
DPM: Overview, Conceptions, Assumption, Governing equations and Limitations
DPM Abstract
In this article, We overview the concept of the discrete phase model, assumptions, governing equations, and some limitations of the model.
Overview of DPM
In fact, any flow consisting of two or more phases is called multiphase. From the analytical viewpoint, we should deal with each phase based on its specifics and conditions. It is estimated that wherever the volume fraction of a phase is below 10%, it is counted as a dispersed phase and can be tracked in a Lagrangian reference frame. Thus, the Discrete phase model (DPM) is prepared in ANSYS Fluent to separate governing equations of the phases in which the continuous and discrete phases are solved through the Eulerian and Lagrangian methods, respectively.
Discrete & Continuous phase coupling
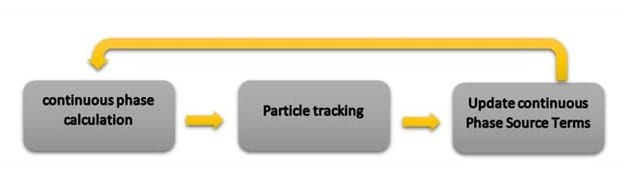
Generally, ANSYS Fluent can ignore the effect of the interaction of the particles with the continuous phase (1-way) or consider the interactions as well (2-way). There is also a supplementary sub-model in which the interactions between the particles are also taken into account (4-way).
When the volume fraction of the discrete phase is low, the continuous phase is dominant in motion. Thus, the impact of a dispersed phase can be ignored. It is called the one-way coupling method. For instance, the one-way coupling method is used in Fly Ash Cyclone project:
Fly Ash Cyclone
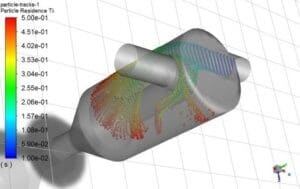
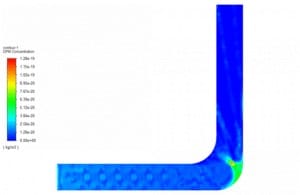
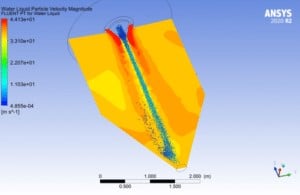
As the dispersed phase concentration increases, the dispersed phase motions can also affect the continuous phase flow. Thus, the one-way coupling method couldn’t satisfy the problem condition. In these cases, the two-way coupling method is the accurate one. As an example, see Particle Flow Inside the Elbow & Spray Drying Chamber projects:
Particle Flow Inside the Elbow, Simulation Using DPM
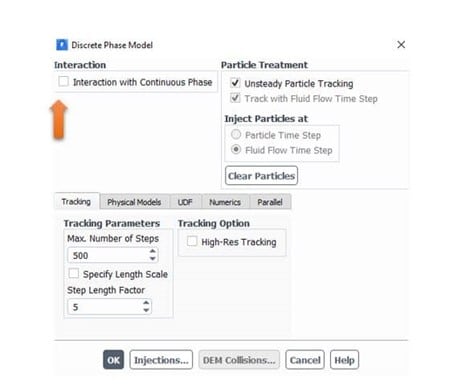
By the way, We can enable the 2-way model by the following option in the DPM panel:
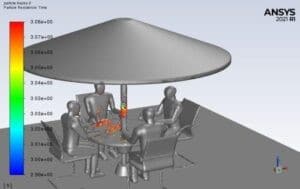
Human Cough Virus Particles in the Coffee Shop
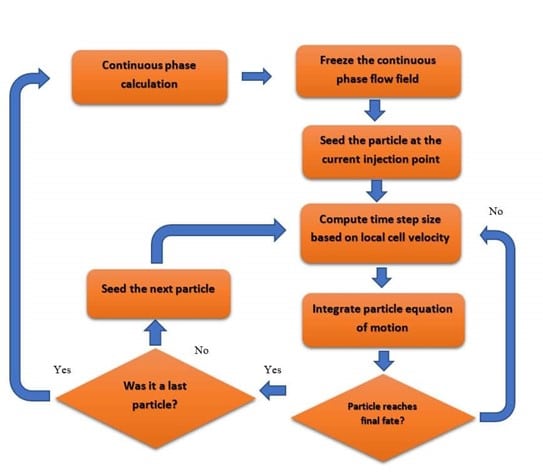
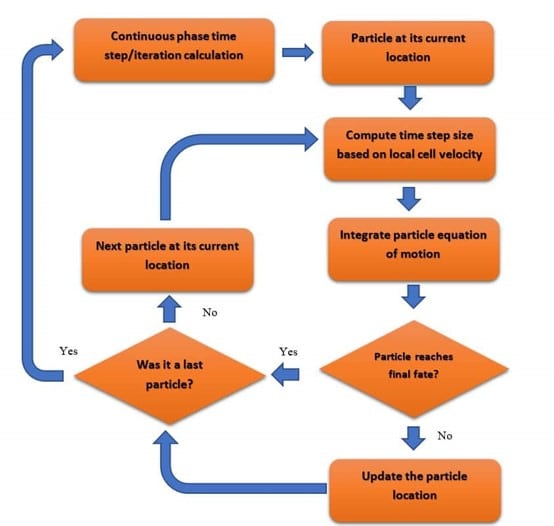
Trajectory Calculations
The governing equation is Based on Newton’s second law: (mp: particle mass, up: particle velocity, Fdrag: drag forces acting on a particle, Fgravitation: gravity force, Fother: other forces acting on a particle, including pressure gradient, Saffman, thermophoretic, virtual mass, Brownian, rotational forces )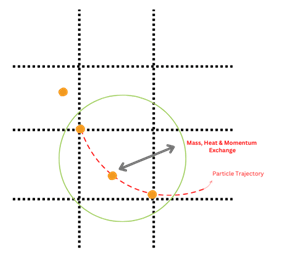
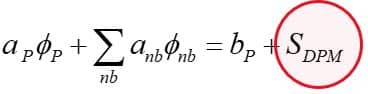
There are some assumptions in this model:
- The model simulates by solving transport equations for the continuous and discrete second phases in a Lagrangian frame of reference. Note that it is not always necessary to solve the continuous phase. In the following tutorial, we only solve the secondary phase:
- The volume fraction of particles is estimated to be less than 10% in each cell. Thus, there are limitations in grid size. If the grids become too small, the DPM model gets grid dependent and needs to be studied.
- By default, although there are sub-models, the second phase is considered to consist of spherical particles.
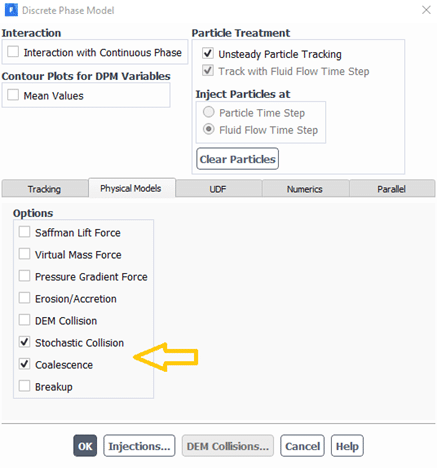
- By default, the interactions between particles are ignored. It can be considered by activating the Stochastic collision/coalescence sub-model.

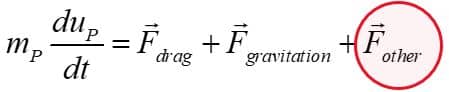




This Post Has 0 Comments