Aorta, Non-Newtonian pulsating blood flow
$120.00 Student Discount
- The problem numerically simulates a non-Newtonian pulsating blood flow in Aorta using ANSYS Fluent software.
- We design the 3-D model with the Design Modeler software.
- We mesh the model with ICEM software, and the element number equals 457864.
- We perform this simulation as unsteady (Transient).
- We use a UDF to define the pulsating inlet velocity to Aorta.
- We use the Carreau model to define a non-Newtonian fluid.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Aorta, Non-Newtonian pulsating blood flow, ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Training
In this study, a non-Newtonian pulsating blood flow in Aorta has been studied by ANSYS Fluent software. The geometry is a *.stl file that should be repaired before generating the mesh.
This aorta geometry is obtained from a real geometry from a CT-Scan. Some powerful tools can assist us in fixing the geometry, such as Spaceclaim, ICEM CFD, and Design Modeler. We used ICEM CFD to fix the geometry and generate a mesh in this study.
First, the mesh was generated using the octree method with 5 layers of prism meshes with a ratio of 1.2. Second, the Delaunay method has been used to improve the quality of the existing mesh. The final number of mesh is 457864 cells.
Aorta Methodology
UDF defines the pulsatile inlet velocity. A non-Newtonian fluid is a fluid that does not follow Newton’s law of viscosity, i.e., constant viscosity independent of stress. In non-Newtonian fluids, viscosity can change when under force to either more liquid or more solid.
In the Carreau Model, viscosity depends upon the shear rate, like in the Power Law Fluid Model. Pierre Carreau first proposed the model. Blood is a non-Newtonian fluid whose behavior follows this model. This model works based on both the shear model and temperature.
