Mechanical Engineering Training Package, Beginners, Part 2, 10 Exercises
Original price was: $981.00.$327.00Current price is: $327.00. Student Discount
This product includes Geometry & Mesh file and a comprehensive Training Movie.
There are some free products to check our service quality.
To order your ANSYS Fluent project (CFD simulation and training), contact our experts via [email protected], online support, or WhatsApp.
Click on Add To Cart and obtain the Geometry file, Mesh file, and a Comprehensive ANSYS Fluent Training Video.To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Mechanical Engineering – ANSYS Fluent Training Package, 10 Practical Exercises for BEGINNER Users (Part 2)
There are 10 practical exercises in this training package by ANSYS Fluent software for Mechanical Engineers. This package presents how to simulate different mechanical devices for all BEGINNER users.
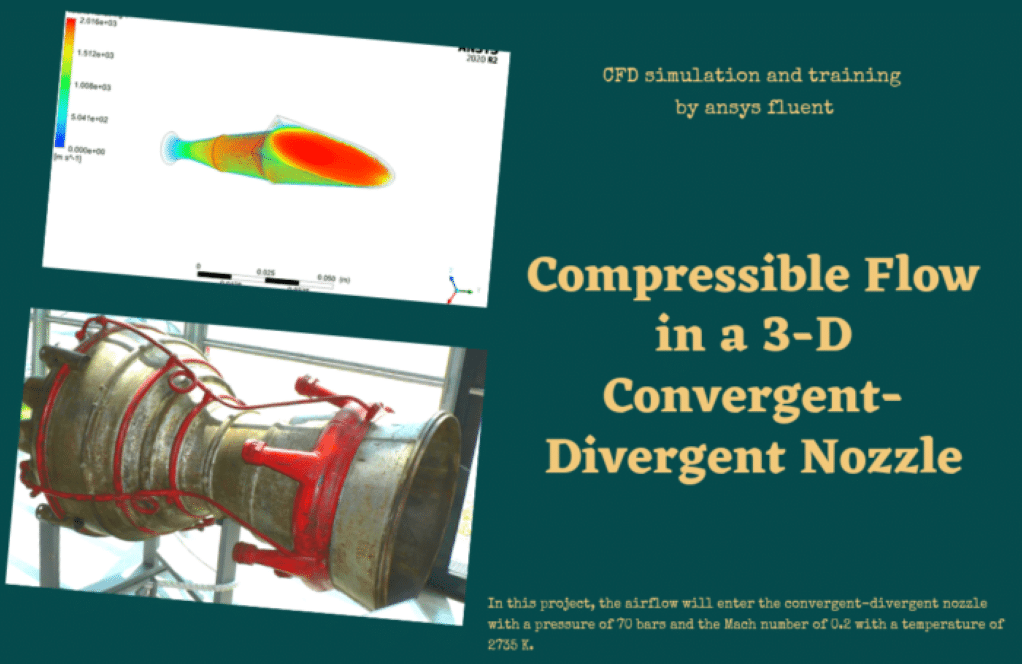
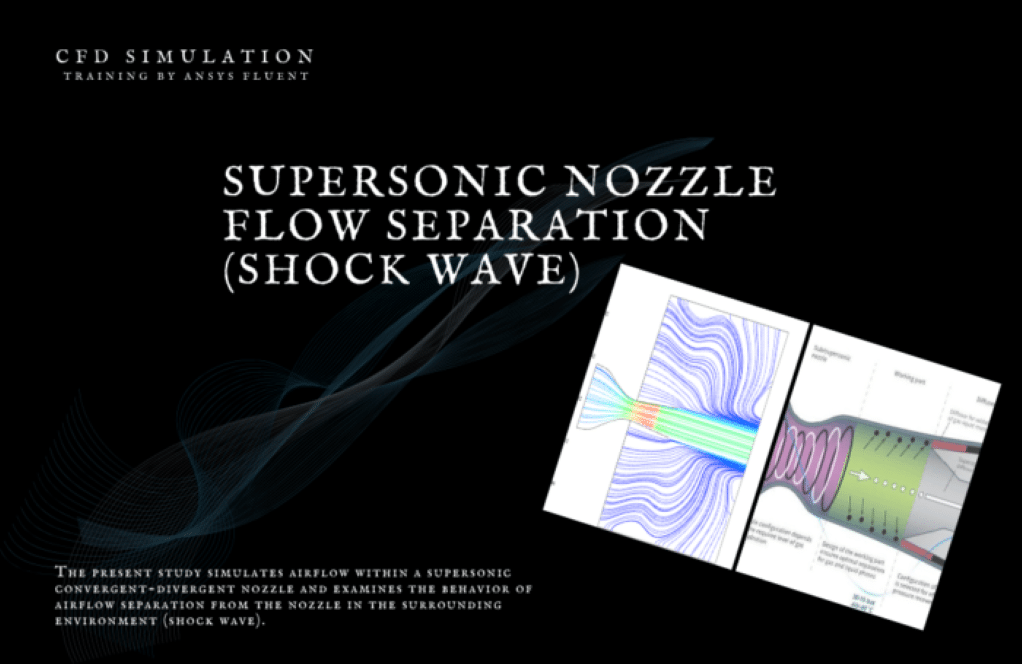
We start this training package with study number 1 which simulates airflow within a supersonic convergent-divergent nozzle and examines the behavior of airflow separation from the nozzle in the surrounding