Wall Wavy Motion CFD Simulation, Dynamic Mesh
$120.00 Student Discount
- The problem numerically simulates the Wall Wavy Motion using ANSYS Fluent software.
- We design the 2-D model with the Design Modeler software.
- We mesh the model with ANSYS Meshing software, and the element number equals 146,998.
- We perform this simulation as unsteady (Transient).
- We use the Dynamic Mesh Model to define deforming and moving zones.
- We use the user-defined function (UDF) to define the wavy motion.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Description
This project is related to the numerical simulation of the Wall with Wavy Motion using ANSYS Fluent software. We aim to consider the effect of a non-stationary wall on the water flow. We assumed that water flows in a two-dimensional channel. We considered that the bottom wall of the channel has wave motion.
This product is the sixth chapter of the Dynamic Mesh Training Course.
In this project, we simulated the water flow inside a channel with wave motion. We aim to model the wavy motion of the bottom wall of the channel. The wavy motion of the wall changes the behavior of the fluid in the channel. So, the mesh of the computing domain deforms over time.
We modeled the geometry of the project using Design Modeler software. The geometry is related to a channel with a non-stationary wall. The computational domain includes the internal space of the channel. Then we meshed the model with ANSYS Meshing software. The model mesh is unstructured, and the number of cells equals 146,998.
