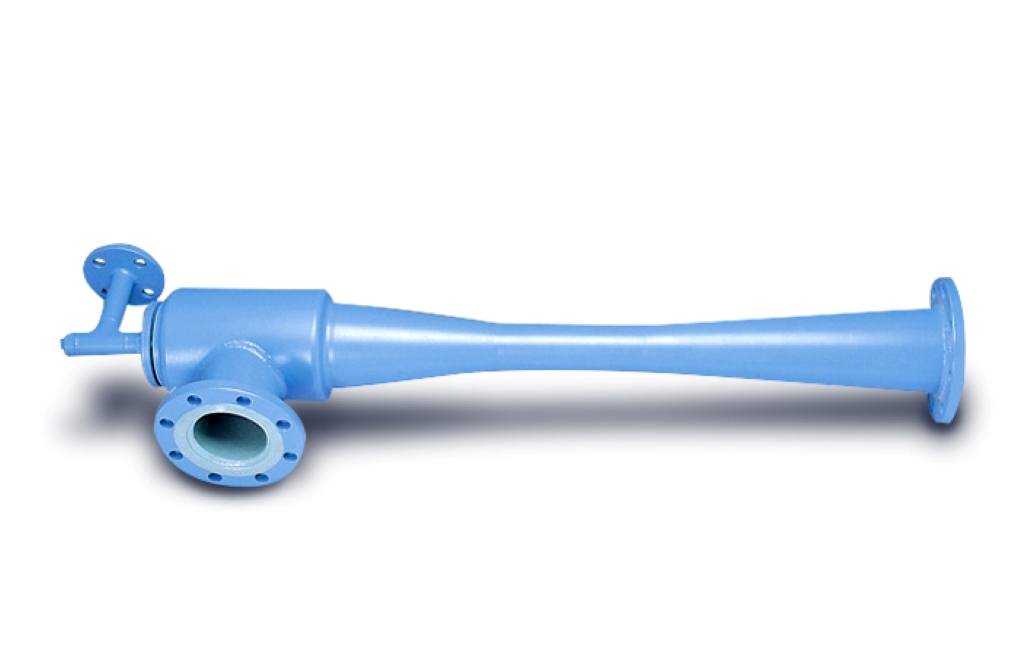
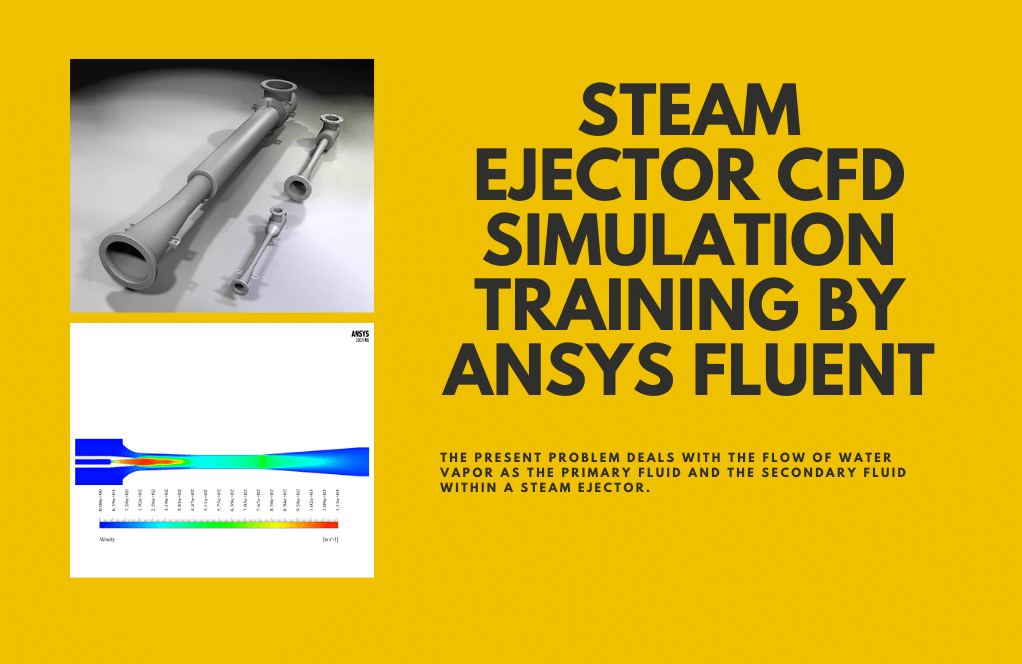
Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial
$100.00 Student Discount
- The present problem deals with the flow of water vapor as the primary fluid and the secondary fluid within a steam ejector by ANSYS Fluent software.
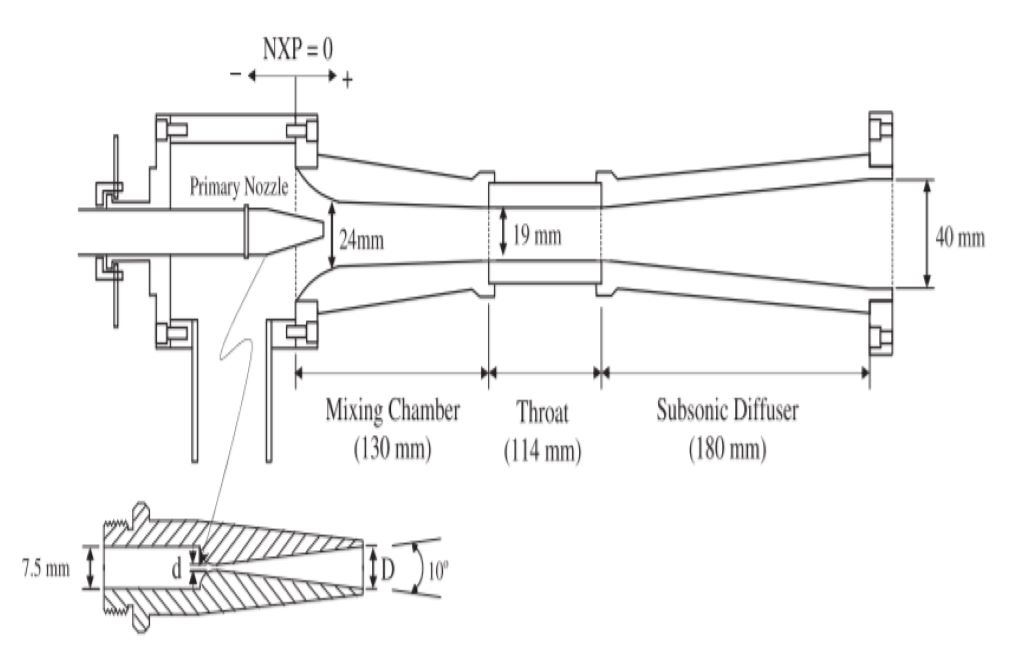
- We design the present 2-D model by the Design Modeler software.