environment. In order to simulate the present model, the pressure condition in the nozzle input section (pressure-inlet condition) and the ambient output sections (pressure-outlet condition) have been used. The nozzle pressure ratio (NPR) is equivalent to the ratio of the inlet air pressure of the nozzle, to the ambient pressure. In practical exercise number 2, the compressible airflow will enter the convergent-divergent nozzle with a pressure of 70 bars and the Mach number of 0.2 with a temperature of 2735 K. After passing the throat zone, the airflow will gain speed and lose its temperature as it passes through the diffuser. The standard k-epsilon model with standard wall function is used to solve fluid flow equations.
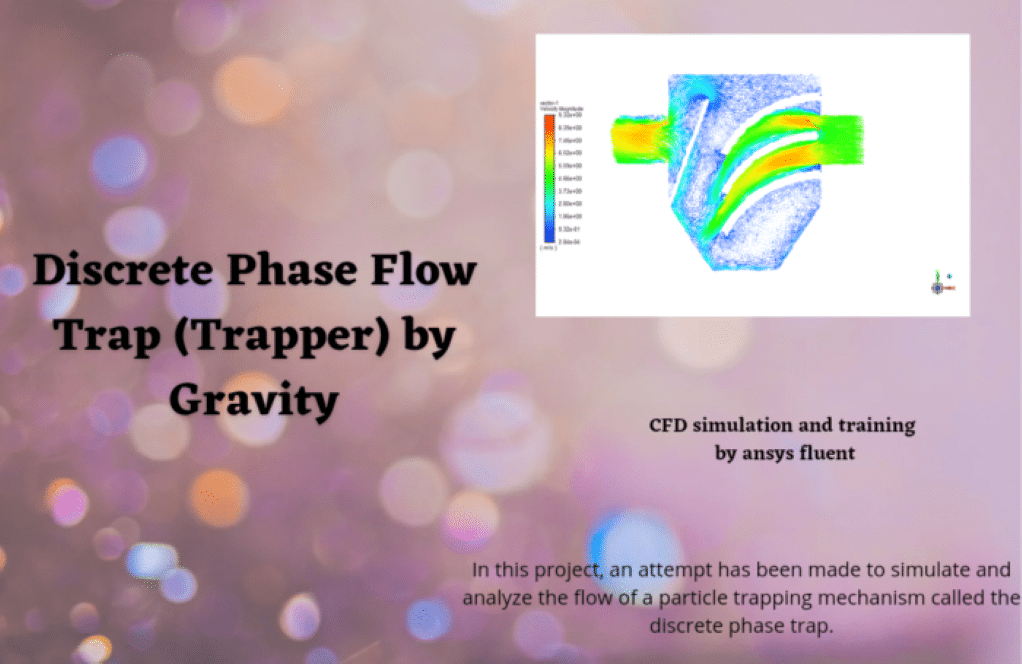
In project number 3, an attempt has been made to simulate and analyze the flow of a particle trapping mechanism called the discrete phase trap (TRAPPER). In order to simulate the particles, the discrete phase model (DPM) is activated and Saffman lift force and pressure gradient forces are also applied to particles. Also, since the trapping mechanism mainly works with gravity, gravity has been taken into account.