Wavy Motion Methodology
The Dynamic Mesh Model is used in this simulation. We generally use a dynamic mesh whenever we have a moving boundary or a deforming zone.
Here, a wall creates a wave motion. So this causes the mesh to deform over time. Therefore, we define a user-defined function (UDF) to define the wavy motion of the wall. To apply the wave motion to the wall, we must use the Grid Motion UDF.
According to the wavy motion of the wall, the mesh zone above the non-stationary wall is deformed. So, for this zone, we use the Deforming option.
Due to the nature of this modeling, fluid behavior is time-dependent. Hence, we use the unsteady (Transient) solver.
Conclusion
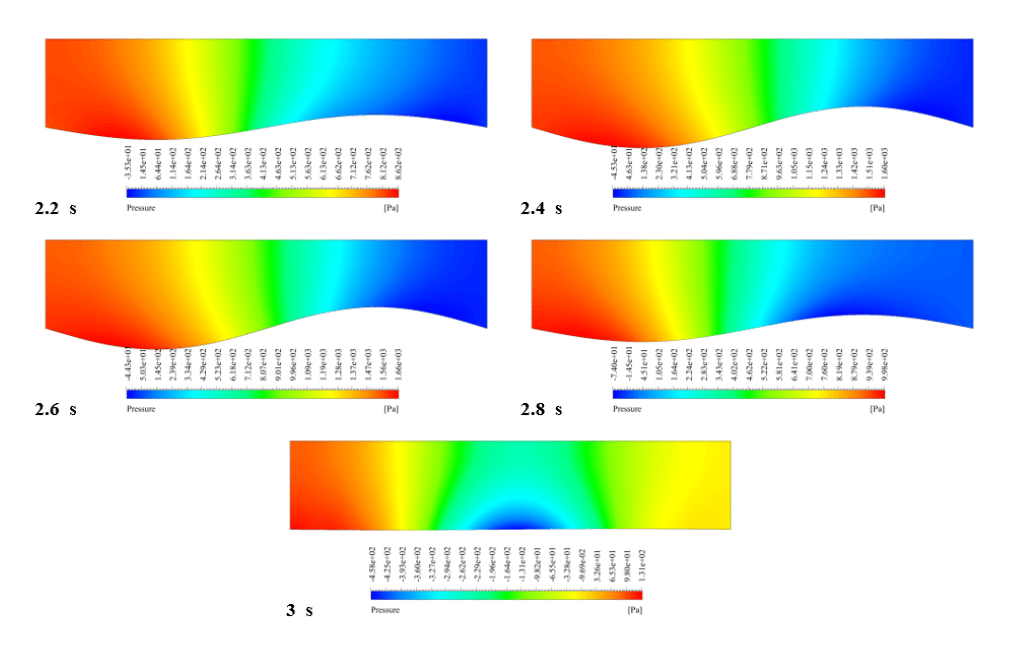
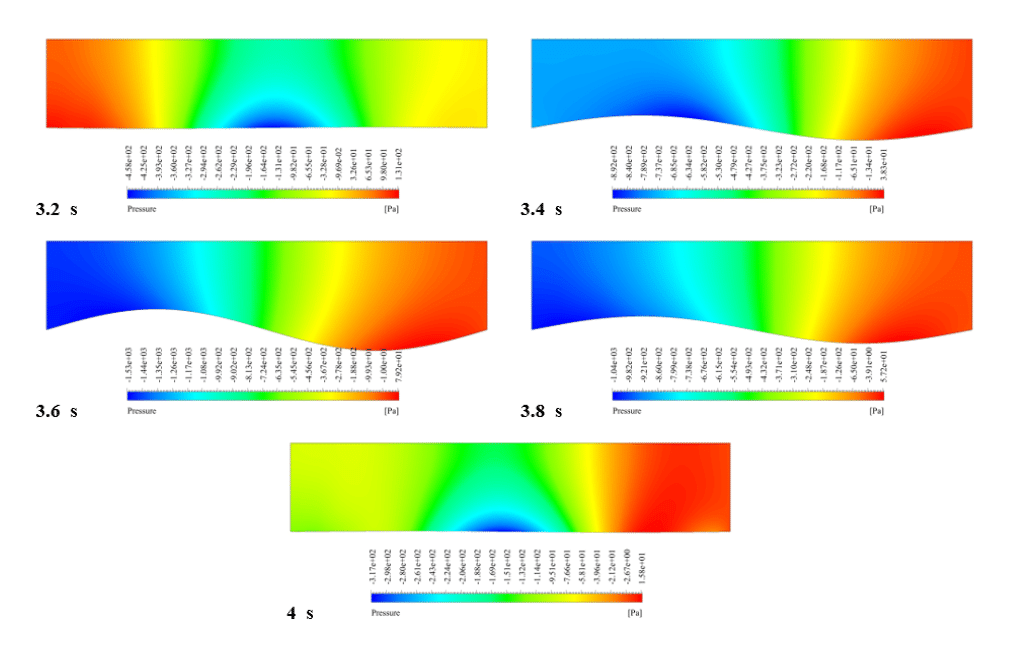
