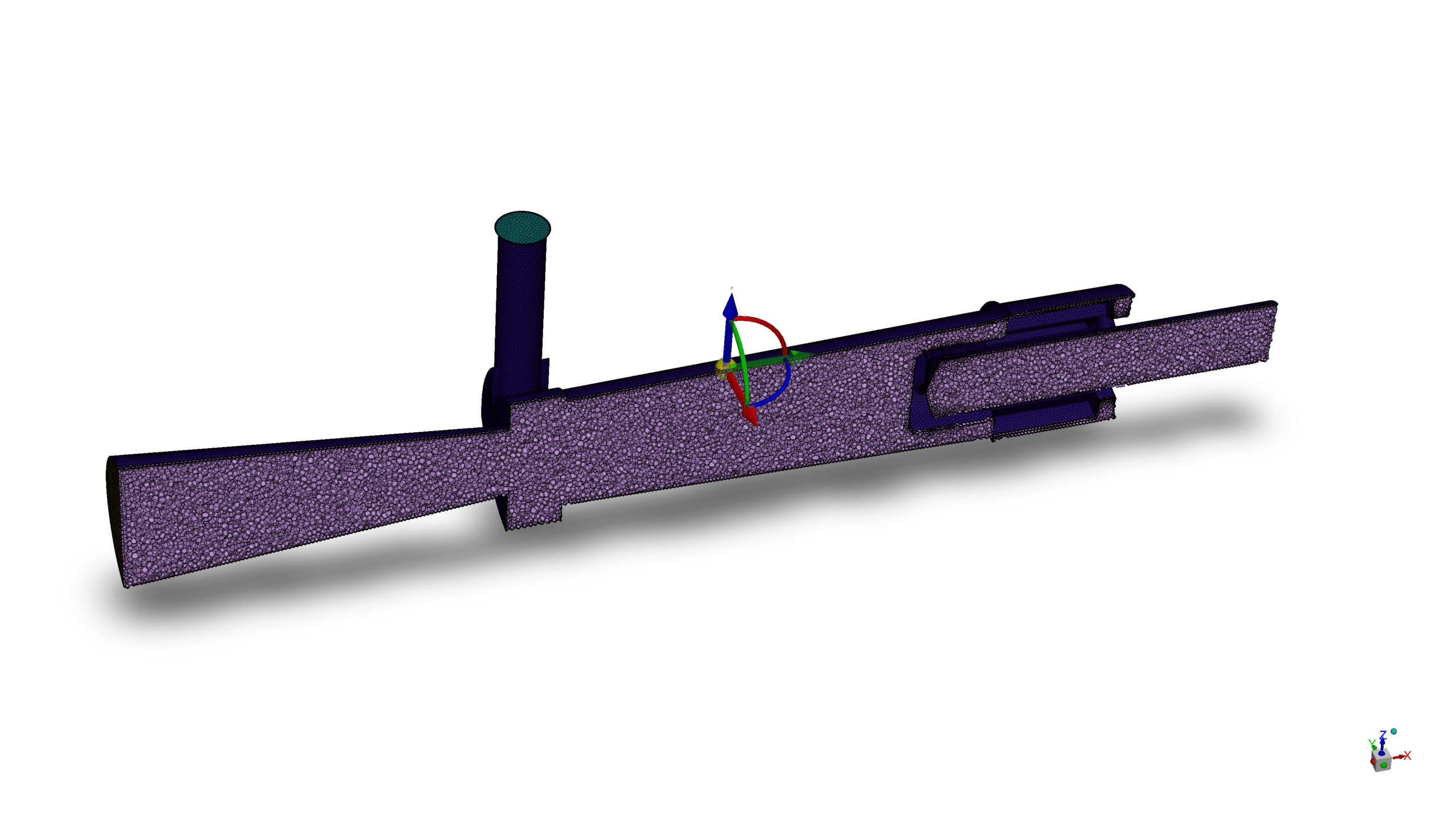
- We used Fluent Meshing Software to generate mesh; the element number equals 497,635.
- Turbulent flow is modeled with the Spalart Almaras model.