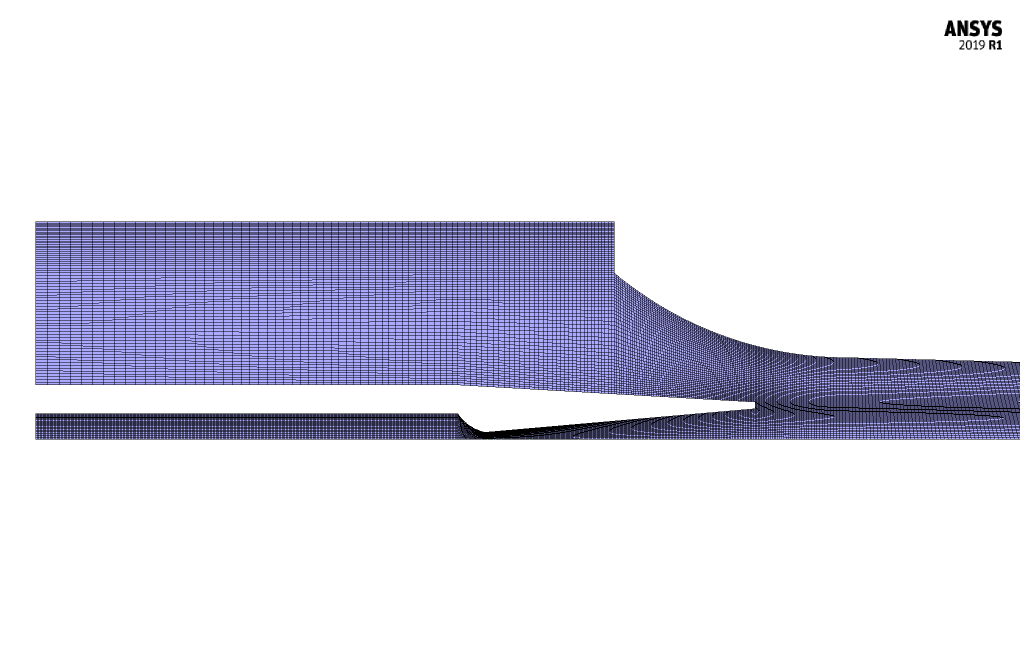
- Meshing was performed by ANSYS Meshing software. The mesh type is structured, and the element number equals 51990.
- We have used a density-based solver due to the compressibility in this project.
Click on Add To Cart and obtain the Geometry file, Mesh file, and a Comprehensive ANSYS Fluent Training Video.
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Steam Ejector Project Description
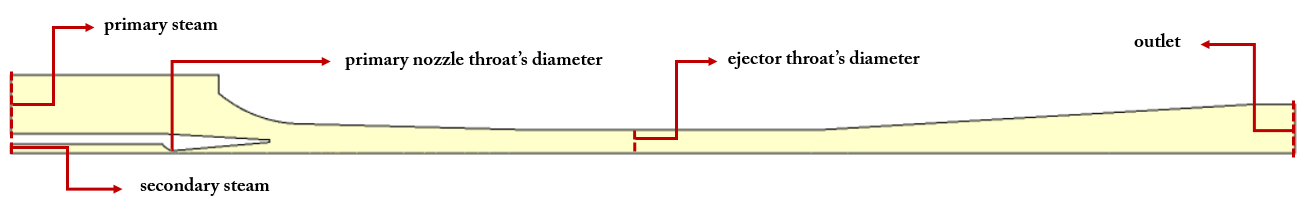
The steam ejector is a mechanical device that uses a primary (motive) fluid to suck up a secondary fluid (gas, liquid, or solid particles). Eventually, the ejector mix the two primary and secondary fluids and they exit from the outlet. Ejectors have two major tasks, including creating vacuum and gas suction and fluid mixing.
The basis of the ejector is to create a vacuum for the suction of the desired fluid (such as powder, granule, sludge, etc.) based on the continuous conversion of kinetic and pressure energy. The present problem deals with the flow of water vapor as the main fluid (primary) and the secondary fluid (suction) within a convergent-divergent steam ejector.
The present simulation aims to investigate the behavior of primary and secondary fluid after passing through the internal including creating vacuum and gas suction and fluid mixing and the steam ejector diffuser. In the present model, due to the vacuum pressure difference between the two inlet fluids, the suction phenomenon for the secondary fluid has to occur.