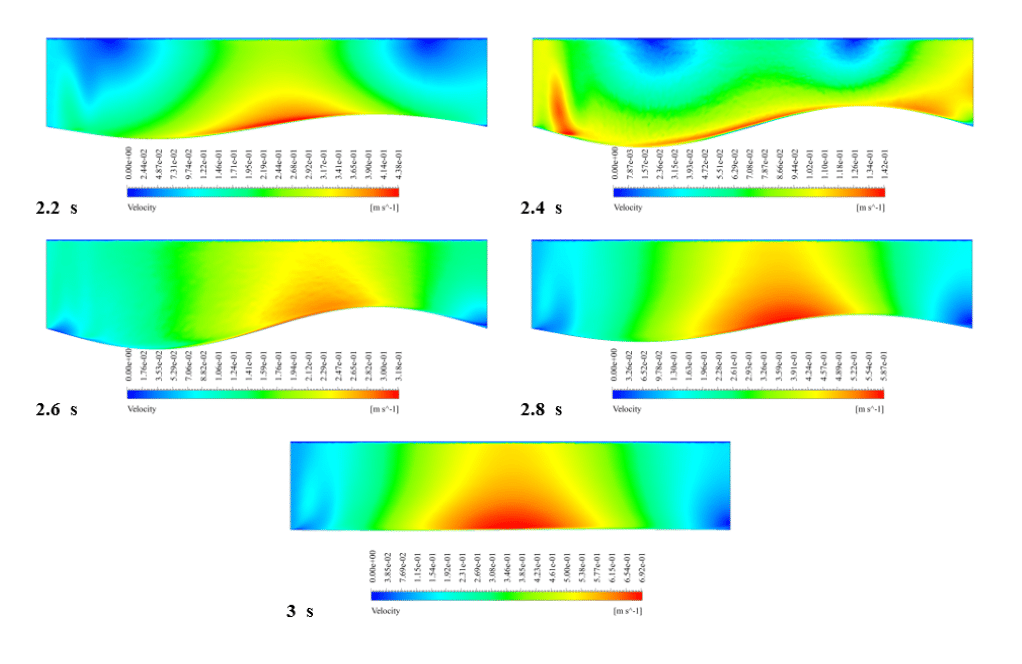
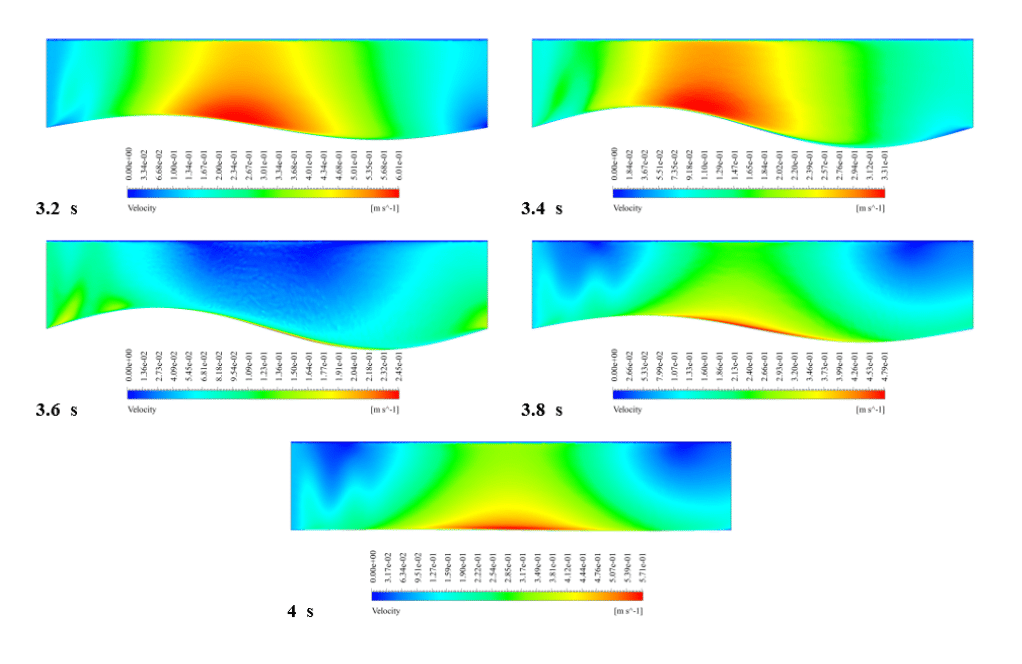
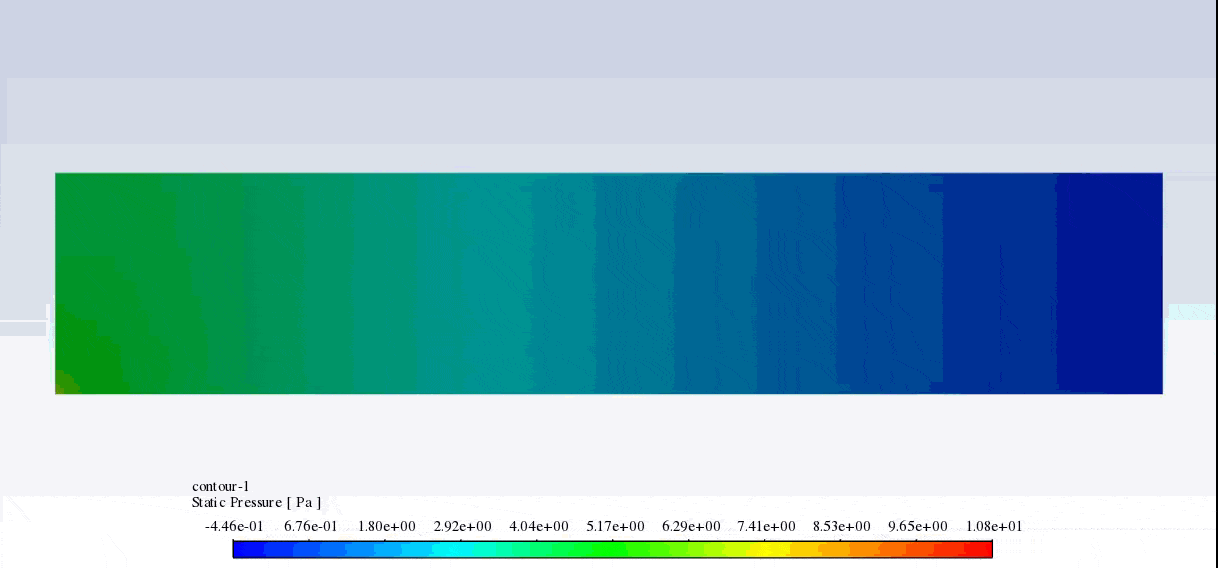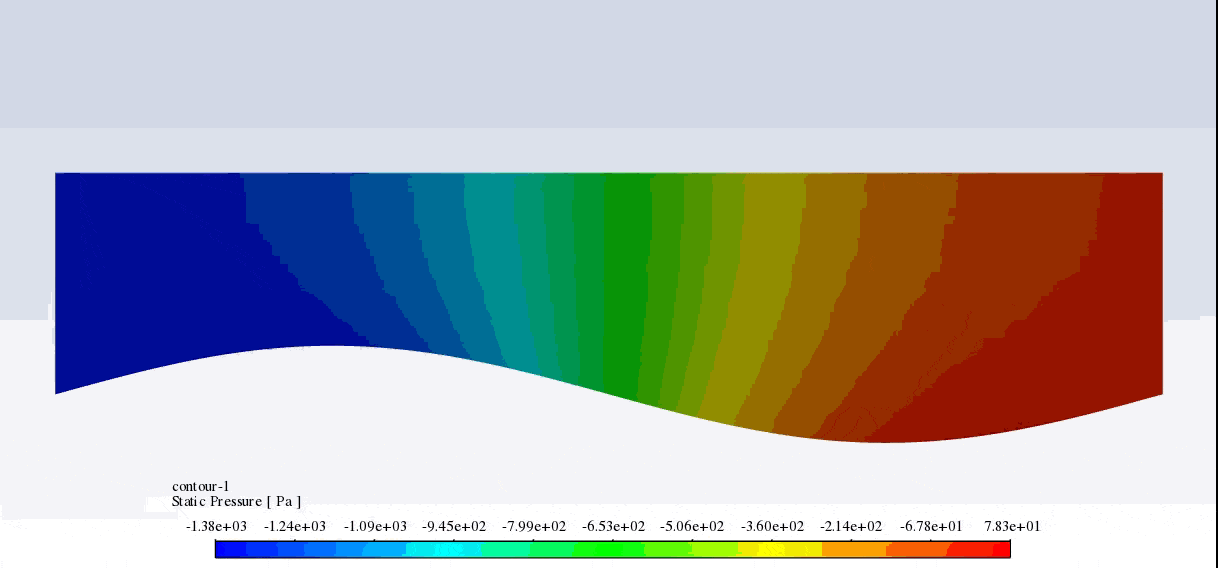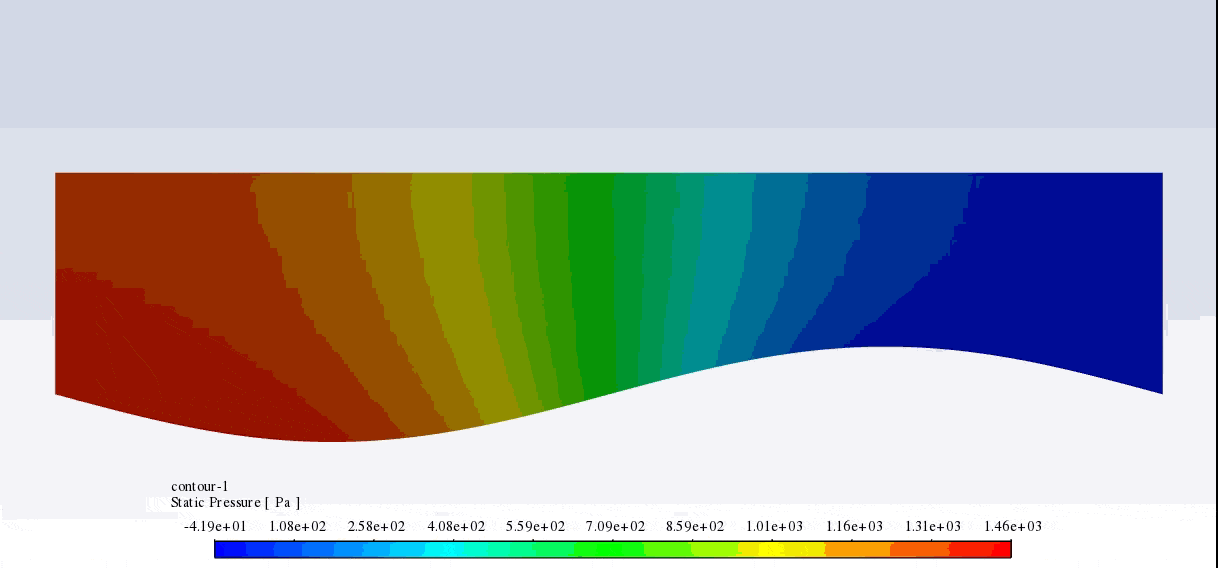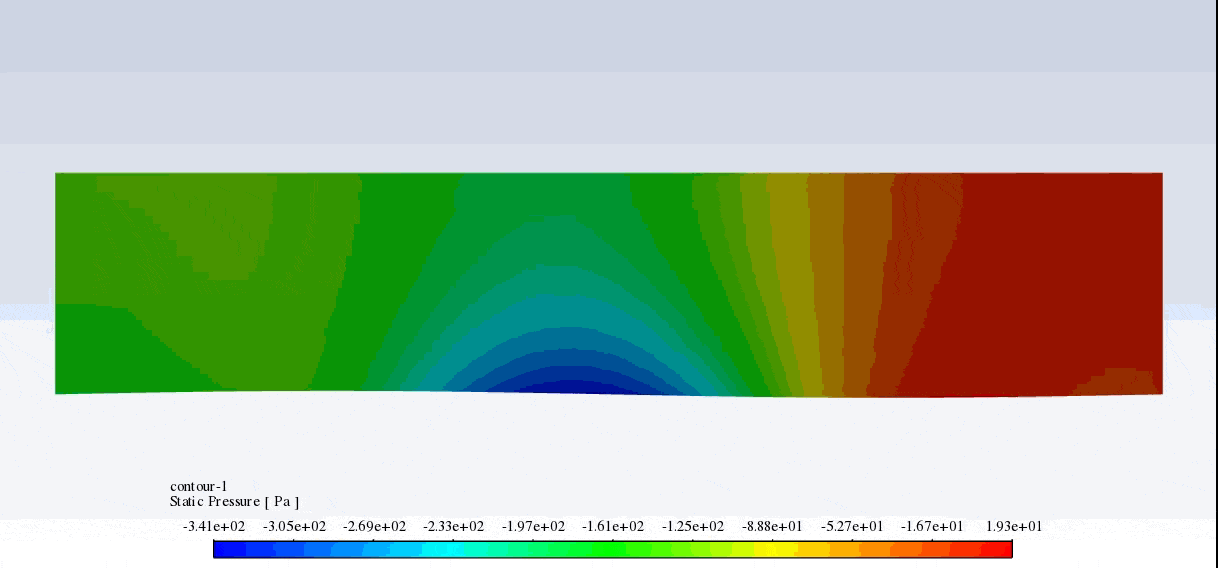
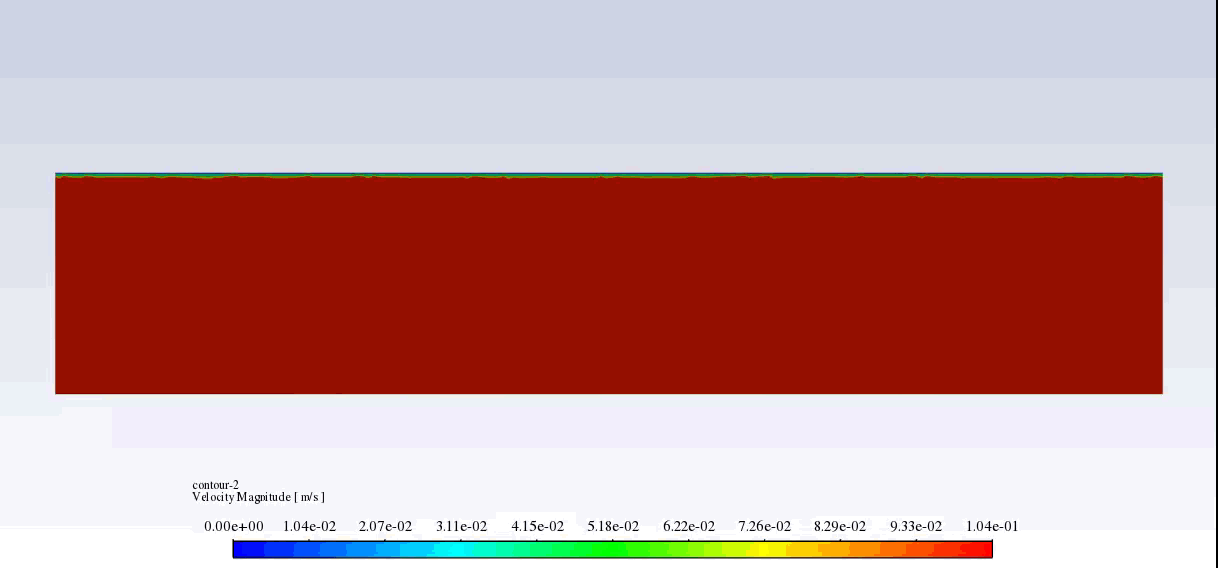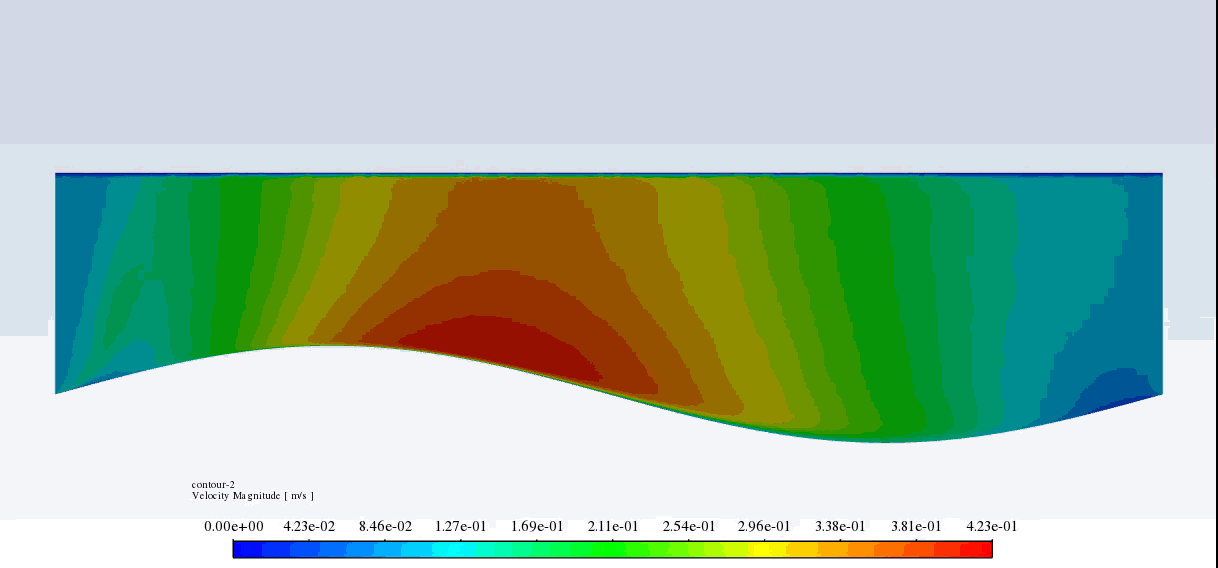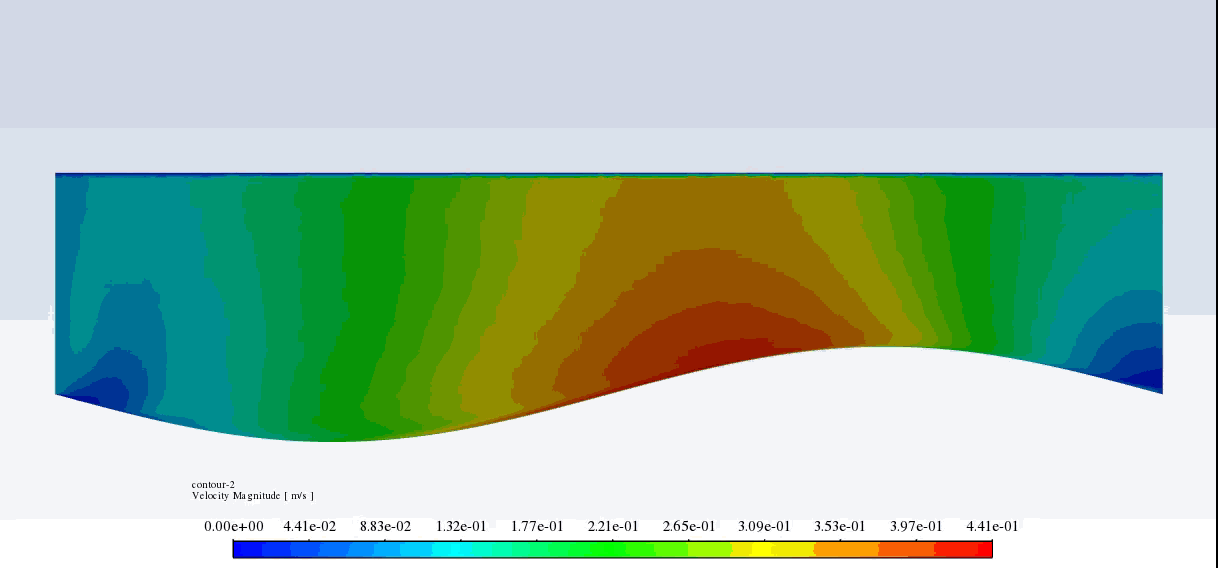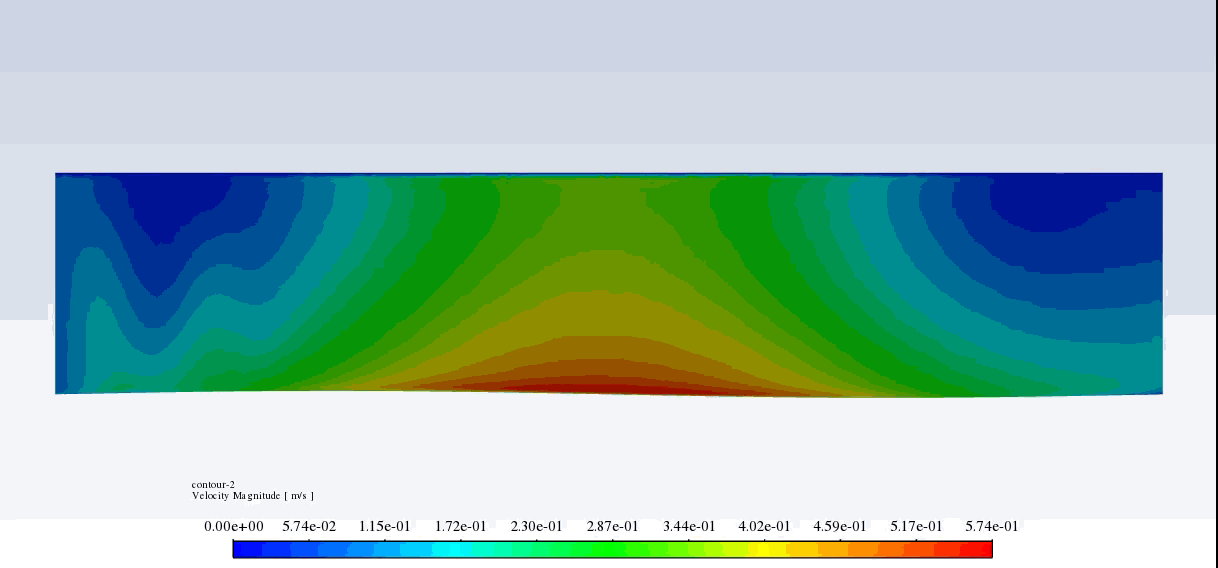
After the solution, we obtained pressure and velocity contours. Because the wall moves over time, we obtained the velocity and pressure contours animation.
The results show that the pressure and velocity are constantly changing under the influence of the wave motion of the channel wall. The wave motion causes the cross-section of the flow to change along the channel. As the cross-section decreases, the velocity increases, and the pressure decreases. If the cross-section increases, the velocity decreases, and the pressure increases.
Dr. Walton Muller –
The animations of velocity and pressure contours were exceptional! Seeing the fluid dynamics in motion provided a clear understanding of the flow changes due to the wavy wall. Learning about dynamic meshes through this simulation has been incredibly insightful. Keep up the excellent work!
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear that you found the animations of velocity and pressure contours enlightening! It’s always rewarding to know that our training materials are helping our customers grasp complex concepts like dynamic mesh and fluid dynamics. Thank you for your positive feedback and encouragement!
Ms. Maryse Lowe –
I’m really impressed with how you’ve managed to simulate the wavy motion of the wall and its impact on the flow within the channel. The dynamic aspect of the mesh really adds complexity to the simulation. Fantastic work!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re pleased to hear that you’re impressed with the simulation and the use of dynamic mesh to accurately capture the complex interactions of the wavy motion with the fluid flow. It’s our goal to provide detailed and practical learning experiences. Your feedback is very encouraging!
Jo Beer –
The UDF you mentioned for the wave motion of the wall, could you explain how exactly it defines the wavy motion?