- The solver is Density-Based and the Sutherland model is used for viscosity.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Vortex Tube CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent Training
description
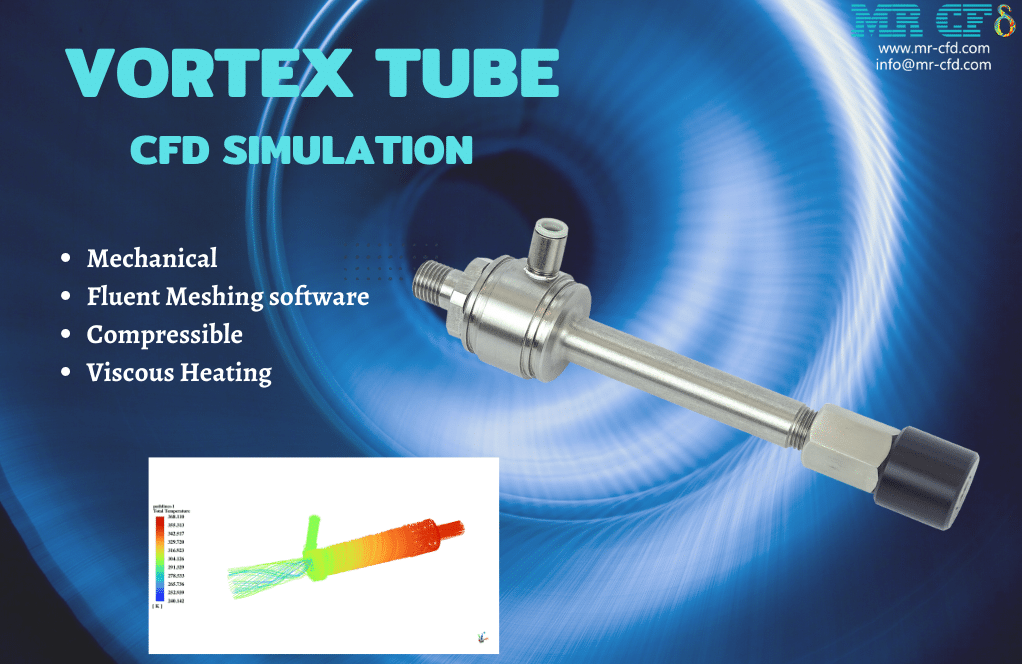
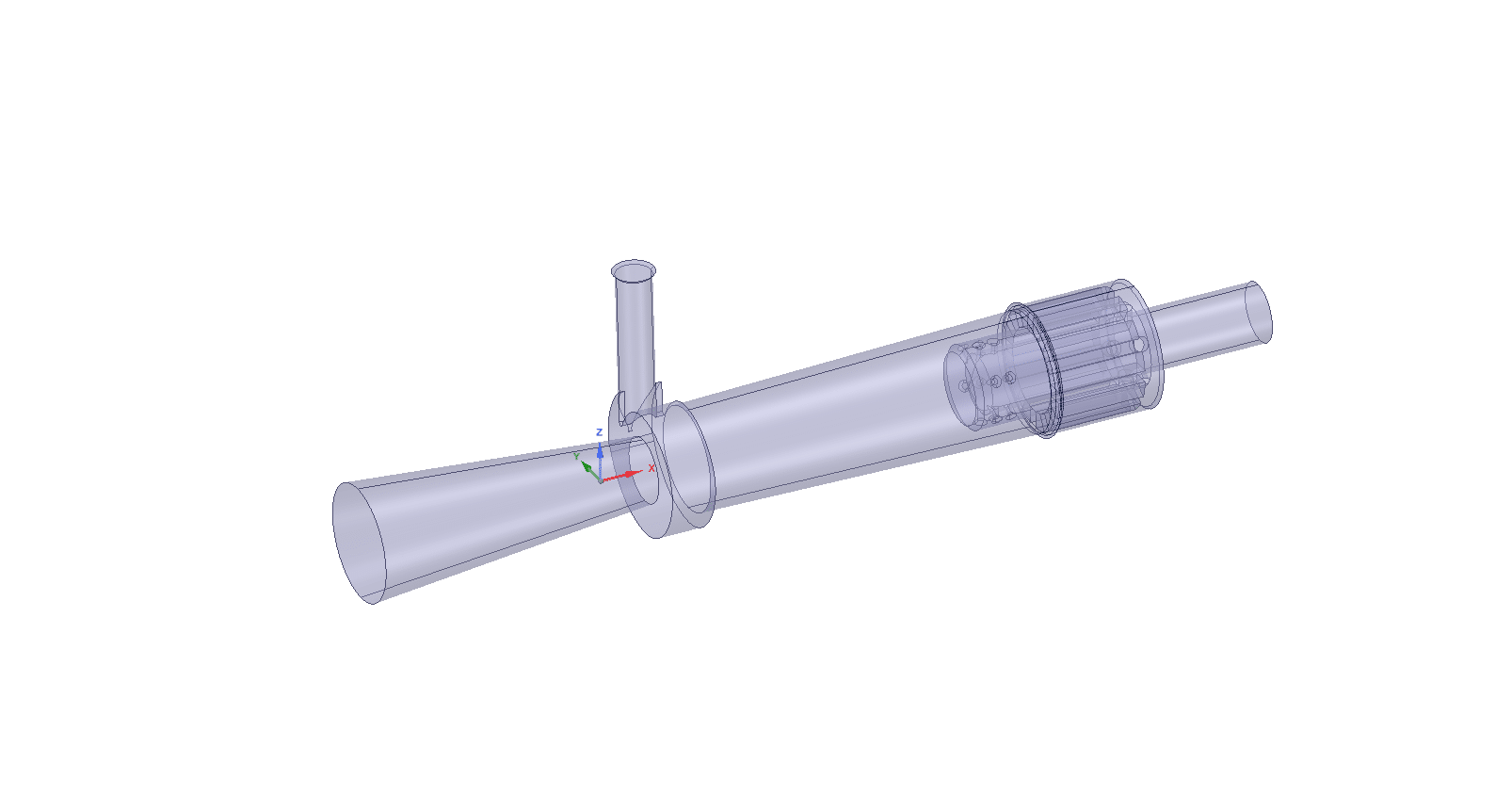
A mechanical-thermal vortex tube splits a compressed air flow (or any inert gas) into hot and cold streams. Standard components of a vortex tube include an inlet nozzle(s), a hot end tube, a vortex chamber, a cold orifice, and a control valve(s) or plug(s) at the hot end. Both left and right-side exits are possible.