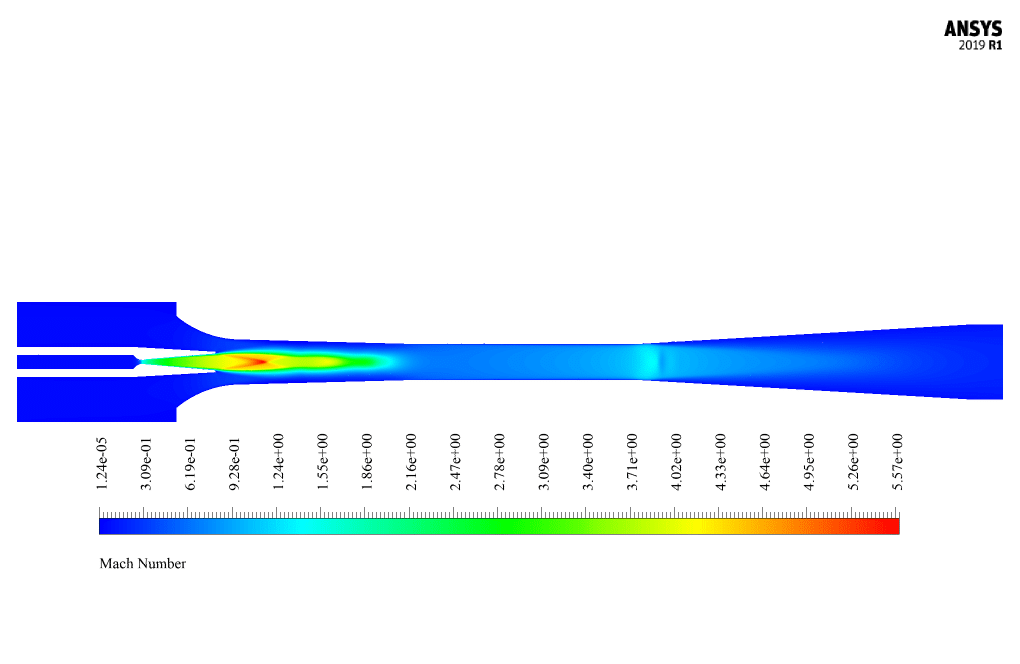
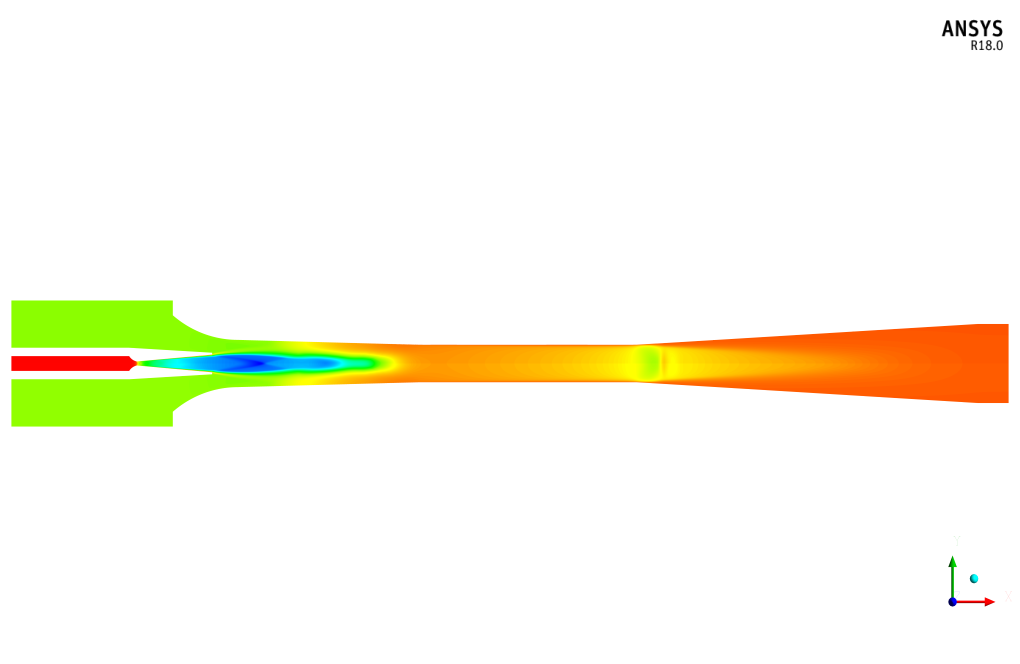
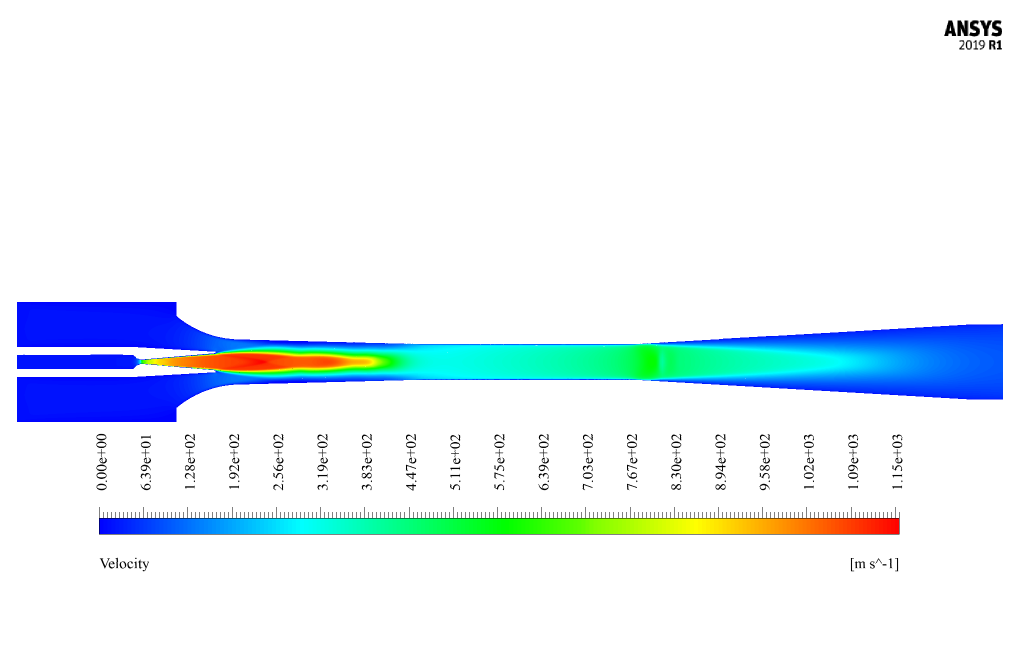
The Mach number corresponding to the fluid flow inside the ejector also increases. To analyze this model, we investigate parameters such as Mach number, velocity, and pressure based on the motion of the fluid flow along with the steam ejector.
We design the present 2-D model by the Design Modeler software. We perform the meshing by ANSYS Meshing software. The mesh type is structure. The element number equals 51990.
Methodology
We have used a density-based solver due to the compressibility in this project.