MR CFD Support –
Certainly! The UDF, or User-Defined Function, is a customized script written in C programming language that defines how the wall’s motion changes over time. This script calculates the motion of the wall at each time step, ensuring that the wave motion is accurately represented in the simulation. The wavy motion is typically defined mathematically by sine or cosine functions wherein the parameters like amplitude, frequency, and phase shift determine the characteristics of the wave motion. The UDF dictates these values to Fluent, which then dynamically adjusts the mesh to adapt to this motion throughout the simulation.
Prof. Santina Dooley –
Wow, the dynamic simulation of a wavy wall effect on fluid flow seems remarkable. The use of a dynamic mesh must have provided great insights into the fluid’s behavior!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that you found the simulation impressive. The dynamic mesh indeed offers a deeper understanding of how changing boundaries affect fluid dynamics. If you ever need more information or further training, don’t hesitate to reach out!
Curtis Deckow –
This training course perfectly detailed the techniques on dynamic mesh and its interactions with moving boundaries. The integration of a UDF to simulate the wall’s wavy motion was well explained and easy to follow.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that you found the course to be informative and user-friendly. If you have any further questions or need clarifications, feel free to reach out!
Clemmie Sipes –
Great course on Dynamic Mesh in ANSYS Fluent! Really helped me grasp the implementation of moving boundaries in simulations. The animations of pressure and velocity changes are very insightful.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our Dynamic Mesh Training Course has been helpful to you and that you found the animations insightful. Understanding moving boundaries is crucial, and we’re glad we could assist with that.
Agustina Nienow V –
The simulation overview was fantastic! The concept of a dynamic mesh adapting to a moving wall was especially intriguing as it reflects real-world fluid behavior around moving boundaries.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that you found the dynamic mesh concept intriguing and the simulation reflective of true fluid dynamics. If you have any further questions or need assistance with similar CFD simulations, feel free to reach out!
Eddie Braun –
I’m thrilled with how well the simulation reflected the actual behavior of fluid against wavy motion. The dynamic response appears to yield very realistic results!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback! We are delighted to hear that our simulation met your expectations and provided you with realistic results. It’s our goal to deliver accurate and high-quality simulations with our products.
Dr. Viola Thompson DVM –
I am very impressed with how the wave motion of the wall was integrated into the ANSYS simulations. It’s clear how the dynamic mesh accommodated this non-stationary boundary to simulate real-life scenarios of changing flow behaviors.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to hear that you appreciated the integration of dynamic mesh techniques to simulate the complex interactions between non-stationary walls and fluid flow. It’s our objective to provide realistic and detailed simulations to help understand and predict fluid behaviors. If there’s anything more you’d like to learn about our simulations or any specific feature that intrigued you, do let us know!
Paula Balistreri –
I watched the pressure and velocity contours animation from the Wall Wavy Motion CFD simulation—it was fascinating to see how the wave motion of the channel wall affects the fluid behavior! I’m impressed by the level of detail and the clarity of the visual effects.
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear that you are impressed with our Wall Wavy Motion CFD simulation and found the visualization of pressure and velocity contours helpful. It’s great to know that the dynamic effects of the wavy wall were clearly demonstrated and appreciated. Thank you for taking the time to share your positive feedback!
Geraldine Spencer –
I’m really impressed with how the waving channel wall dynamics were handled. The visuals must be captivating with the fluid’s behavior changing throughout the simulation. Great job on demonstrating fluid adaptability in varying cross-sections!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the feedback! We’re glad to hear you appreciated the wave motion dynamics and the impact on fluid behavior in our simulation. It’s rewarding to know that our efforts to accurately portray the fluid’s adaptation to the dynamic environment within the simulation were successful. We’re looking forward to bringing more quality simulations to you!
Keanu Steuber –
The Wave Motion Wall simulation looks fascinating! The dynamic interaction between the moving wall and fluid flow must provide unique insights. The results in changing pressures and velocities across the channel section could be crucial for design optimizations of similar systems.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive review! We’re glad to hear that you found our Wall Wavy Motion simulation fascinating and insightful. Dynamic mesh simulations do provide unique challenges and opportunities for understanding fluid-structure interactions and optimizing designs. If you have any further questions or need assistance with similar simulations, feel free to reach out!
Arthur Gutmann –
The wavy motion simulation appears fantastic! Learning to use dynamic meshing for channels with non-stationary walls opens up many possibilities for solving practical engineering problems. The results with the time-dependent behavior of fluid due to wall motion must provide great insights.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback on our wavy motion CFD simulation tutorial! We strive to provide comprehensive courses that enable our customers to tackle complex fluid dynamics challenges. It’s gratifying to hear that you found the dynamic mesh application insightful. Keep exploring our Dynamic Mesh Training Course for more advanced scenarios!
Mrs. Libbie Cremin Sr. –
I’m so impressed by how dynamic mesh and the wavy motion of the wall have been modeled. Great job on demonstrating how fluid behavior adapts over time due to wall movement!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you very much for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that you found the dynamic mesh modeling and the display of changing fluid behavior due to the wavy wall motion insightful. Your appreciation truly motivates us to keep providing high-quality CFD educational material.
Mabel Frami V –
The dynamic mesh capabilities sound fascinating. Does the predefined wavy motion in the user-defined function align well with the actual wave motion observed in the results, and how accurately are these wave motions visualized in the post-processing phase?
