Biomedical and Healthcare Training Package, Advanced Users, 10 Projects
$1,582.00 Original price was: $1,582.00.$527.00Current price is: $527.00. Student Discount
This training package includes 10 practical exercises, using ANSYS Fluent software. MR CFD suggests this training package for all engineers interested in the BIOMEDICAL & HEALTHCARE field, who will learn CFD simulation in this field at the ADVANCED level.
Click on Add To Cart and obtain the Geometry file, Mesh file, and a Comprehensive ANSYS Fluent Training Video.To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Biomedical & Healthcare Training Package for ADVANCED ANSYS Fluent Users
This training package includes 10 practical exercises, using ANSYS Fluent software. MR CFD suggests this training package for all engineers interested in the BIOMEDICAL & HEALTHCARE field, who will learn CFD simulation in this field at the ADVANCED level.
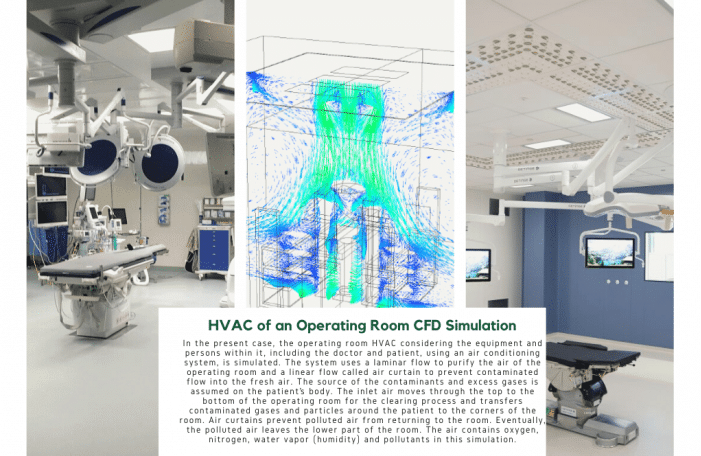
OPERATING ROOM HVAC
In case number 1, the operating room HVAC, using an air conditioning system, is simulated considering the equipment and persons within it, including the doctor and patient. The system uses a laminar flow to purify the air of the operating room and a linear flow called an air curtain to prevent contaminated flow into the fresh air. The source of the contaminants and excess gases is assumed on the patient’s body.
CORONAVIRUS (Biomedical)
In project number 2, based on the CFD method, an attempt has been made to simulate the respiration of viral air from the mouths of several patients carrying coronavirus in the aircraft. This model includes a computational domain in the form of an airplane and seats inside it, on each of which a passenger is modeled. For each of these passengers, a surface is defined as the mouth as the source of respiration and transmission of the coronavirus. In practical exercise number 3, an attempt has been made to simulate the respiration of viral air from the mouth of sick coronavirus carrier students in the classroom. This model includes a computational domain in the form of a classroom and chairs inside which a student is modeled on each of the chairs. For each student, a surface is defined as the mouth as the source of the virus’s respiration and transmission.
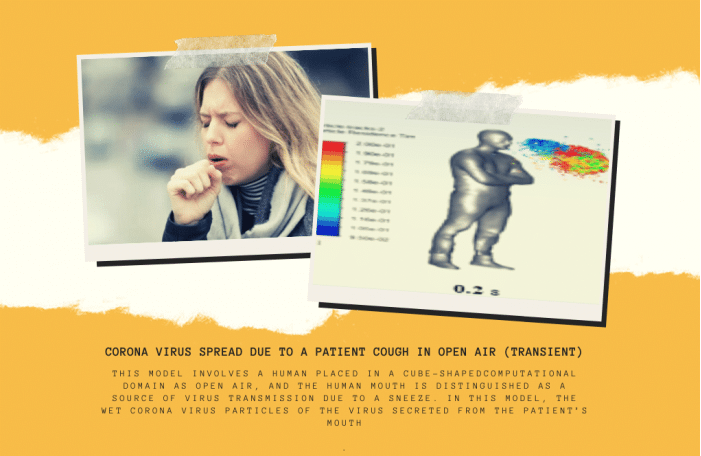
Training number 4 simulated the release of coronavirus particles from the patient’s mouth during coughing in the open air. This model involves a human placed in a cube-shaped computational domain in the open air, and the human mouth is distinguished as a source of virus transmission. To simulate this model, a discrete phase model (DPM) must be used. In project number 5, human cough virus particles in the coffee shop have been simulated using two-way DPM. According to this definition of injection, human cough virus particles are physically expelled from the patient’s mouth by water droplets evaporating in space. These virus droplets have a temperature of 310 K, a velocity of 31.85 m.s-1, and a mass flow of 0.018 kg.s-1, emitted at intervals of 0s to 0.1s.