In this study, there is no energy equation. Therefore, the temperature was ignored. The following equation shows the viscosity relation with the shear model.
Where µ0, µ∞, n, and λ are zero shear viscosity, infinite shear viscosity, power index, and relaxation time, respectively.
The solver is Transient; the flow is turbulent, and the density is constant and equals 1060 kg/m3. The working fluid (Blood) is non-Newtonian. No-slip condition for the inner surface of the vessel wall.
Here we provide you with the UDF used to define the pulsating inlet velocity to that Aorta.
Aorta Conclusion
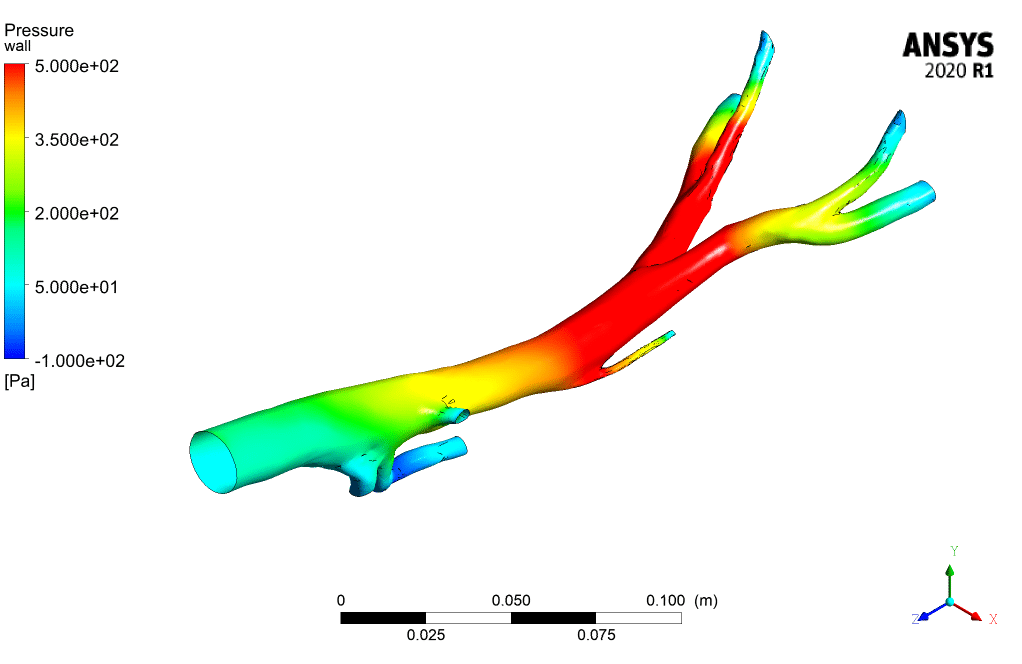
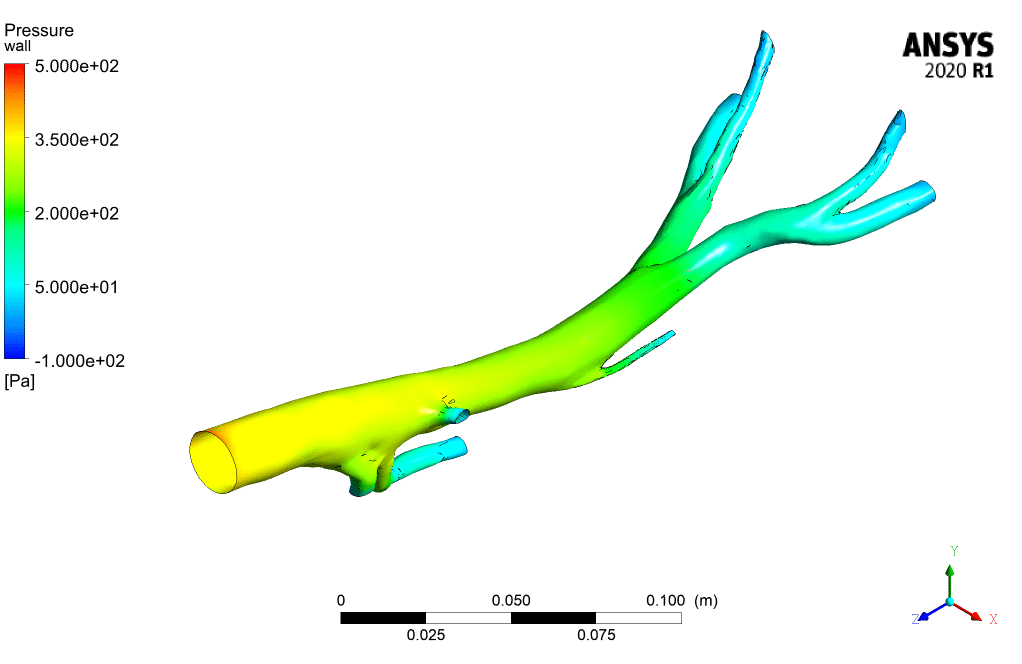
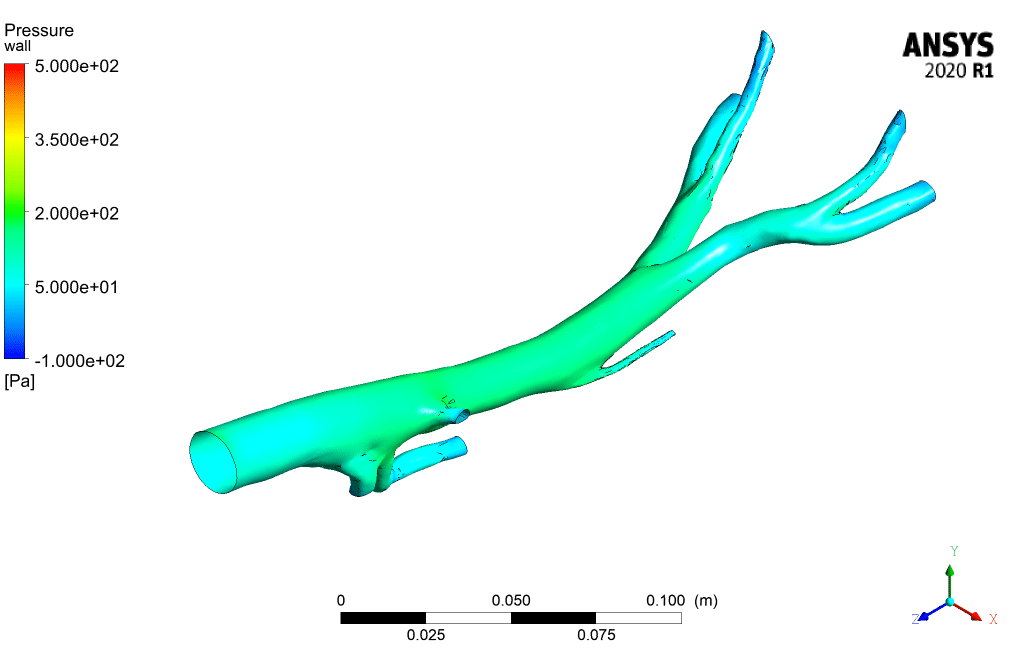
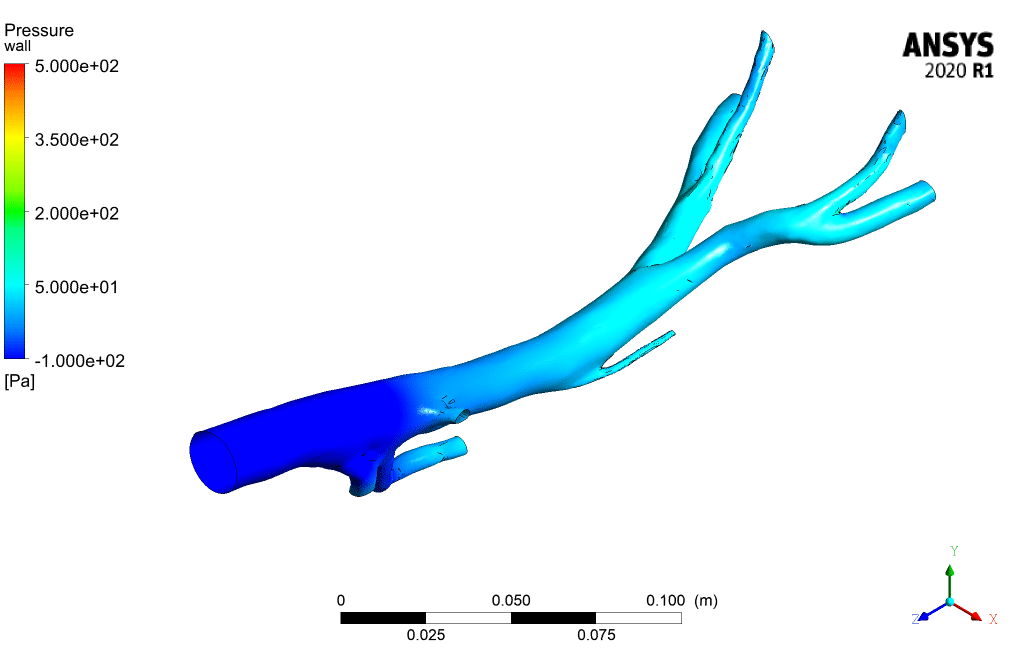
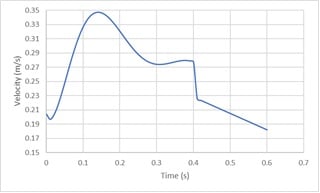
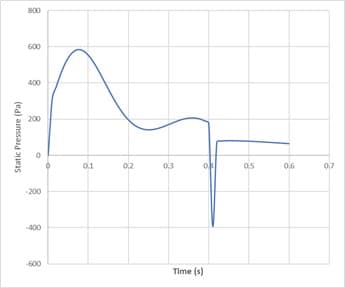
The following figures illustrate inlet velocity and pressure drop, respectively. As the figures show, the maximum velocity is at the time of 0.15 (s).