Steam Ejector Conclusion
At the end of the solution process, we obtain contours of pressure, velocity, and Mach number. The present model uses a convergent-divergent nozzle to drive the fluid. The fluid velocity significantly increased so that the fluid velocity exceeds the velocity of sound within the fluid.
The actuator fluid and the secondary fluid then mix and compress.

Monroe Nitzsche –
How accurate are the performance predictions from your steam ejector simulation?
MR CFD Support –
Our steam ejector simulation is designed to provide highly accurate performance predictions. We use advanced meshing techniques and robust solvers to ensure the reliability of our results.
Melisa Waelchi –
How does your simulation account for the effects of heat transfer on the performance of the steam ejector?
MR CFD Support –
Our simulation includes heat transfer effects by solving the energy equation along with the fluid flow equations. This allows us to accurately capture the effects of heat transfer on the performance of the steam ejector.
Mr. Osborne Gusikowski II –
Hi, with the help of this tutorial, I was able to simulate most of the CFD issues I was dealing with. Thanks to MR-CFD.
Rose Langosh –
How does your simulation model the complex flow phenomena inside a steam ejector?
MR CFD Support –
Our simulation uses advanced CFD techniques to model the complex flow phenomena inside a steam ejector. This includes modeling the interaction between the primary (high-pressure) and secondary (low-pressure) steam flows, as well as the resulting mixing and condensation processes.
Felicia Welch –
This tutorial was incredibly informative. The explanation of how ejectors work, along with the integration of practical examples into the tutorial, was helpful. Seeing the results, especially the Mach number contour, helped me understand the performance of steam ejectors better.
MR CFD Support –
We are thrilled to hear that our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial was both educational and practical for you. Understanding complex mechanical devices like ejectors can be challenging, and we’re glad that our tutorial made the concept clearer. Stay tuned for more practical and informative tutorials from our team!
Leon Kertzmann MD –
This course helped me understand steam ejectors thoroughly! The increased understanding of Mach number, velocity, and pressure behavior in the system is invaluable. Thank you MR CFD for such an informative tutorial.
MR CFD Support –
We’re overjoyed to hear that you found our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial helpful! Understanding the complex behaviors of fluid dynamics within mechanical devices is essential, and we’re glad we could contribute to your learning experience. Thank you for choosing MR CFD, and we look forward to providing you with more comprehensive and informative tutorials in the future!
Chance Bogan –
This tutorial helped me to fully understand how a steam ejector works. The contours of pressure, velocity, and Mach number were particularly informative.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are delighted to hear our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial provided you with a clear understanding of the mechanics and fluid dynamics involved in a steam ejector’s operation. If you have more questions or need further assistance with CFD simulations, please feel free to reach out.
Lennie Ryan –
I’m impressed by how the steam ejector system creates a vacuum for suction—it seems quite efficient! Are the simulations detailed enough to help in improving real-world ejectors design too?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! Yes, the simulations are specifically crafted to provide insights for improving real-world steam ejector designs. They help in understanding the flow dynamics, allowing engineers to optimize performance, efficiency, and structural properties of actual ejector systems.
Daisy Beatty –
I loved going through the Steam Ejector CFD Simulation tutorial! The step-by-step guidance made the process clear and taught me a lot about density-based solvers and Mach number behavior in ejectors. Thanks for creating such an informative and easy-to-understand resource!
MR CFD Support –
We appreciate your positive feedback and are thrilled to hear that our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial was helpful to you. Thank you for acknowledging our efforts to create a clear and informative learning resource. If you have any further questions or need assistance with other simulations, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
Clifton Gerhold –
I’m thrilled with how the steam ejector simulation turned out. It’s incredibly detailed and provides thorough insights into the behavior of primary and secondary fluids, which is vital for my research. I’m impressed by the clarity of the contours and the accuracy of the produced vacuum and mixing processes!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re glad to hear that the simulation exceeded your expectations and provided the detailed information you needed for your research. If you have any further queries or require additional support, feel free to reach out.
Dr. Elaina Koch –
I’ve gone through the steam ejector tutorial and found it to be very detailed. The step-by-step approach with the 2-D model made understanding the complex phenomena of vacuum creation and fluid mixing a breeze. I especially appreciate the inclusion of Mach number analysis—it was fascinating to see how the velocity of the fluid exceeded the speed of sound through the device.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are thrilled to hear that our tutorial on the steam ejector was helpful and that the details provided met your learning needs. Understanding such complex fluid dynamics concepts is definitely challenging, and we’re glad that our explanations, especially regarding the Mach number analysis, enhanced your comprehension. If you have any more questions or need further assistance with your simulations, feel free to reach out to our support team.
Miss Lydia Schuppe PhD –
I had a final project. It helped me.
Thank you very much.
Edna Waelchi –
I’m impressed with the detailed analysis and outcome of the Steam Ejector simulation. The understanding of such complex flow dynamics using ANSYS Fluent is quite remarkable. Great tutorial!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for taking the time to provide feedback on our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial. We’re delighted to hear that you found the tutorial informative and impressive in terms of demonstrating the complex flow dynamics. Stay tuned for more such detailed tutorials!
Henri Lubowitz –
I found the real-world application of the ejector system very interesting. Could you provide more insights into where steam ejectors are primarily used in industry applications?
MR CFD Support –
Steam ejectors are commonly used in several industrial applications, such as chemical processing, power plants, refrigeration systems, and vacuum distillation processes, to create vacuum and evacuate gases. They are also valuable in industries handling gas suction and mixing fluids, like in the petrochemical or the pharmaceutical sector, for example, for venting reactors or transferring materials.