In practical exercise number 4, a three-phase flow fuel injector has been simulated. The standard k-epsilon model is used for flow analysis. The Mixture multi-phase model for three phases of air, liquid, and vapor has been used to investigate the phase interactions.
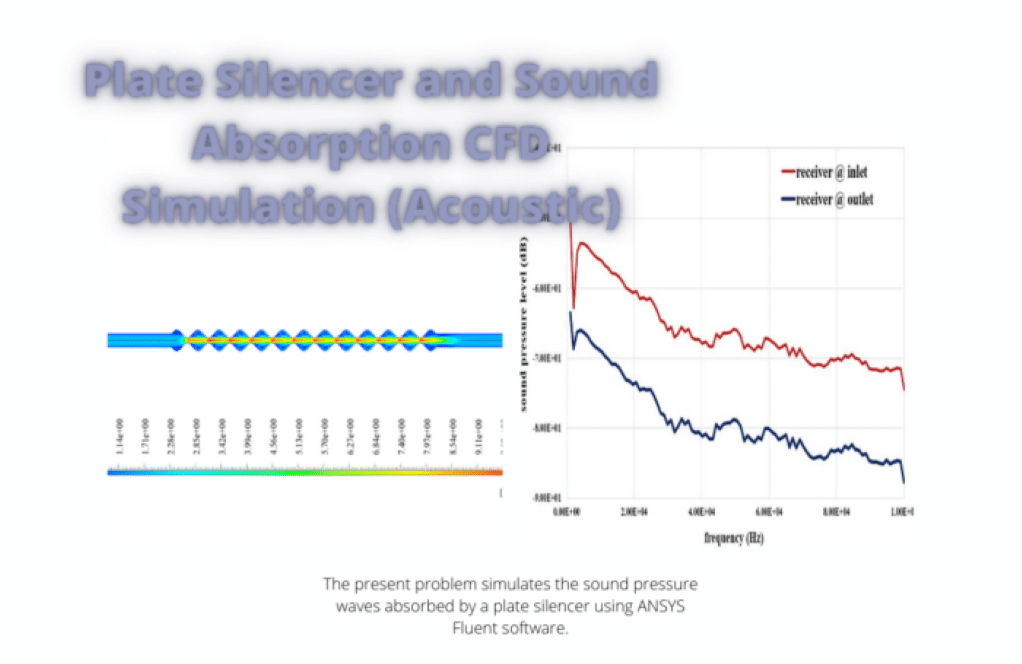
Problem number 5 simulates the sound pressure waves absorbed by a plate silencer. To simulate and analyze sound or acoustic waves, the acoustic model has been used in the software. To define the acoustic model in the present simulation, the Ffowcs-Williams & Hawkings model is used.