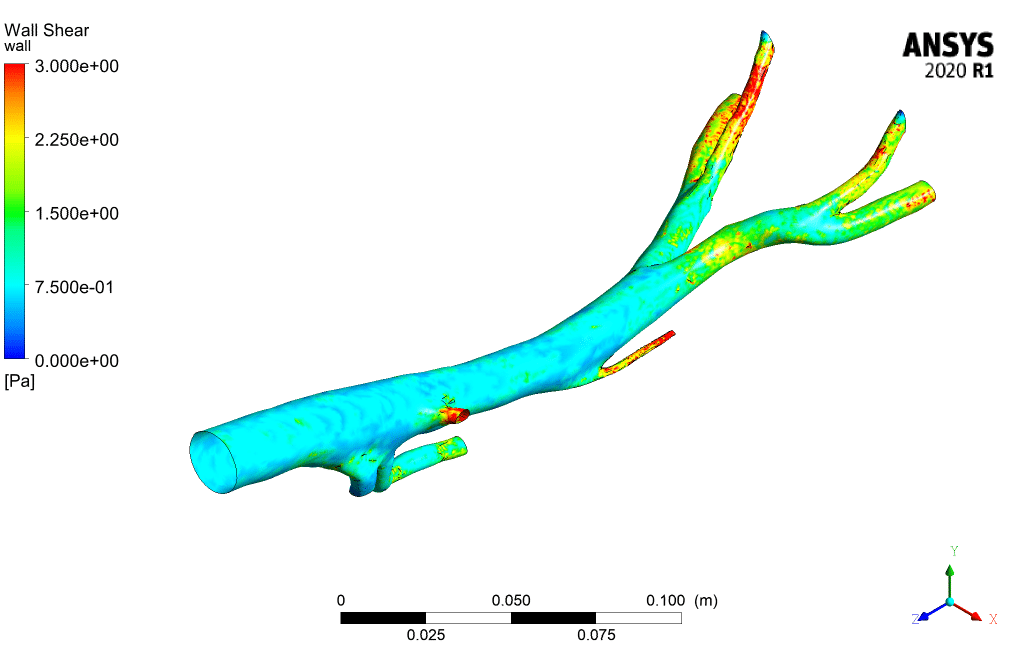
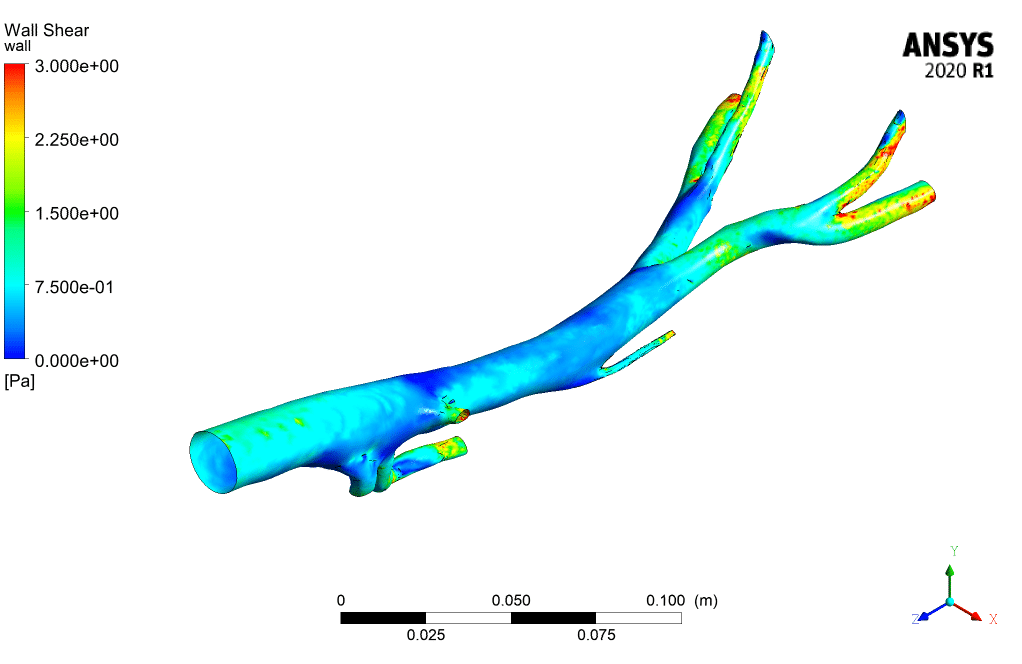
According to the contours, the WSS (wall shear stress) has the maximum value in the Aorta sections whose diameter is less than others. Also, the contours of static pressure show, at the beginning of the pumping of blood, at the entrance of the branches, the pressure is maximum.
When the suction occurs at the time of 0.4 s, it has the most significant impact on the inlet section of the Aorta. To see the pluses and better understand the flow condition, animation files of pressure and shear stress have been attached to this report.
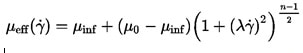
Llewellyn Sauer MD –
Outstanding details and work on the Aorta CFD Simulation! The pulsating effect to replicate the blood flow was particularly interesting. Your simulation technique aligns with the real physiological conditions impressively. The incorporation of non-Newtonian fluid behavior in showing blood’s true properties is great for research and educational purposes. Thanks for providing UDF for the inlet pulsating velocity – that must have taken the realism of the simulation to another level!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that the simulation met your expectations and provided you with valuable insights into the complex behavior of blood flow. Our goal is always to ensure our simulations reflect real-world conditions as accurately as possible. If you have any further questions or need assistance with your simulations, feel free to reach out to us. We look forward to supporting your future projects or learning needs!