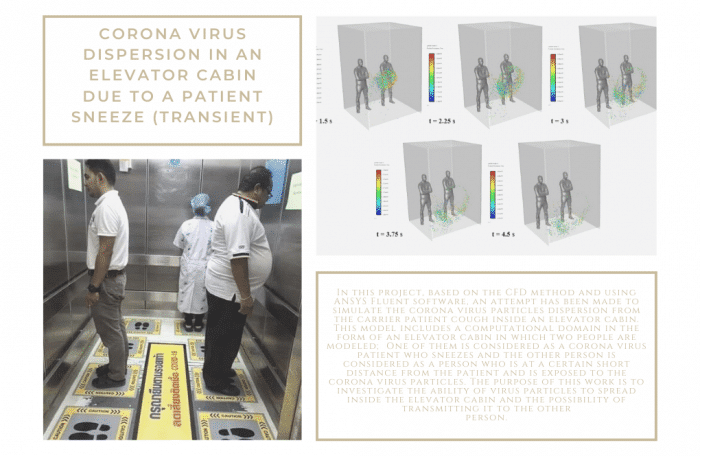
In project number 6, based on the CFD method, an attempt has been made to simulate the coronavirus particles dispersion from the carrier patient sneeze inside an elevator cabin. This model includes a computational domain in the form of an elevator cabin in which two humans are modeled; One of them is considered a coronavirus patient who coughs or sneezes and the other person is considered a person who is at a certain distance from the patient and is exposed to the coronavirus particles (Social Distance). In project number 7, based on the CFD method, an attempt has been made to simulate the release of virus particles from the mouth of a corona carrier patient inside a car. The purpose of this study is to investigate the diffusion power of virus particles inside the car interior. For the present simulation, the discrete phase model (DPM) is used.
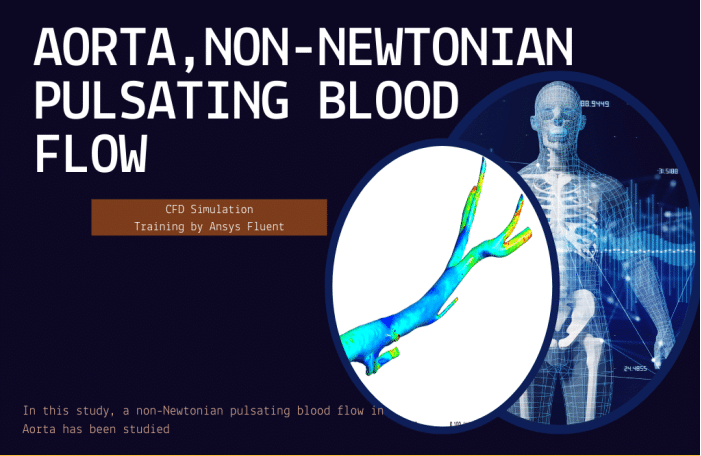
Blood Flow (Biomedical)
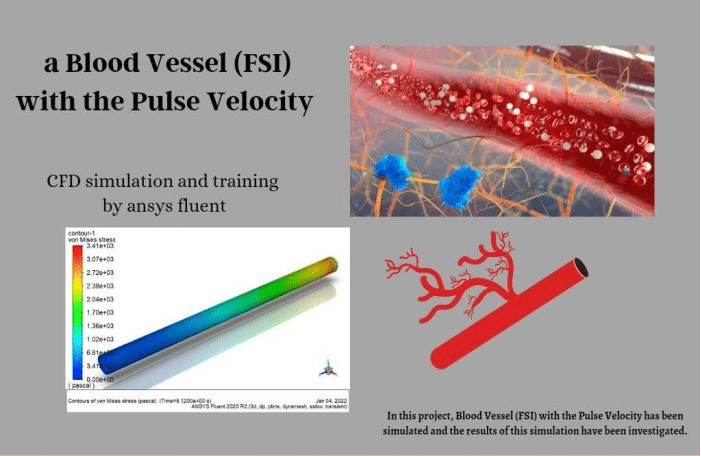
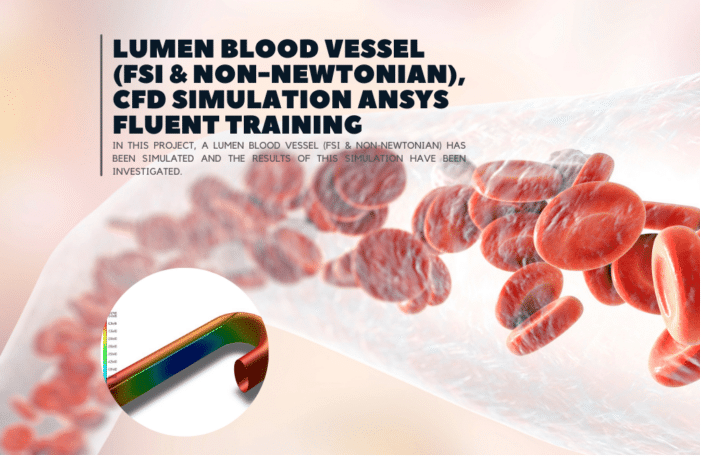
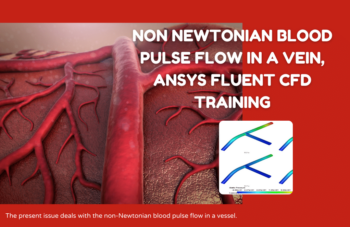
In study number 8, a non-Newtonian pulsating blood flow in Aorta has been studied. A UDF defines the pulsatile inlet velocity. A non-Newtonian fluid is a fluid that does not follow Newton’s law of viscosity, i.e., constant viscosity independent of stress. In project number 9, a blood vessel is simulated with a wall, where the displacement of the wall is also visible. We have defined the pulse velocity using UDF for the input, and the output is atmospheric pressure. This FSI simulation was performed inside the Fluent software. Finally, in project number 10, a Lumen Blood Vessel (FSI & Non-Newtonian) has been simulated. Also, the wall displacement is considered. For the inlet boundary condition, We have defined the pulse velocity using UDF, and for the outlet, the pulse output pressure is defined using UDF.
Related products
-
Non Newtonian Blood Pulse Flow in a Vein, ANSYS Fluent CFD Training
Rated 4.75 out of 5$122.00 Student Discount






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.