MR CFD Support –
The user-defined function (UDF) for setting up the wavy wall motion has been developed to approximate the motion as accurately as possible. In the post-processing phase, animations of velocity and pressure contours are created to effectively visualize the impact of this motion on the flow, allowing for accurate representations of the wave effects over time.
Mrs. Marlene Wilkinson –
The project was fascinating, and the animations of velocity and pressure contours truly helped to visualize the impact of the wavy wall motion on fluid behavior. Well-done on incorporating dynamic mesh effectively to capture the changes!
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear you found the animations informative and that the dynamic mesh feature enhanced your understanding of the fluid’s response to the wavy wall motion. Thank you for your appreciation of our efforts!
Israel Lesch –
I was thoroughly impressed with the Wall Wavy Motion CFD Simulation project. The animations of pressure and velocity contours effectively demonstrated the impact of the non-stationary wall on water flow, exemplifying the depth of analysis that could be achieved using ANSYS Fluent. Great work!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you very much for your positive feedback on the Wall Wavy Motion CFD Simulation! We are delighted to hear that the project met your expectations and that you found the animations informative and indicative of the fluid dynamics involved. Your appreciation motivates us to continue providing high-quality educational materials. Don’t hesitate to reach out if you have more questions or need further assistance.
Christophe Weissnat –
The dynamic wavy motion simulation results sound fascinating. What kind of patterns did you observe in pressure and velocity fields over multiple cycles of wave motion? Were there any periodic or changing trends over time?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your interest! The excitation of wavy motion on a wall within a channel indeed presents intriguing fluid dynamics characteristics. As per the simulation outcomes, the pressure and velocity fields demonstrated noticeable fluctuations correlating to the wavy wall motion. These fields responded variably as the wave peaks and troughs moved along the channel. Specifically, with the wall elevating to form a peak, the channel’s cross-sectional area available for flow shrank, leading to augmented velocity and diminished pressure in that segment. Conversely, as the wall dipped creating a trough, the cross-sectional area expanded, causing the fluid’s velocity to diminish and its pressure to expand. These reciprocating alterations forged a periodic pattern in the channel, creating a complex interplay of fluid forces directly linked to the wall motion.
Benjamin Jenkins II –
I’m fascinated by the concept of dynamic mesh and the wavy motion of the wall. Can you please explain how the use of Grid Motion UDF improved the simulation outcomes for this project?
MR CFD Support –
In this simulation, the Grid Motion UDF (User-Defined Function) was fundamental to accurately model the non-stationary wavy motion of the bottom wall in the channel. By incorporating the UDF, we define the exact motion and deformation that occurs on the wall over time. This approach enhances the realism of the simulation by allowing the mesh to adapt dynamically to reflect the changing geometry. As a result, it ensures that the fluid dynamic calculations account for the wall’s movement, providing more accurate representations of pressure and velocity changes within the water flow.
Evangeline Quigley V –
I’m delighted with the Wall Wavy Motion simulation tutorial; the dynamic mesh technique was very well explained. It made understanding the complex interaction between the moving wall and the fluid dynamics much clearer!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled our Wall Wavy Motion tutorial on dynamic mesh helped clarify the intricate dynamics involved. Your success encourages us to continue delivering high-quality learning material.
Kelton Harber –
I’m very impressed with the Wall Wavy Motion CFD Simulation! The dynamic mesh technique obviously provided a detailed understanding of the flow changes due to the wavy wall motion. Excellent approach!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our Wall Wavy Motion simulation met your expectations and provided you with the detailed insights you were looking for. It’s great that you recognized the benefits of our dynamic mesh technique. If you have any further questions or need assistance with other projects, we’re here to help.
Joyce Streich –
The Wall Wavy Motion CFD simulation’s concept is fascinating. The application of dynamic mesh to account for non-stationary walls paints a holistic understanding of fluid behaviors under such conditions.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback on the Wall Wavy Motion CFD Simulation course. We’re pleased to hear that you appreciate the application of dynamic mesh to understand fluid dynamics in changing conditions. If you have any more questions or need further clarification on any aspects of the simulation, feel free to reach out. Happy learning!
Prof. Charles Turcotte –
Amazing detail and application! The concept of the wavy wall motion and its influence on flow behaviour beautifully unfolds in this simulation, showcasing Fluid Dynamics in all its complexity and wonder. Kudos to MR CFD for creating such an insightful educational product.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled that you found the Wall Wavy Motion CFD Simulation insightful and educational. At MR CFD, we are passionate about helping others understand complex fluid dynamics phenomena through practical simulations. We look forward to providing you with more innovative learning experiences!
Mireille Johnston –
This project was very educational for understanding fluid behavior in non-stationary environments. Your application of the dynamic mesh model through a UDF effectively demonstrated the continuous interplay between water flow and a changing boundary condition. I appreciated the visual results showing pressure and velocity changes over time, mapping the direct influence of the wall’s wave motion on the internal fluid dynamics.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your review! We’re glad you found the simulation with the application of the dynamic mesh model using UDF to be educational and effective in demonstrating fluid behavior in a variable environment. It’s great to hear that the visual results were helpful in understanding the impact of wave motion on fluid dynamics. Your feedback is appreciated!