Jonathan Gibson –
Which non-Newtonian fluid model is used for simulating blood in this aorta simulation and why is it suitable for this case?
MR CFD Support –
The non-Newtonian fluid model used for simulating blood in this aorta simulation is the Carreau Model. This model is suitable because blood, being a non-Newtonian fluid, exhibits changes in viscosity at different shear rates, which the Carreau Model can accurately represent. This is critical for modeling blood flow since different regions and conditions in the aorta will experience different shear rates, and thus the model allows for accurate simulation of blood behavior under a variety of physiologically realistic conditions.
Mr. Lorenz McKenzie Jr. –
I’m really interested in the non-Newtonian blood flow simulation for the Aorta. Does the UDF provided for the pulsating inlet cover the entire cardiac cycle and what’s the level of difficulty to implement it for someone with intermediate knowledge in Fluent?
MR CFD Support –
The provided UDF does indeed cover the entire cardiac cycle to accurately capture the pulsatile nature of blood flow. For someone with intermediate knowledge in Fluent, understanding and implementing the UDF should be manageable. It will require knowledge of how to work with User-Defined Functions in Fluent, but the detailed context in our training materials can assist in this process.
Clark Hettinger –
Is the non-Newtonian behavior of blood considered in this simulation?
MR CFD Support –
Yes, the simulation accounts for the non-Newtonian behavior of blood by using the Carreau Model, which allows the viscosity to change depending on the shear rate.
Octavia Homenick –
The UDF for defining pulsating inlet velocity is mentioned. Could you please explain how it is implemented in the simulation?
MR CFD Support –
The UDF, or User-Defined Function, is a custom script used in ANSYS Fluent to define specific conditions that are not available by default in the software. For a pulsating inlet velocity, the UDF would describe the variation in velocity over time according to a prescribed formula or data set that matches the non-Newtonian pulsatile flow of blood. This script is compiled and loaded into the Fluent simulation to apply the described inlet conditions throughout the transient analysis.
Olen Jones –
Fantastic explanation and in-depth analysis. It’s so impressive to see real CT-Scan data represented in the simulation. The use of UDF for pulsating flow and non-Newtonian fluid modelling with Carreau’s model paint a detailed picture of blood flow in the aorta.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re delighted to hear that you appreciated the in-depth analysis and realistic representation of pulsating blood flow in the aorta through our simulation. Our goal is to provide insightful and accurate simulations that can be valuable for educational and research purposes. If you have any further questions or need additional information, feel free to reach out.
Lloyd Keeling DDS –
The detailed analysis sounds fascinating! I’m curious, how does the use of a non-Newtonian model like the Carreau model compare to using a Newtonian model in simulating blood flow, particularly in complex geometries like the aorta?
MR CFD Support –
Using a non-Newtonian model like the Carreau model is a more accurate representation of blood behavior, especially under varying shear rates within the aorta. Blood, as a non-Newtonian fluid, experiences changes in viscosity under stress. Newtonian models assume a constant viscosity and may not capture these dynamic fluid characteristics, potentially leading to underprediction of blood’s shear-dependent viscosity and overprediction of velocity profiles, particularly in areas subject to pulsatile flow or in geometries with stenosis or aneurysms.
Ashley Beahan –
I’m impressed with the level of detail in the pulsating blood flow simulation of the aorta. The use of the non-Newtonian Carreau model seems very appropriate for blood’s complex behavior. The attention to realistic geometry from a CT-Scan and meticulous mesh refinement demonstrates MR CFD’s commitment to accuracy. Fantastic work integrating the user-defined function for inlet velocity!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your thoughtful review! We’re delighted to hear that you appreciate the intricacies of the non-Newtonian pulsating blood flow simulation. Our team strives for simulation accuracy and realism, and we’re pleased that this attention to detail has enhanced your learning experience. Should you have any further questions or need additional information on our products, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
Geraldine Schroeder –
I want to know more about the UDF mentioned for the pulsating inlet velocity. How is it implemented in the simulation?
MR CFD Support –
The User-Defined Function (UDF) for pulsating inlet velocity is a script written to define the time-varying velocity profile at the entrance of the aorta in the simulation. The UDF is written in C programming language, which is then compiled and hooked into ANSYS Fluent. Through the UDF, you can prescribe complex boundary conditions that vary over time to accurately model physiological blood flow which typically follows a pulsatile pattern in accordance with the cardiac cycle.