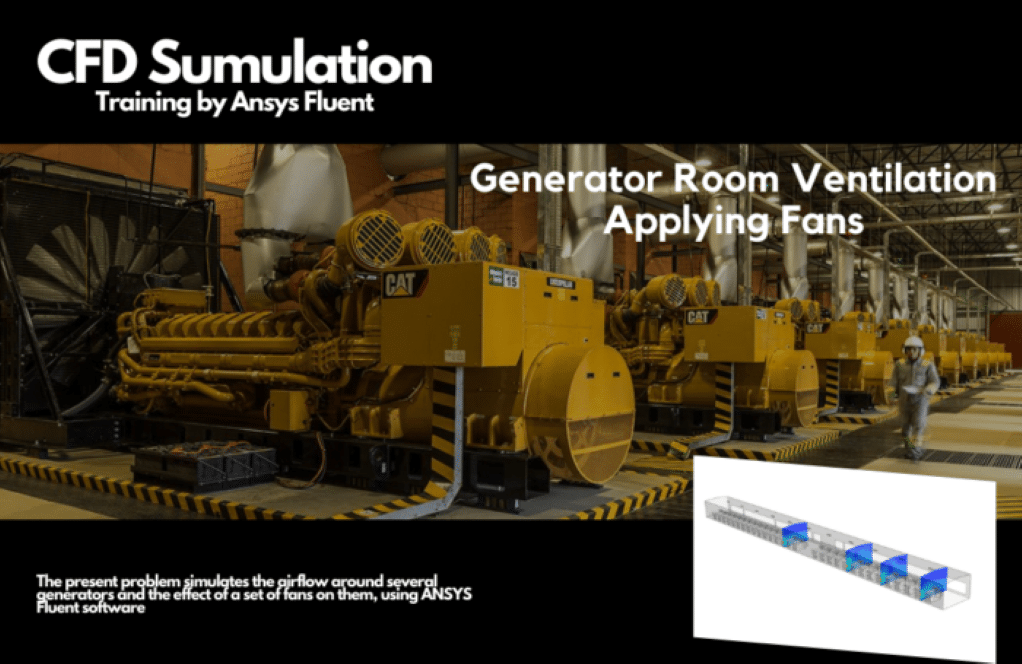
Practical exercise number 6 simulates the airflow around several generators and the effect of a set of fans on generator room ventilation. In this simulation, a shed is modeled as the location of 30 rows of generators. The open airflow enters the interior of the generator room from the roof of the shed and in front of each of the generator devices.
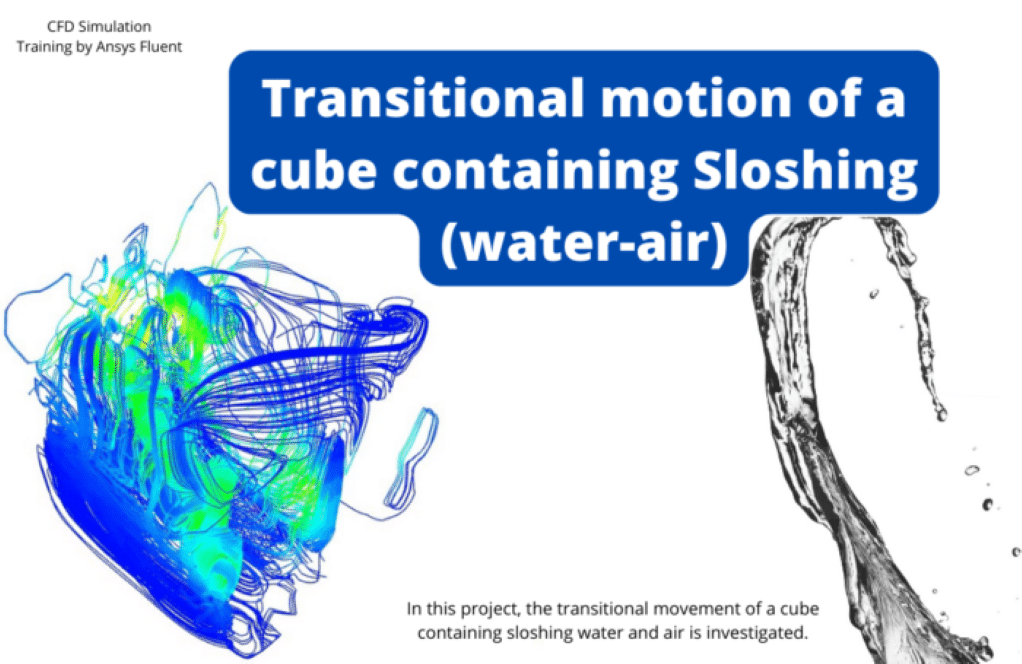
In project number 7, the transitional motion of a cube containing SLOSHING water and the air is investigated. The interaction of water and air inside the cube is modeled using the Volume of Fluid (VOF) multiphase approach. Cube accelerates in the X direction with an acceleration equal to 5 m/s2, while gravitational acceleration in the –Y direction affects the multiphase entity.