Presley Kunde Jr. –
This is such a detailed tutorial! I really appreciate how the steam ejector mechanism is thoroughly explained and how the simulation covers all essential aspects of fluid behavior in the ejector, including velocity, Mach number, and pressure. I learned a lot about the conversion of kinetic and pressure energy to create a vacuum, as well as the significant increase in fluid velocity within the ejector. The structured methodology definitely made it easier to grasp complex concepts, and the 51990 elements illustrations provided a crystal-clear understanding of the mixing and compressing process of the fluids. Great job on the tutorial!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback on the Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial! We’re delighted to know that you found it detailed and educational. Our team works hard to ensure that our tutorials cover all critical aspects of the simulation process and are easy to understand. Your appreciation truly motivates us to continue creating high-quality learning materials. If you have any more questions or need further clarification on any topics, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
Jeromy Kiehn –
I’m impressed with the level of detail in the steam ejector simulation! But I was wondering, what kind of applications can benefit from using this type of simulation analysis?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your compliment on our steam ejector simulation! This type of simulation analysis can benefit a variety of applications including, but not limited to, chemical processing, oil and gas industries, refrigeration and air conditioning, power plants, and wastewater treatment facilities. It is particularly useful in any process which requires the creation of a vacuum, gas suction, or the efficient mixing of two different fluids. The insights gained from such simulations can optimize the design and operation of ejectors for specific industrial needs.
Garrett Williamson –
I was fascinated by the way you incorporated both primary and secondary fluids in the steam ejector design. I wonder if adjusting the inlet velocities could lead to different suction efficiencies?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your insightful comment. Adjusting the inlet velocities of both primary and secondary fluids can indeed result in different efficiencies for the suction process. Variations can greatly affect the fluid dynamics within the ejector and hence the overall performance of creating a vacuum and fluid mixing.
Ron Stamm –
I just completed the Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial. I was thoroughly impressed by how detailed the process was and how easy the tutorial made it to understand topics like creating a vacuum and fluid mixing with steam ejectors. The structured progression through such a complex phenomenon with clear goals like analyzing Mach number and pressure changes truly enhanced my grasp of the concepts. Wonderful learning resource!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that our tutorial on Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD was helpful and that you found the instructions clear and informative. It’s great to hear that it enhanced your understanding of the CFD principles involved in the process. If you have any more questions or need further assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out.
Mrs. Mable Kassulke DDS –
I’m particularly impressed by the mesh complexity and the use of a density-based solver. Do you often need a structured mesh for this kind of simulation, and if so, why?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your review! Yes, using a structured mesh is typical for this type of simulation because it provides a high level of control over mesh distribution. This is especially useful for capturing the gradient changes that occur in high-speed, compressible flows often seen in steam ejector simulations. The structured mesh ensures accurate representation of the flow characteristics, crucial for predicting the performance of the ejector and analyzing parameters such as Mach number, velocity, and pressure.
Nestor Kuhic –
I’m quite impressed with the detailed explanation of the steam ejector simulation process! Could you tell me how the mixing of the primary and secondary fluids was visualized in the simulation?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! In the simulation, the mixing process of the primary and secondary fluids is visualized using detailed velocity and Mach number contours. These contours show how the streams interact and combine along the length of the ejector, providing a comprehensive understanding of the mixing dynamics. Additionally, pressure contours help visualize the behavior of the fluids, especially where the vacuum is created and the suction effect occurs.
Herminia O’Kon –
This tutorial indeed did a fantastic job explaining steam ejectors. The visuals and step-by-step instructions were particularly helpful for visualizing the process.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear you found the tutorial on steam ejectors helpful and easy to follow. We always strive to provide clear and informative content, and your comments reaffirm the work we are doing. If you have any further questions or need additional assistance with the subject, please don’t hesitate to reach out!
Martina Littel –
The tutorial on Steam Ejector CFD Simulation was excellent! I altogether appreciated the effective explanation of each step of the process and the detailed investigation of fluid interactions. Can’t wait to apply these concepts to my project. Special thanks for the clear insights on the vacuum creation and fluid mixing mechanics – it made complex concepts much easier to grasp. Well done!
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear that you found the Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial so helpful and informative! It’s fantastic that the tutorial could clarify complex topics for you. Your enthusiasm for applying what you’ve learned to your project is the best feedback we could hope for. Thank you so much for taking the time to share your positive experience. If you ever have more questions or need further assistance during your project, feel free to reach out. Your success is our success!
Vanessa Braun –
I followed the tutorial for the steam ejector CFD simulation and I am quite impressed with the clarity of instructions. The part where the vacuum effects were shown through Mach number variations was particularly engaging. Can you suggest any additional tutorials that might help deepen my understanding of the simulation of ejectors or similar devices with phase changes like refrigeration cycles?
MR CFD Support –
We’re very glad to hear that you found the tutorial helpful and engaging. For further learning, you might want to look at tutorials that cover refrigeration cycle simulations or other equipment related to phase change phenomenons in ANSYS Fluent. These typically involve tutorials focused on modeling and simulation of vapor compression refrigeration systems, or the study of multi-phase flows within different components like condensers or evaporators. Make sure to check our tutorial section for up-to-date and comprehensive learning materials that can further enhance your CFD skills.
Lora Lowe –
This tutorial was incredibly detailed and well-structured. Seeing the behavior of both primary and secondary fluids in this steam ejector CFD simulation bring theories to life. The vacuum and gas suction phenomena were particularly fascinating to observe and the clear representation of Mach number changes within the ejector was educational. Excellent work on demonstrating fluid mixing and compression!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words and positive feedback on our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial! We are glad that you found the tutorial detailed and educational. It’s wonderful to hear that the phenomena of vacuum creation, gas suction, and fluid mixing were clearly presented and helped bring complex theories to reality. Our team strives to produce high-quality learning materials, and your observation confirms the effectiveness of our approach. If you have any more inquiries or need further assistance with CFD simulations, please reach out. Thank you again for your review!
Santa Lind –
I was absolutely amazed by the level of detail that the Steam Ejector CFD Simulation tutorial provided! The step-by-step approach and comprehensive explanation of the methodology made it so much easier to understand and follow through the entire process.
MR CFD Support –
We are thrilled to hear that the tutorial was helpful and clear for you! It’s wonderful to know that the content met your expectations and aided you in your understanding. Thank you for taking the time to share your positive experience with us. We appreciate your feedback and look forward to continuing to assist you with your CFD learning journey!
Dr. Marisa Turcotte IV –
The tutorial was incredibly detailed and easy to follow. Thanks to the clear steps, I was able to understand the ejector’s operation and simulate the vacuum creation and fluid mixing effectively.