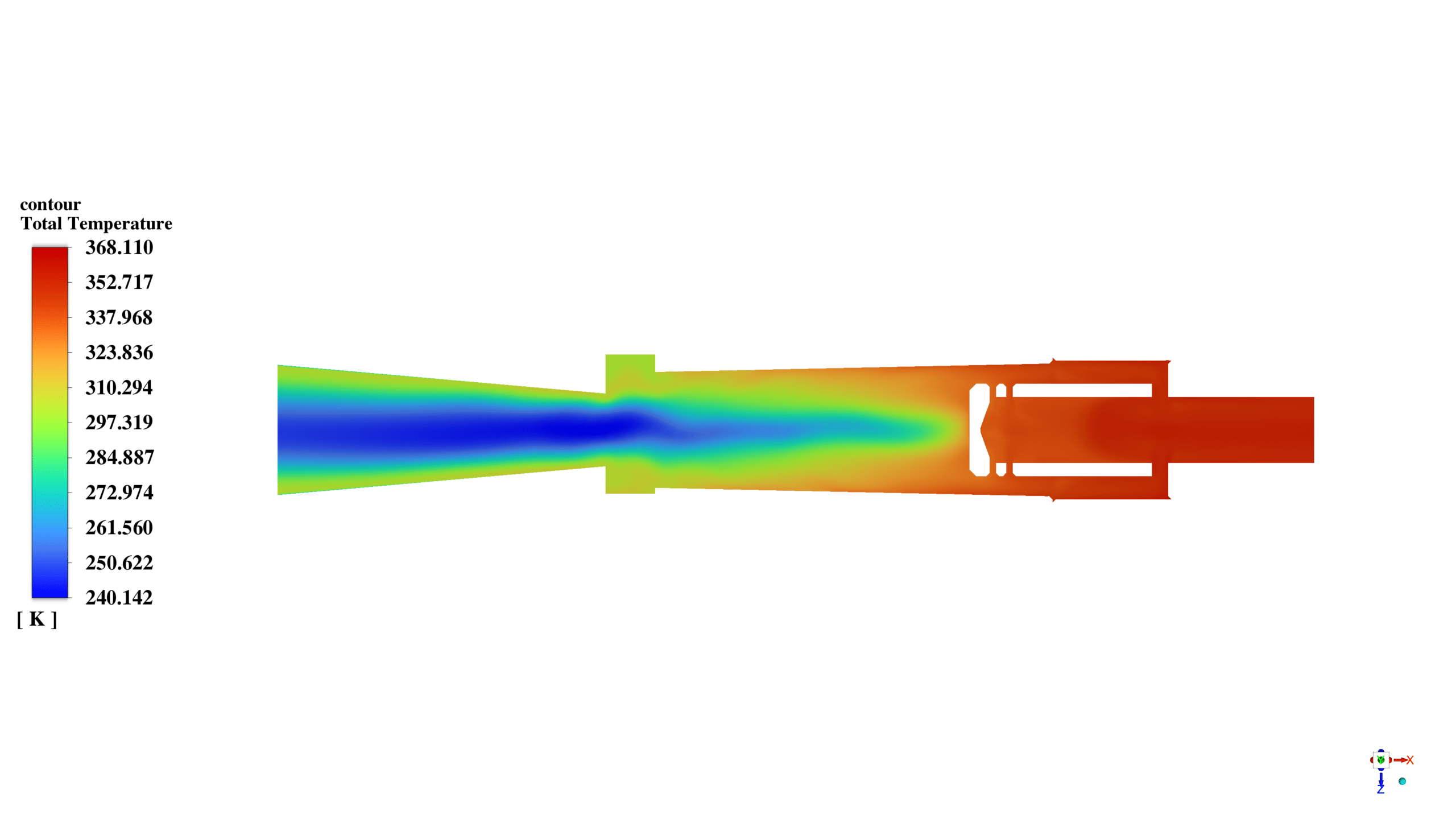
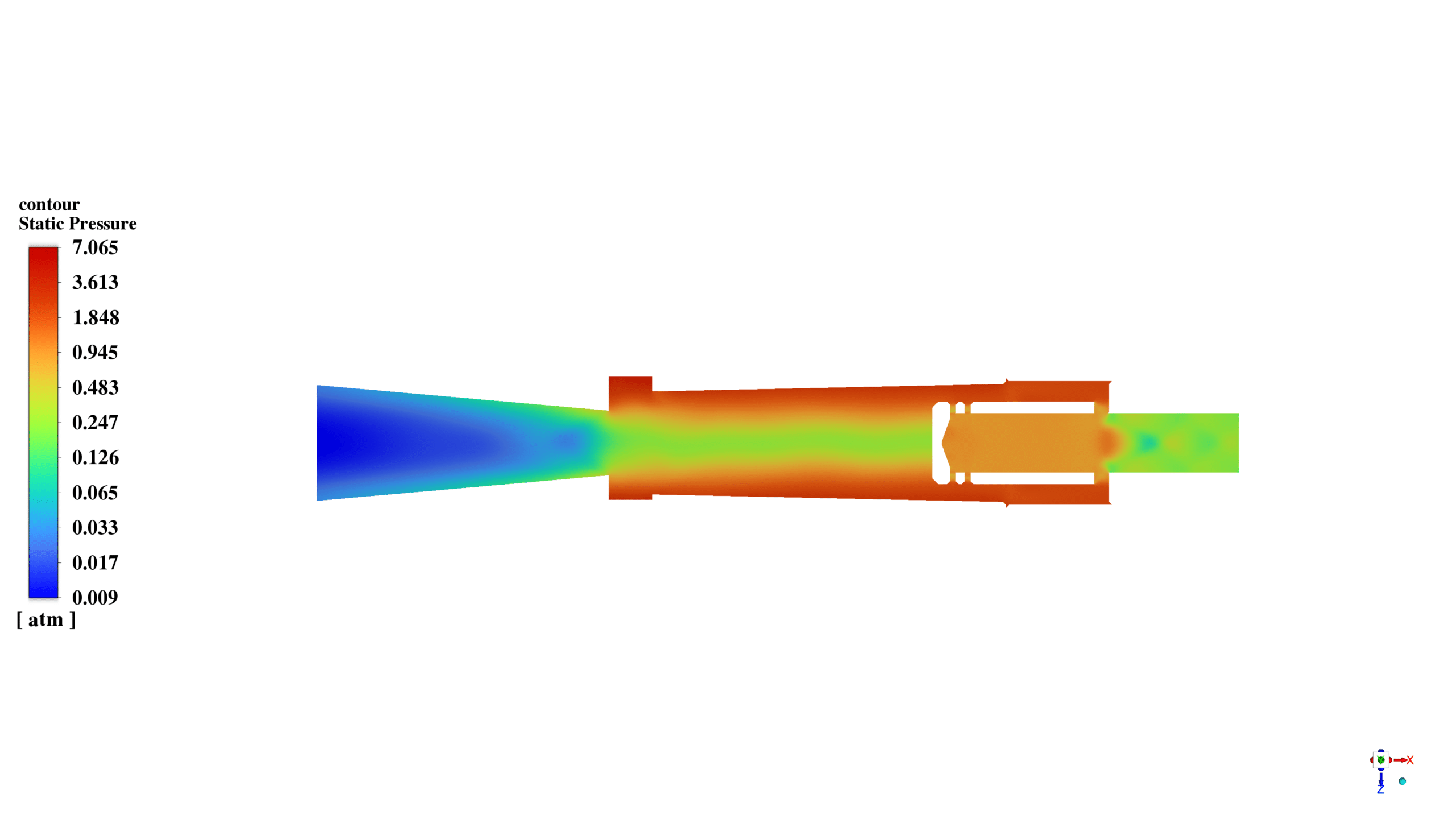
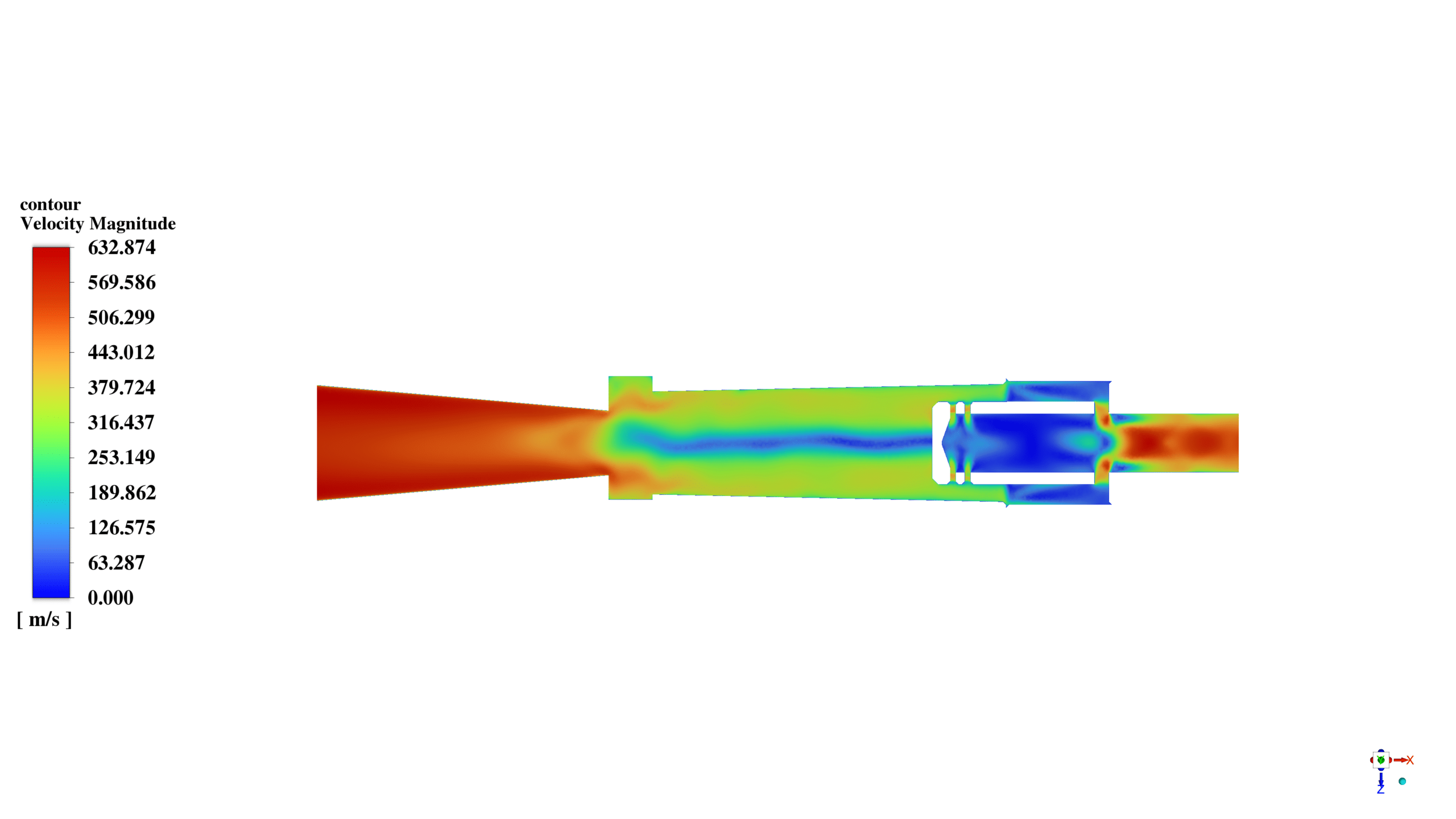
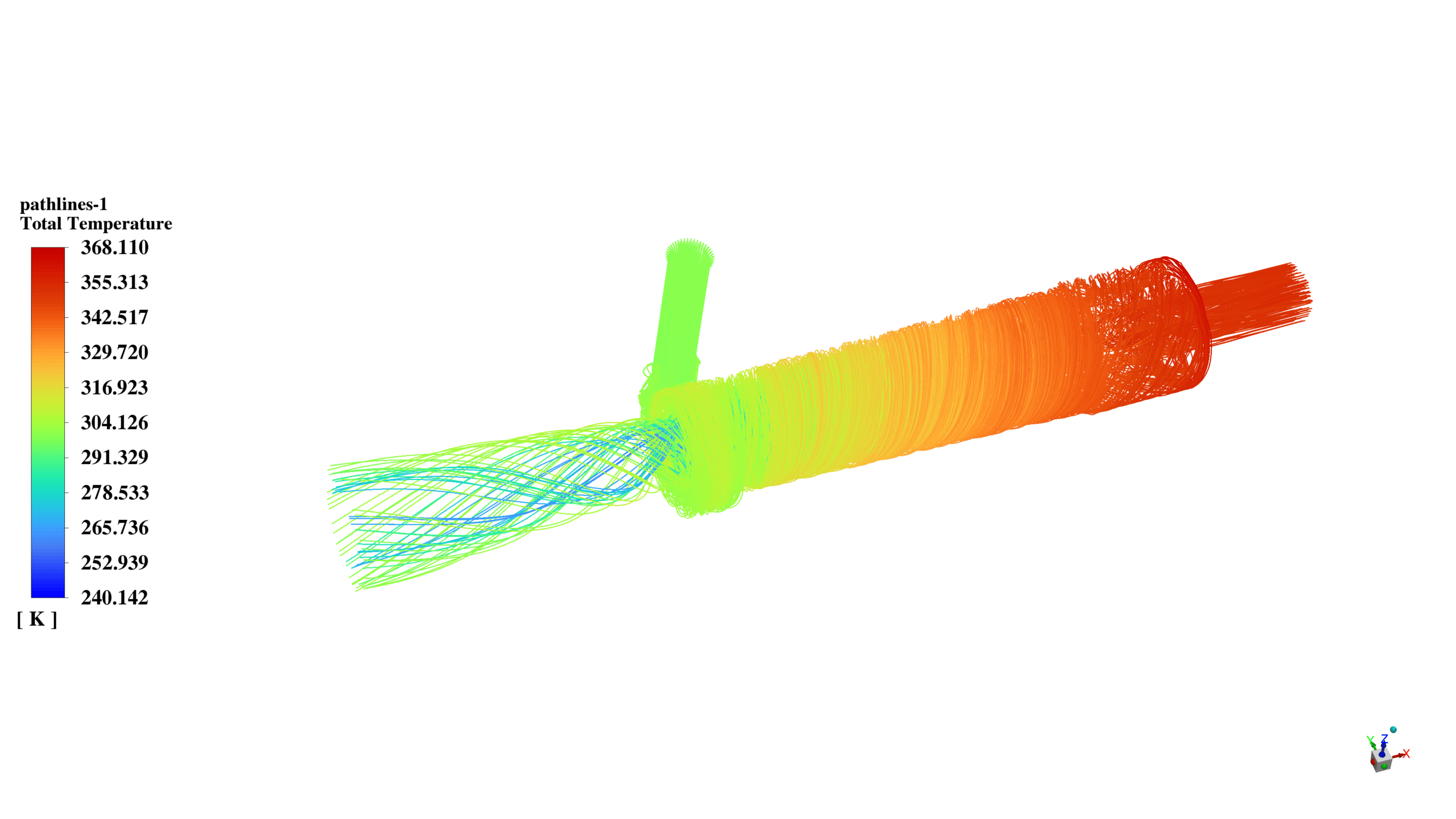
In this project, a vortex tube is simulated using ANSYS Fluent software. The air enters the domain with a static pressure of 7 bars and a total temperature equal to 300K. After that, it starts to rotate inside the tube in a high-speed vortex motion.
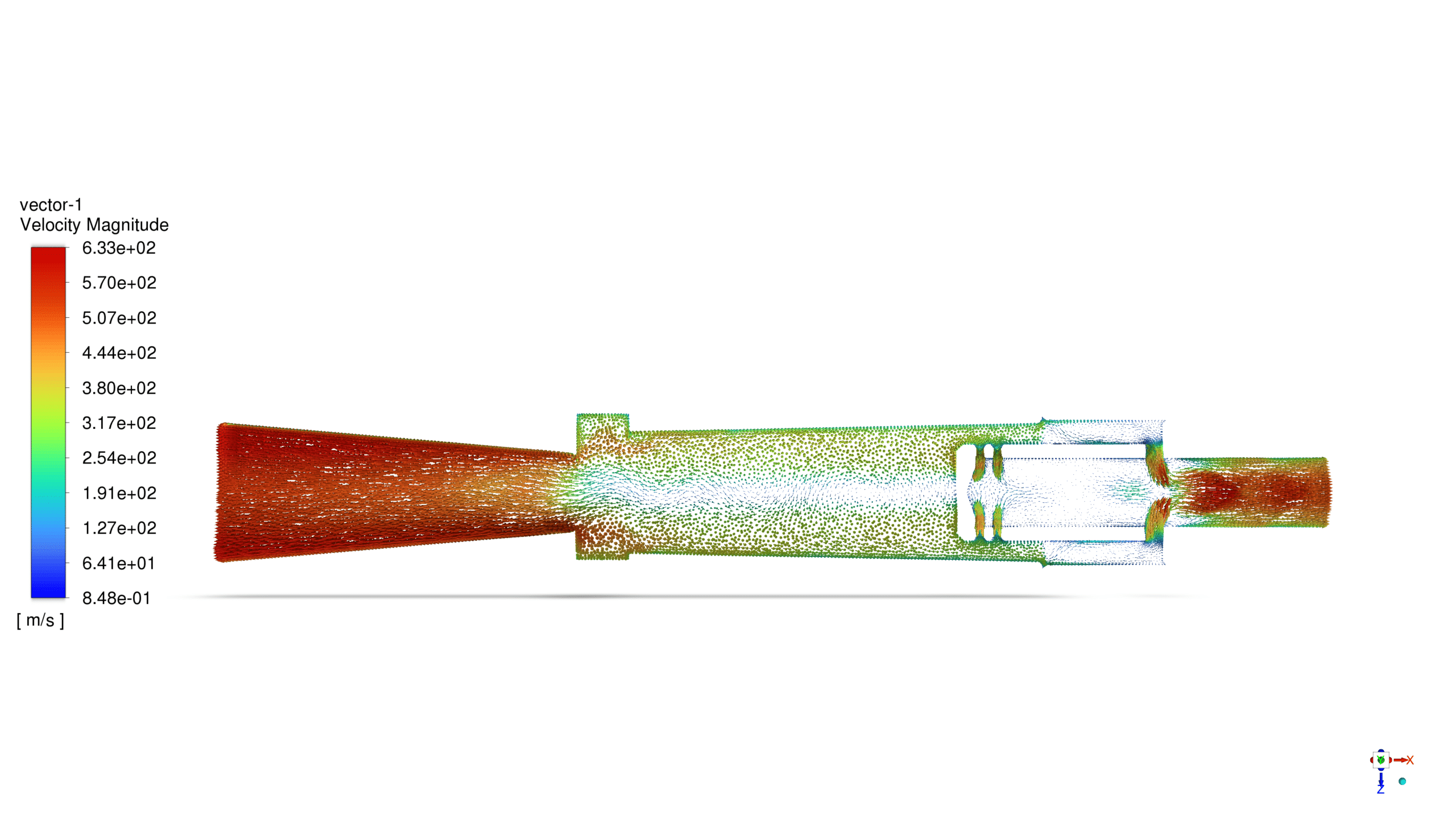
The rotating gas creates hot and cold streams within the vortex tube. The separation of the hot and cold streams occurs due to the difference in angular momentum between the gas particles.
Finally, the hot airflow enters the outlet chamber, while the cold airflow returns and passes through the left side.
The geometry of the solution is created using SpaceClaim,the polyhedra-type mesh is generated via Fluent Meshing software. After all, the whole number of elements is 497,635.
Vortex Tube CFD Simulation Methodology