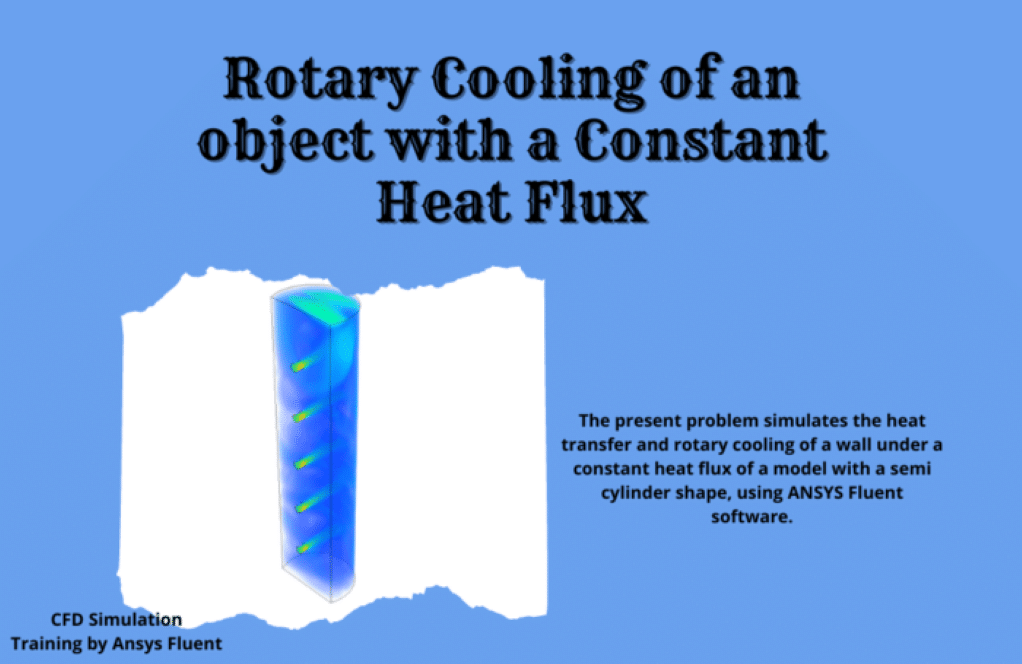
Problem number 8 simulates the heat transfer and cooling of a rotating mechanical device with a semi-cylinder shape. The model rotates around a particular axis (model z-axis) at a speed equivalent to 400 rpm. Therefore, to define this rotational motion in the model, the frame motion (MRF) technique with a rotational speed of 400 rpm has been used.