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear that our tutorial was helpful to you! Understanding the complex dynamics of a steam ejector can be challenging, but we’re glad our step-by-step guidance made the process understandable. Thank you for your feedback, and we wish you success in your future simulations!
Magdalena Kertzmann Jr. –
The tutorial you provided was really useful in understanding the concept and application of steam ejectors. The step-by-step instructions made it much easier to follow along and set up the CFD simulation. Plus, the explanation of the Mach number’s role and how the fluids mix was enlightening. Great job!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are thrilled to hear that our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD simulation tutorial was helpful and easy to follow. Your understanding of the Mach number and fluid dynamics is exactly what we aim to facilitate with our learning materials. If you have any more questions or need further assistance with CFD simulations, please don’t hesitate to reach out!
Quinten Williamson DVM –
I had a blast going through the ‘Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial’. The visualization of the fluid flows and understanding the pressure dynamics really augmented my grasp of steam ejector functions. It was particularly satisfying to see the Mach number changes as fluid velocities approached and exceeded the speed of sound. Cheers for such a comprehensive learning tool!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the fantastic feedback! It’s great to hear that the tutorial enhanced your understanding of steam ejector mechanics and the fluid dynamics involved. We’re delighted that our efforts to provide comprehensive learning resources are appreciated and helpful to our customers.
Dillon Howe –
This steam ejector tutorial was concise yet packed with practical info. I was able to understand the function and simulation process quite easily. Kinetic and pressure energy conversions were well-explained!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are thrilled to hear that you found the tutorial on steam Ejector especially insightful and that it helped clarify the conversion concepts of kinetic and pressure energy. If you delve into any other projects or need further guidance, don’t hesitate to reach out to us or explore more of our tutorials!
Joanny Harvey –
I found the tutorial for the Steam Ejector to be informative and well-structured, especially the detailed analysis of Mach number and velocity changes throughout the steam ejector.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad you found the tutorial informative and well-structured. We strive to provide comprehensive content to help our users understand CFD concepts better.
Hannah Heidenreich –
Your tutorial for the steam ejector simulation was straightforward. Seeing the Mach number and velocity contour visualizations really made the fluid dynamics concepts click for me.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words. We’re glad to hear that the visualizations in the steam ejector tutorial were helpful for you and contributed to your understanding of fluid dynamics. We strive to provide clear and well-explained simulations and are always pleased to know when our efforts resonate with our users.
Yazmin Heaney –
The results in this CFD simulation of a steam ejector are fascinating. I’m impressed by the detailed analysis of parameters such as Mach number and how you can visualize fluid behavior, vacuum creation, and mixing efficiency. Excellent work!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to hear that the detailed analysis and visualization in the steam ejector CFD simulation were helpful. It’s rewarding to know that the effort put into explaining the behavior of the fluids and their interaction in the ejector was appreciated. If you have any further questions or need additional information on our products, feel free to ask.
Dr. Mikel Bashirian DDS –
This tutorial sounds very informative on the workings of steam ejectors. The detail about creating vacuum pressure is particularly helpful.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re glad you found our tutorial on steam ejectors helpful and informative, particularly the part about creating vacuum pressure. If you have any further inquiries or need more assistance with our tutorials, please feel free to reach out.
Justen Bechtelar –
I really enjoyed going through the Steam Ejector tutorial. The step-by-step explanation made complex fluid dynamics concepts much easier to understand and relate to. It’s great to see both vacuum creation and fluid mixing in action, and observing how changes in Mach number, velocity, and pressure affect the overall behavior of the fluid flow. Kudos to MR CFD for putting together a comprehensive and user-friendly learning resource.
MR CFD Support –
We’re glad to hear that our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial was helpful to you! It’s wonderful to know that you found the step-by-step guidance clear and valuable for understanding fluid dynamics concepts. Thank you for your positive feedback, and we look forward to providing you with more educational materials that aid in learning and development. If you have any more questions or need further tutorials, feel free to reach out!
Prof. Austin Rogahn III –
Extremely detailed and informative tutorial! I was especially impressed by the clarity on the mechanisms behind vacuum creation and fluid mixing in the steam ejector context. The parameters analyzed provided deep insights into the working process.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re glad to hear that you found the steam ejector tutorial both informative and useful. Your feedback motivates us to continue producing high-quality, detailed tutorials for our users. If you have any further questions or need assistance with CFD simulations, don’t hesitate to reach out!
Dr. Ruthie Ruecker –
The tutorial was super helpful for understanding the operation of steam ejectors in CFD environments! The visuals and step-by-step instructions made complex concepts easy to grasp.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re delighted that our tutorial on Steam Ejector CFD Simulation was informative and easy to understand. It’s always encouraging to hear that our efforts to create clear and effective learning materials are appreciated. If you ever have more questions or need further guidance, don’t hesitate to reach out!
Marquise Emmerich PhD –
I’m impressed by how the steam ejector simulation captures the behavior of the fluids in creating a vacuum and mixing. It shows the power of using CFD tools to understand complex engineering devices.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re thrilled that our CFD simulation tutorial for the steam ejector was able to provide you with valuable insights into fluid behavior and the mechanics of vacuum creation and mixing. It’s great to hear that it impressed you, and we hope it has been a beneficial learning experience.
Julio Pacocha IV –
I am impressed with the visuals on the Mach number and velocity contours in the Steam Ejector simulation! It really helped understand fluid behavior within the ejector.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our simulation visuals aided your understanding of the ejector’s fluid dynamics. Your satisfaction with our educational material is a top priority for us, and we love knowing that it’s making a difference. If there’s anything more we can do to enhance your learning experience, please let us know!
Adrianna McLaughlin –
I really appreciated the detailed explanation of the ejector’s tasks and the physics behind its operation. The step-by-step methodology, complemented by clear visuals in the tutorial, greatly helped in understanding the complex flow dynamics within the ejector.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to hear that the tutorial was helpful and the visuals clarified the complex flow dynamics of the steam ejector for you. If you have further questions or need assistance with similar projects, don’t hesitate to reach out to us.