The Density-Based solver is chosen to model the airflow. The air density is selected as the ideal gas, and its viscosity is Sutherland.
The Spalart Almaras model is used to model the turbulence of the fluid.
Conclusion
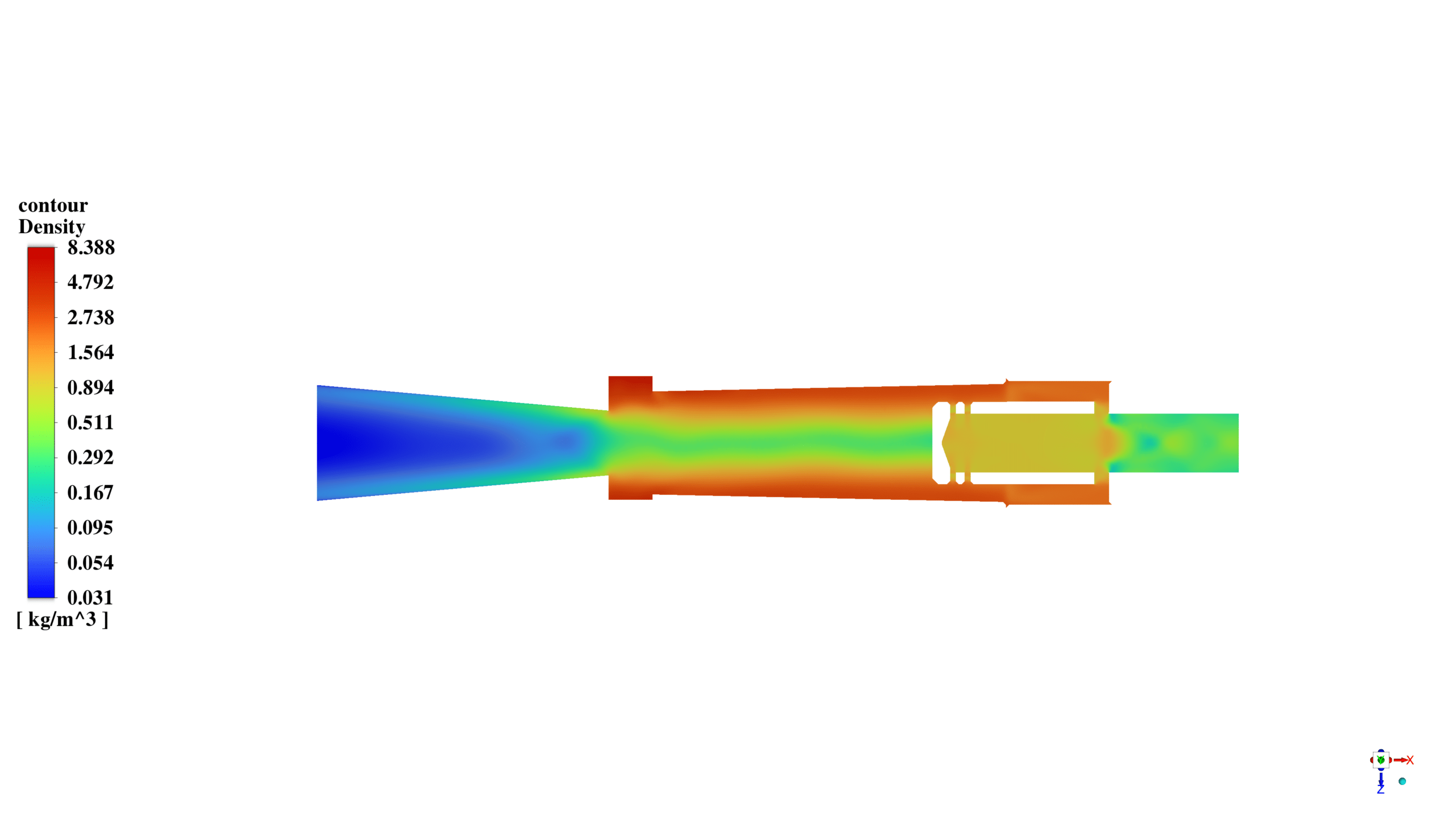
After the solution, we obtained the temperature, pressure, and velocity contour inside the vortex tube. The flow vectors show the air’s rotational movement and how the air with the lower momentum returns to the cold outlet.
Also, the static pressure, the temperature of the air, and the change in its density are apparent in contours.
In conclusion, the temperature of the left and right outlets, which are named as cold and hot outlets, are lower and higher than the inlet temperature, respectively.
The following table shows the temperature of the airflow at different boundaries.
Mass-Weighted Average of Total Temperature [K]
——————————– ——————–
cold_outlet 287.24653
hot_outlet 353.01502
inlet 300





Harmon Cronin III –