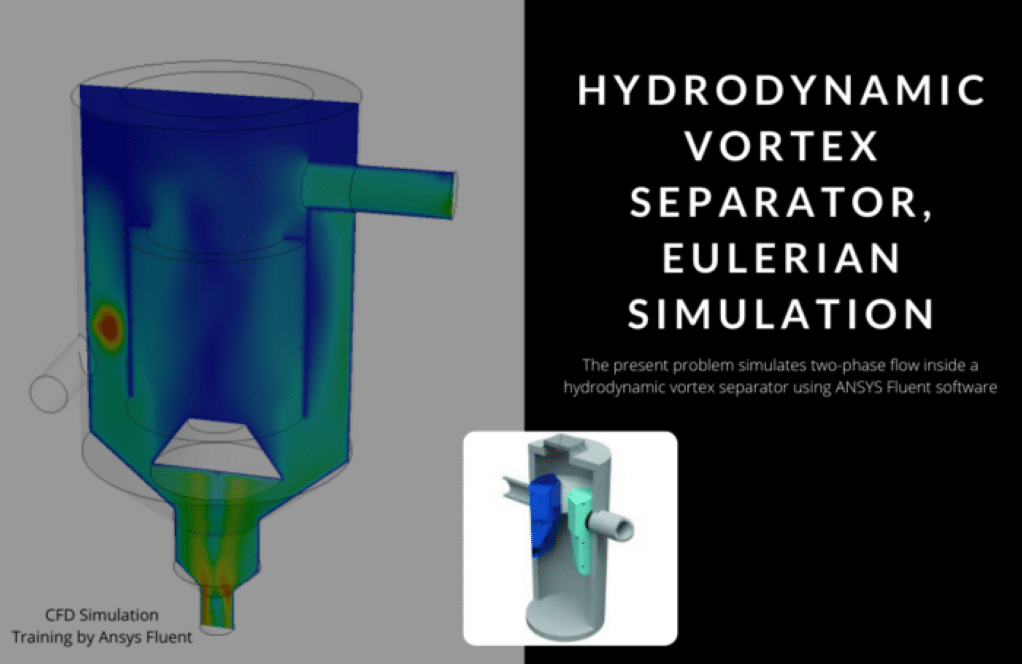
Practical exercise number 9 simulates hydrodynamic two-phase flow inside a vortex separator. These hydrodynamic vortex separators (HDVS), can separate soluble particles in a fluid from the base fluid. The structure of these devices is such that the flow of the solution entering the system is significantly rotated.
Finally, problem number 10 simulates the effect of cohesion and adhesion on a fluid. In this project, it is assumed that there is a T-shaped computational domain; So that the fluid flow enters from the bottom and exits from the top.
You can obtain Geometry & Mesh file and a comprehensive Training Movie that presents how to solve the problem and extract all desired results.







Antonina Cummerata PhD –
I’m interested in understanding how to use ANSYS Fluent for heat transfer simulations. Does this package cover that?
MR CFD Support –
Hi! Yes, this package definitely covers heat transfer simulations using ANSYS Fluent. It’s designed to give you a practical, hands-on understanding of how to conduct these simulations. We can also tailor the exercises to suit your specific requirements. We appreciate your feedback!
Rachelle Corkery –
I’m curious about the meshing techniques used in CFD. Are they covered in this package?
MR CFD Support –
Hello! Yes, the package does cover meshing techniques, which are a fundamental part of CFD. We can also customize the exercises based on your specific needs. Your input is really important to us!
Ryan Witting PhD –
I’m totally impressed with the Mechanical Engineering Training Package for beginners! Each exercise introduces a new concept and builds on the last, giving a well-rounded experience in understanding different simulations. I particularly enjoyed the particle trapping analysis and the intricate work with the sloshing dynamics. These are not simple topics, but the way they were unravelled made them highly accessible. Kudos to MR CFD for crafting such a practical learning journey!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for taking the time to write such a positive review. We’re thrilled to hear that you found the training package practical and comprehensible. It’s wonderful that the particle trapping and sloshing dynamics exercises stood out to you. We always strive to make learning both accessible and enjoyable. We look forward to offering you more valuable learning experiences!
Lauryn Dooley –
The training package seems very comprehensive. Could you let me know if each practical exercise comes with detailed step-by-step instructions for beginners?
MR CFD Support –
Yes, each practical exercise in the Mechanical Engineering Training Package comes with detailed step-by-step instructions. These guides are designed to assist beginners with completing the simulation tasks and to understand the fundamentals of how to work with ANSYS Fluent software. Additionally, the package includes Geometry & Mesh files as well as a comprehensive training movie for each exercise to further facilitate the learning process.
Kris Cronin –
The Mechanical Engineering Training Package for beginners looks well-rounded. From nozzle dynamics to acoustic waves and fluid-structure interaction, it seems like a comprehensive introduction to various fundamental topics in the field. I’m particularly impressed by the use of various phase models and the DPM method. The training might just offer the right balance between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear that you’re impressed with the Mechanical Engineering Training Package for beginners! We believe practical experience is critical for learning, especially when it comes to complex simulations. It sounds like the variety of models and methods within the exercises met your expectations for both foundational learning and hands-on application. Thank you for taking the time to share your positive review!