Miss Mina Parisian –
My compliments to the team at MR CFD for the comprehensive tutorial on the steam ejector CFD simulation! The step-by-step explanation provided a crystal-clear understanding of the complex interaction between primary and secondary fluids. Your meticulous attention to detail in the methodology ensures a thorough grasp of kinetic and pressure energy conversion in this device. Hands down, one of the best learning experiences!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that the tutorial on the steam ejector CFD simulation was helpful and provided you with a clear understanding of the dynamics at play. At MR CFD, we strive to offer detailed and comprehensive training that enables our users to undertake complex simulations with confidence. Your feedback is greatly appreciated, and we look forward to offering you more valuable learning experiences in the future!
Prof. Richie Lueilwitz MD –
I thoroughly enjoyed the tutorial on the Steam Ejector simulation in ANSYS Fluent. The explanations and visuals were clear and concise, which allowed me to understand the fluid dynamics involved in steam ejectors. The part where both the primary and secondary fluids mix was particularly interesting to me. Great job on showcasing the vacuum creation and the changes in Mach number through the system.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our Steam Ejector tutorial met your expectations and that the mixing of primary and secondary fluids aspect was of particular interest to you. It’s our goal to provide clear and informative content to help our users understand complex fluid dynamics concepts. Thank you for taking the time to review our product – your support motivates us to continue delivering quality educational resources!
Dr. Theron Brown PhD –
The steam ejector tutorial was superbly detailed. Seeing the pressure and velocity contours really helped me understand the dynamics at play. I was particularly impressed with how the simulation captured the fluid mixing!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad that the pressure and velocity contours enhanced your understanding of the steam ejector’s fluid dynamics, and that you appreciated the detail in our tutorial. If you have any further questions or need more information, feel free to ask. Happy learning!
Rosalind Barrows –
What a great learning tool! The CFD simulation’s integration of complex concepts such as vacuum creation, fluid mixing, and Mach number analysis was really informative, especially with the structured approach to teaching about steam ejectors.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your appreciation and taking the time to highlight the key concepts covered in our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial. We’re delighted to hear that you found it informative and helpful!
Mr. Kayden Gorczany V –
I really appreciated how the tutorial explained the ejector’s vacuum creation and fluid mixing. The step-by-step details for setting up and analyzing the parameters were very insightful.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive review! We’re delighted to hear that our tutorial on Steam Ejector CFD Simulation was informative and helpful for you.
Dr. Elfrieda Wuckert –
What a great learning tool! The ANSYS Fluent tutorial for the steam ejector made the concept so much clearer. Seeing the whole process—including creating the model, meshing, and interpreting the results—was very helpful for understanding ejectors and their fluid dynamics.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re thrilled the Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial was helpful for you. Understanding the dynamic behaviors and intricate work of an ejector system can be complex, and we are glad the tutorial made the learning process clear and accessible. If you have any further feedback or require more tutorials, feel free to let us know. Your continued learning is important to us!
Kennith Lebsack I –
Fantastic learning tool! I was able to understand the steam ejector principles and simulate accordingly. The tutorials were clear and insights from the contour plots were very helpful for my project.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our tutorial on steam ejector simulation in ANSYS Fluent was helpful and clear. It’s great to know that the contour plots provided valuable insights for your project. If you need further assistance or more tutorials, don’t hesitate to contact us. We’re here to help!
Carmine Stark –
I’m really impressed with how the steam ejector simulation captures the fluid mixing and vacuum creation—excellent work demonstrating complex fluid dynamics!
MR CFD Support –
We’re so thrilled to hear that you appreciate the capabilities of our steam ejector simulation! We strive to create highly detailed and accurate simulations to help users like you understand complex fluid dynamics. Thank you for your positive feedback—it means a lot to us!
Nikki Murphy I –
The tutorial really helped me to understand how steam ejectors work. Your explanation made the concept of kinetic and pressure energy conversion very clear. Thanks!
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear that our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial was helpful to you! Understanding the principles of kinetic and pressure energy conversion is essential for mastering this topic, and we’re glad we could make it clear. Thank you for your kind words and for choosing our tutorial!
Andre Mitchell –
The tutorial for the Steam Ejector in ANSYS Fluent was incredibly helpful. The step-by-step guide helped me understand the entire process from setting up the problem to analyzing the results. It was fascinating to see how you managed to capture the behavior of the primary and secondary fluids within the ejector through the use of a density-based solver. It totally clarified the concepts of Mach number, velocity, and pressure changes within the system.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are pleased to hear that our tutorial was clear and understandable, and that it helped you grasp the complex fluid dynamics within the steam ejector simulation. Please reach out if you have any more questions or if there is another topic you would like us to cover.
German Osinski –
Can your simulation predict the performance of the steam ejector under different operating conditions?
MR CFD Support –
Yes, our simulation can predict the performance of the steam ejector under different operating conditions. You can adjust parameters such as steam pressure and temperature to study their effects on ejector performance.
Prof. Bonnie Funk –
I learned a lot from the Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent tutorial! The explanations on vacuum creation and fluid flow behavior were insightful. Really appreciated the sections on Mach number analysis and fluid mixing.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your review! We’re delighted to hear that our tutorial on the Steam Ejector was helpful and provided you with a clear understanding of vacuum creation, Mach number, and fluid dynamics. It’s great to know that the content was insightful and appreciated. If you need further assistance or have any more queries, please feel free to contact us.
Kiel Williamson –
The tutorial was really well explained. I learned a lot about setting up simulations for ejectors and controlling their parameters to create a realistic representation of fluid behavior in such systems.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you very much for your kind words! We’re glad to hear that our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial was helpful and clear. It’s great to know that you have gained valuable knowledge about simulating ejectors. If you have any more feedback or need further assistance, feel free to contact us.
Colton Spinka –
Fantastic learning material! It clarified many details about steam ejector simulations and the understanding of compressible flows. The visuals were really helpful.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! It’s great to hear that our tutorial on Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent simulation was informative and that the provided visuals aided your understanding. We are committed to delivering quality educational content, and it pleases us to know it’s making an impact. If you have any more questions or need further assistance in your learning journey, please do not hesitate to reach out.
