Non-Newtonian Blood Flow in a Clogged Vessel CFD Simulation, ANSYS Fluent
$80.00 Student Discount
The present problem simulates non-Newtonian blood flow within a clogged vessel using ANSYS Fluent software.
Click on Add To Cart and obtain the Geometry file, Mesh file, and a Comprehensive ANSYS Fluent Training Video.To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Project Description
The present problem simulates blood flow within a clogged vessel using ANSYS Fluent software. Fluids are divided into two categories according to their viscosity: Newtonian and non-Newton fluids. Viscosity of a fluid is a parameter that indicates the resistance of that fluid to flow. Newtonian fluids are fluids that follow Newton’s law of viscosity (shear stress in a Newtonian fluid changes linearly with strain rate) and also their viscosity depends only on the temperature and pressure of the fluid and by applying force to them in constant temperature and pressure, their viscosity does not change.
Non-Newtonian fluids, on the other hand, are fluids that do not follow Newton’s law of fluids, and their viscosity changes with the application of force. In this simulation, blood with a density of 1050 kg.m-3 is used as a fluid that is considered a non-Newtonian fluid. Therefore, the Carreau equation model is used to define the fluid viscosity in the software. In this model, the viscosity value at zero shear stress is defined as 0.022 kg.m-1.s-1 and the viscosity at initial shear stress is defined as 0.0022 kg.m-1.s-1. Blood flow enters the vessel at a rate equivalent to 0.25 m.s-1 and exits at a pressure equivalent to atmospheric pressure. The equation of the Carreau model is defined as follows:
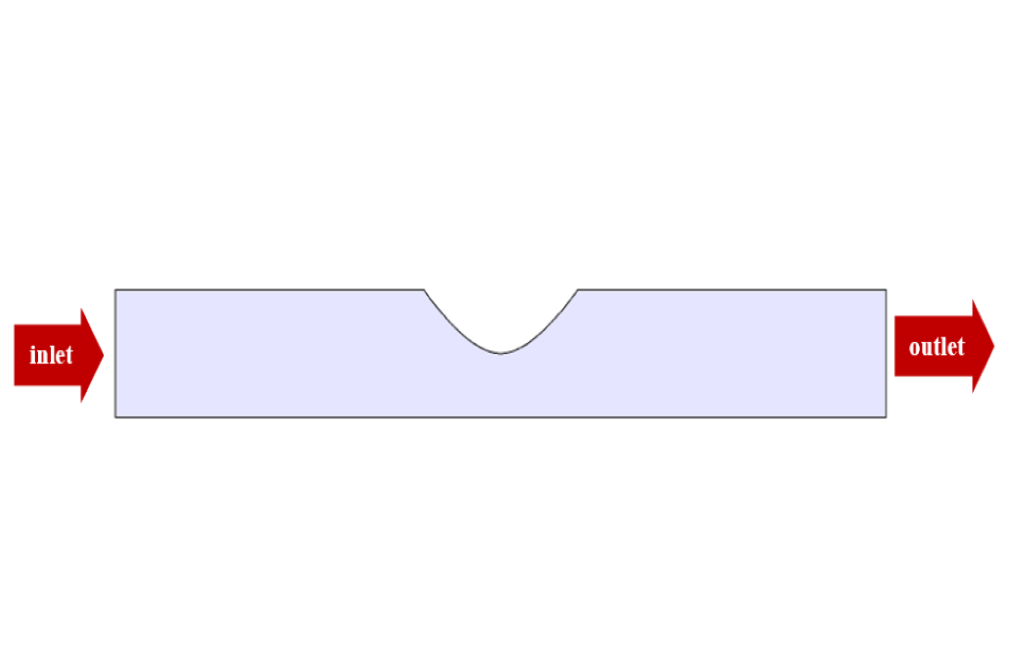
Clogged Vessel Geometry & Mesh
The present model is designed in two dimensions using Design Modeler software. The model is designed as a symmetrical part of a three-dimensional model that includes an inlet and an outlet and a recessed wall.