Hans Oberbrunner –
The non-Newtonian simulation for pulsating blood flow in the aorta looks impressive. The methodology used showcased great attention to detail in replicating physiological conditions. Which shear rate dependent viscosity model was used in this study, and why was it chosen over others for simulating the blood flow in the aorta?
MR CFD Support –
In this study, the viscosity of blood was modeled using the Carreau Model, which is a non-Newtonian fluid viscosity model that accounts for the shear-dependency of blood’s viscosity. The Carreau Model was chosen because it accurately represents blood’s shear thinning behavior, which is significant in larger vessels like the aorta. Other models, such as Newtonian, do not account for the variable viscosity of blood under different shear rates, making them less suitable for such simulations.
Bella Ferry I –
Absolutely outstanding detail on the non-Newtonian blood flow simulation! The applied methodology using ANSYS Fluent sounds incredibly robust with a focus on realistic modeling of the biological phenomenon. Fantastic to hear that the aorta geometry was so accurately derived and the UDF for pulsating inlet velocity adds such a depth to the study. Kudos to the team!
MR CFD Support –
We are thrilled to hear that you’re pleased with the level of detail and accuracy in our non-Newtonian blood flow simulation training using ANSYS Fluent. Our goal is to provide comprehensive and realistic studies that cater to learners’ needs effectively. Thank you for your appreciation and recognition of our team’s efforts!
Dr. Linwood Schneider –
I was impressed by the level of detail in the Aorta simulation process! The use of UDF for the pulsating inlet velocity and the non-Newtonian modeling with the Carreau Model for blood viscosity made the training incredibly intuitive. Thank you for a resource that supports complex biomedical engineering concepts so thoroughly!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that the Aorta simulation training was helpful and met your expectations. The application of realistic physiological conditions is key in biomedical simulations, and we’re glad you found the use of UDF and the Carreau Model for blood flow impactful. Your feedback is greatly appreciated, and if you ever need more insights or further training products, feel free to reach out to us!
Alia Schamberger III –
This is a highly intriguing study with critical applications in healthcare! I’m particularly impressed with the usage of UDF for pulsating inlet velocity. Can this simulation be adapted for patient-specific cases using different geometries obtained from CT scans?
MR CFD Support –
Absolutely! The simulation approach described can be tailored for different patient-specific geometries taken from CT scans. Customized geometric models, boundary conditions, and fluid properties can be adjusted to match each patient’s unique aorta structure and blood flow characteristics, ensuring more accurate diagnostics and treatment plans.
Mrs. Etha Walsh –
Is this training suitable for beginners who are not familiar with non-Newtonian fluid simulations or should they have prior experience with these types of fluid dynamics before attempting to understand the pulsating blood flow in the aorta?
MR CFD Support –
This training includes detailed steps and methodologies, which could be beneficial for beginners. However, a basic understanding of CFD principles and some familiarity with ANSYS Fluent would be advantageous. Prior experience with non-Newtonian fluid simulations isn’t a must, but it would certainly help grasp the concepts quicker.
Dr. Miracle Olson PhD –
Was the pulsatile nature of the blood flow also causing time-varying WSS on the aorta’s wall? How is this implemented in the simulation?
MR CFD Support –
Yes, the pulsatile nature of the blood flow leads to time-varying Wall Shear Stress (WSS) on the wall of the aorta. This is implemented in the simulation through the use of a user-defined function (UDF) to specify the pulsating inlet velocity of the blood according to realistic physiological conditions. The transient nature of the flow requires the solver to capture the variations over time, thereby providing a detailed distribution of WSS on the aorta’s wall during the cardiac cycle.
Ms. Cydney Lueilwitz II –
Impressive training! The inclusion of UDF for pulsatile inlet velocity and the Carreau model for blood’s non-Newtonian behavior likely make the simulation very realistic. Also, animations of pressure and shear stress provide a dynamic perspective of the flow condition which must be quite insightful.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that you found the training insightful and that the non-Newtonian behavior modeling and inclusion of pulsatile velocity via UDF enhanced the realism of the simulation. It’s great that you appreciate the dynamic visualizations provided by the animations. If you need any further assistance or information, please let us know.