Roderick Oberbrunner –
The tutorial for the steam ejector CFD simulation was very informative. It helped me understand the complex fluid dynamics involved. The visual data on pressure, velocity, and Mach number clarified many concepts for me!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re thrilled the tutorial was helpful and that the visuals enhanced your understanding of the steam ejector simulation. Please reach out if you have any more questions.
Prof. Abby Sauer MD –
The tutorial was really comprehensive and provided a thorough understanding of the steam ejector simulation. I’m impressed with the clarity of the instructions and the detail in the methodology section.
MR CFD Support –
We appreciate your positive feedback! It’s great to hear that our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial was clear and valuable to you. Thank you for taking the time to compliment our product.
Miss Madaline Wolff I –
I’m really impressed with the detailed results on Mach number and fluid velocities in the steam ejector. It has provided insightful data into the performance of the ejector.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback on the steam ejector simulation tutorial. We are delighted to hear that you found the data on Mach number and fluid velocities insightful and that it has enhanced your understanding of the ejector’s performance.
Anthony Koss –
This simulation sounds quite complex. Could you explain how the secondary fluid suction mechanism is modeled within the steam ejector during the simulation?
MR CFD Support –
In the simulation for the steam ejector, the secondary fluid suction mechanism is modeled by setting the inlet boundary conditions in a way that represents a vacuum pressure difference between the primary and the secondary inlet fluids. This setting triggers the fluid suction because the higher pressure of the primary fluid entrains the secondary fluid into the steam ejector. The convergence-divergence structure of the ejector further facilitates this mechanism, boosting the primary fluid’s velocity to supersonic speeds and thereby creating the vacuum necessary for suction. All fluid interactions, including the mixing and compressing phases, are directly analyzed and interpreted through the resulting pressure, velocity, and Mach number contours obtained from the ANSYS Fluent simulation.
Terrell Schoen –
The tutorial was quite insightful! The way it handles the compressible flow dynamics in the steam ejector and the creation of a vacuum for suction was presented logically. It also excellently described how the ejector mixes primary and secondary fluids. A job well done!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear the tutorial on the steam ejector was helpful and that the complex flow dynamics were made clear. We appreciate your feedback and are glad you enjoyed using our learning product.
Moses Johnston MD –
I’m impressed with how the steam ejector’s functionality has been investigated in this simulation! It sounds like a comprehensive study combining vacuum creation and fluid dynamics.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to hear that you found our simulation on the steam ejector informative and comprehensive. It’s our goal to provide detailed and practical insights into fluid dynamics through our CFD simulations.
Alanna Carroll II –
I am so impressed with the way the steam ejector simulation showcases the mixing of two fluids. The detailed contours really helped me to visualize the process.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial was helpful and that the detailed contours provided clear visualization of the fluid mixing process. We appreciate your review and are glad that our product could exceed your expectations.
Prof. Giuseppe Altenwerth PhD –
I appreciate the thorough attention to detail in the tutorial for the Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation. The underlying physical principles were clearly explained, making it easier to understand the dynamics of the process. The step-by-step approach was particularly helpful in grasping the intricacies involved in setting up and solving the problem within ANSYS Fluent. An excellent learning aid for those studying ejectors and their applications!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that our tutorial provided a clear and detailed explanation of the Steam Ejector simulation within ANSYS Fluent. That the learning process was made easier through our step-by-step approach is exactly what we aim for. Should you have any questions or need further assistance in your learning journey, feel free to reach out!
Alfred Bailey –
I really appreciated the detailed explanation of steam ejectors in your tutorial. The images and step-by-step breakdown made it very easy to understand the concept of vacuum creation and fluid mixing within the device.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re glad to hear that our tutorial on the steam ejector and its CFD simulation was helpful and easy to understand. It’s our aim to provide detailed and clear explanations to assist our users in mastering the concepts of CFD analysis.
Misty Huel –
I found the step-by-step process of how the steam ejector works in the tutorial truly fascinating. Mixing two different fluids and creating a vacuum in such a precise way is incredible. The interplay of energy conversion and pressures producing high Mach numbers was well-demonstrated. One can learn a lot about CFD and nozzle design from this.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are delighted to hear that the tutorial was effective and informative. Understanding the mechanics and physics behind devices like steam ejectors is key to mastering CFD analyses. We’re glad we could provide you with detailed insights into nozzle design and fluid interactions. If there’s anything else you’re curious about, feel free to explore more of our tutorials and learning materials!
Karl Barrows –
I’ve always been fascinated by the functionality of steam ejectors and their applications. This tutorial seems comprehensive and quite beneficial for understanding the complex interactions within ejectors. I am looking forward to applying these insights to my own projects!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your review! We’re thrilled to hear that our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation Tutorial has provided valuable insights for you. It’s great to know that you’re keen on applying what you’ve learned to your projects. If you ever have any questions or require further guidance, do not hesitate to reach out. Best of luck with your endeavors!
Heidi O’Hara –
The clear explanations and visual representations of the fluid behavior in the steam ejector simulation are exceptional. It provided a comprehensive understanding of the vacuum creation and the mixing process.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are thrilled to hear that our tutorial on steam ejector CFD simulation was clear and helpful in visualizing the concepts involved. It’s always great to receive positive feedback. If you have any more questions or need further assistance, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
Prof. Jay Reilly Sr. –
Wow! The mastery in designing steam ejectors in this tutorial seems outstanding. I appreciate how the fluid behavior, including velocity and pressure changes, was effectively modeled and simulated. It certainly helps in understanding the practical applications of steam ejectors in various industries.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your compliments! We are glad to hear that our Steam Ejector ANSYS Fluent CFD Simulation tutorial has provided valuable insights and understanding of the fluid dynamics within ejectors. Your feedback is appreciated, and we hope our other learning products will continue to aid in your studies and industry applications.
Camden Howe –
I’m impressed by the complexity of this simulation and how the steam ejector behavior is captured. The investigation of Mach number and the fluid’s state transition shows thorough analysis in designing ejectors.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are pleased to know that you appreciate the depth of analysis conducted to capture the behavior of the steam ejector using CFD. Should you have any further inquiries or require additional information on the simulation process, don’t hesitate to contact us.