The meshing of the model has been done using ANSYS Meshing software and the mesh type is unstructured. The element number is 5302. The following figure shows the mesh.
Non-Newtonian Flow CFD Simulation
To simulate the present model, we consider several assumptions:
- We perform a pressure-based solver.
- The simulation is unsteady.
- The gravity effect on the fluid is equal to -9.81 m.s-2 along the Y-axis.
A summary of the defining steps of the problem and its solution is given in the following table:
| Models | ||
| Viscous | k-epsilon | |
| Boundary conditions | ||
| Inlet | Velocity Inlet | |
| velocity magnitude | 0.25 m.s-1 | |
| Outlet | Pressure Outlet | |
| gauge pressure | 0 pascal | |
| Walls | Wall | |
| wall motion | stationary wall | |
| Methods | ||
| Pressure-Velocity Coupling | SIMPLE | |
| Pressure | second order | |
| momentum | second order upwind | |
| Initialization | ||
| Initialization methods | Standard | |
| gauge pressure | 0 pascal | |
| axial velocity | 0.25 m.s-1 | |
| radial velocity | 0 m.s-1 | |
Results
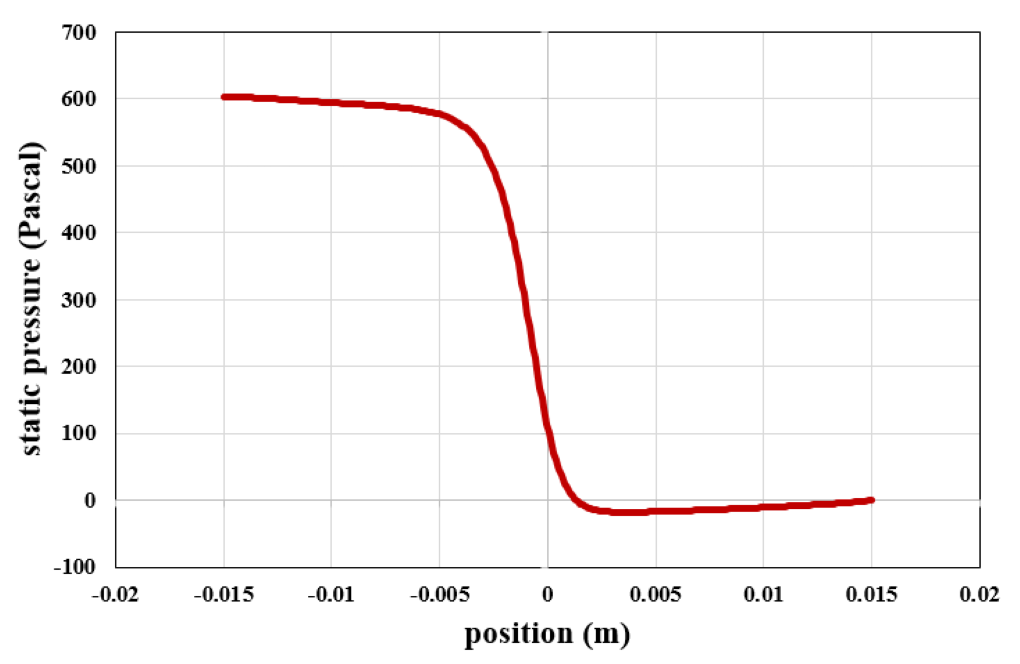
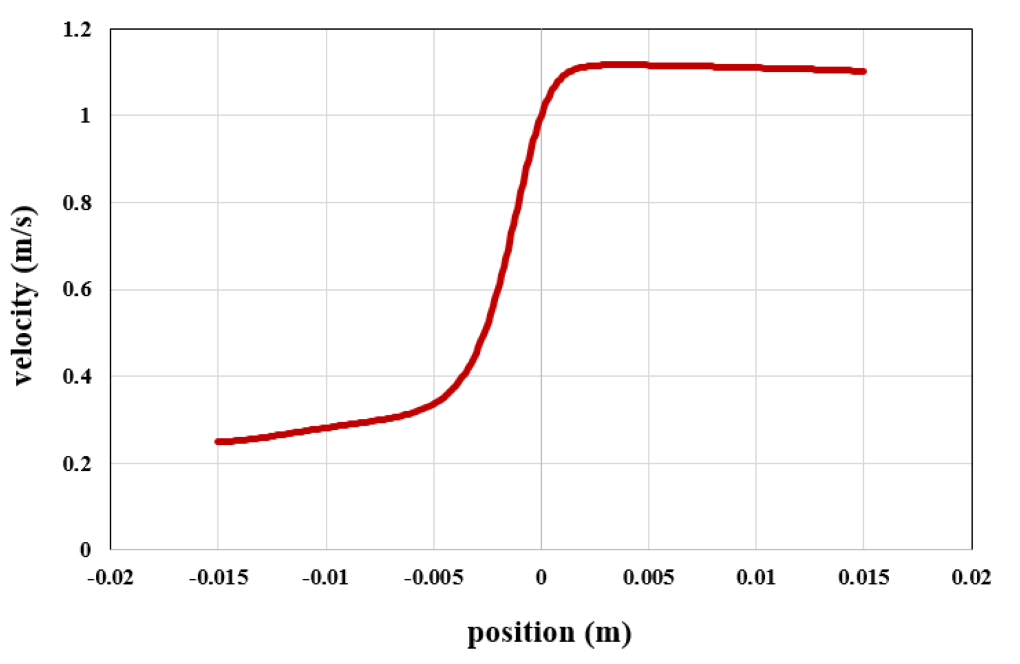
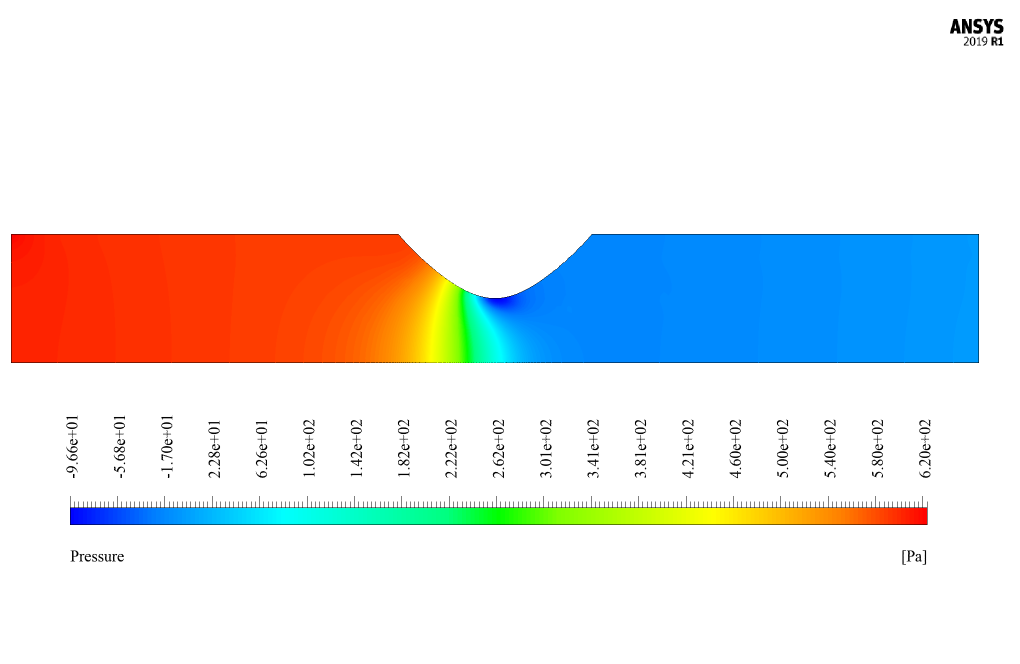
At the end of the solution process, we obtain two-dimensional contours related to pressure and velocity as well as diagrams of changes in pressure and velocity along the central axis of the model and diagrams of shear stress changes in the wall along the outer surface of the vessel wall.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.