I just completed the Vortex Tube CFD Simulation using ANSYS Fluent, and I’m impressed! The step-by-step methodology made complex concepts much easier to grasp. The simulation results provided clear insights into thermal separations. Credits to the team for a high-quality learning resource!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind review. We’re thrilled to hear that you found our Vortex Tube CFD Simulation training so informative and clear. Our team strives to provide the best learning experience possible, and it’s always rewarding to hear that our efforts are making a difference. If you have any further questions or need more in-depth learning materials, please let us know!
Prof. Amaya Lang IV –
I just wanted to express my appreciation for the Vortex Tube CFD Simulation training using ANSYS Fluent. The breakdown of the methodology and the clarity of the results, especially the clear contours and flow directions, contributed significantly to my understanding of the physics behind the vortex tube. Well done on creating such a detailed and informative learning resource.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that our Vortex Tube CFD Simulation training has enhanced your understanding and provided clear insights into the vortex tube mechanics. We continually strive to offer detailed and useful instructional content, and your appreciation motivates us to keep doing our best!
Miss Leanna Champlin –
This course was really impressive on explaining the vortex tube phenomenon. It was neat to see the separation of temperatures visually. It helped me to understand the underpinnings of the process that allows hot and cold air separation from a single stream. The data provided was clear and informative.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are delighted to hear that the Vortex Tube CFD Simulation training helped you understand the process more clearly, and you found the visualization of temperature separation insightful. Your feedback is appreciated and motivates us to keep providing high-quality training materials!
Carmella Dickens –
I was really impressed by how the CFD simulation could predict the temperature separation in the vortex tube! The results seem very consistent with physics.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback on the Vortex Tube CFD Simulation using ANSYS Fluent. We are glad to hear that the simulation results met your expectations and aligned well with the physical phenomena. We strive to provide detailed and accurate simulations to help our users understand complex systems better. If you have any more questions or need further insights, do not hesitate to reach out.
Monserrate Prohaska –
This was a phenomenal training resource. I could really grasp the intricate workings of a vortex tube thanks to the clear simulation setup. The temperature differences at the cold and hot outlets showed exactly what I hoped to learn from the principle of angular momentum separation in gases.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re thrilled that the training on the Vortex Tube CFD Simulation using ANSYS Fluent was valuable to you and that you could effectively understand the core concepts of temperature separation based on angular momentum. We always aim to provide clear and educational simulations to help our users grasp complex principles. If there’s anything else we can assist you with, don’t hesitate to ask.
Retta Medhurst –
I appreciated learning about the vortex tube simulation—the temperature range achieved from the compressed air is fascinating! Well presented and extremely useful for any analysis involving thermal separation techniques.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are glad that you found the vortex tube simulation insightful and helpful for your thermal separation analyses. Should you have any further questions or need more assistance, please feel free to contact us.