Marta Wintheiser DVM –
The training package really took me from being a novice to confidently performing simulations!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that our Mechanical Engineering Training Package for Beginners helped you gain confidence in performing simulations with ANSYS Fluent. Your success is our success, and we are excited that you found the practical exercises valuable. We aim to support learners like you in becoming proficient in CFD analysis. Keep up the great work, and don’t hesitate to reach out if you have any further questions or need more guidance. Happy simulating!
Jewell Crona –
I’m thrilled with the Mechanical Engineering Training Package for beginners! The variety of exercises provided deep insights into mechanical phenomena, and the step-by-step tutorials were especially helpful for a newbie like me. The use of real-world scenarios made the learning process engaging and highly practical. Hats off to the creators of this package!
MR CFD Support –
We’re delighted that you found the training package engaging and helpful! We aim to create content that strengthens understanding while being practical and user-friendly. Thanks for taking the time to provide your positive feedback. We appreciate it and look forward to continuing to support your learning journey!
Mr. Jensen Schneider –
I am very pleased with how the Mechanical Engineering Training Package for beginners has been structured. The step-by-step approach in going through the 10 exercises has been incredibly useful in helping me understand fluid dynamics concepts and the functionality of ANSYS Fluent. It’s particularly impressive how different types of simulations are included, ranging from airflow in nozzles to multiphase flow in complex systems. This diversity ensures a well-rounded introduction to CFD for anyone just starting out. Well done on putting together such a thorough and practical training package for beginners.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for taking the time to share your positive experience with our Mechanical Engineering Training Package for beginners. We’re thrilled to hear that the variety and structure of the exercises have been beneficial to your understanding of fluid dynamics and the use of ANSYS Fluent. It’s our pleasure to provide a foundational training resource that enables learners to develop a strong start in CFD. Should you need any further support or advanced training materials, please know that we are here to support your learning journey. Keep up the great work!
Jaren D’Amore –
I’m impressed with how well the traning package covers diverse mechanical simulations. The practical exercises seem well designed to provide a comprehensive learning experience for beginners.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that our Mechanical Engineering ANSYS Fluent Training Package met your expectations. The diversity in simulations and tailored exercises are indeed aimed at providing a solid foundation for beginners. If you have any further questions or need assistance as you work through the exercises, feel free to reach out to our support team.
Zakary Hand –
I truly appreciate this Mechanical Engineering Training Package! The variety of exercises ensured that as a beginner, I got to understand different concepts and apply various ANSYS Fluent tools. The mix of problems covering diverse areas, from airflow analysis in nozzles, particle trapping simulation, multiphase flow in fuel injectors, acoustic modeling of a silencer, sloshing dynamics, simulation of a rotating device’s cooling, vortex flow in separators, to the study of cohesion and adhesion effects in fluids, provided a broad learning scope. Particularly useful was the comprehensive Training Movie – it was like having a tutor guiding through every step of the problem-solving process!
MR CFD Support –
We are thrilled to hear that our training package has been beneficial to your learning journey! It is wonderful to know that the comprehensive training content and the variety of practical exercises have provided broad exposure to ANSYS Fluent tools and concepts. Thank you for recognizing the efforts we’ve put into making the learning process as effective and engaging as possible through the Training Movie. We look forward to supporting your continuous growth in mechanical engineering simulations!
Ethelyn Bins –
This Mechanical Engineering Training package has been a fantastic resource for me starting out in ANSYS Fluent. The step-by-step guidance through different simulations has greatly enhanced my understanding. The variety of exercises ensures that I not only learn the basics but also get exposed to specific scenarios, which I find immensely valuable. Well structured and informative!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for such positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our Mechanical Engineering Training Package has been beneficial for you. It’s rewarding to know that the structured exercises and scenarios have contributed to your learning experience. If you ever need further guidance, or have suggestions for future packages, don’t hesitate to reach out. Keep up the great work!
Dr. Ari Blick –
I’m impressed with the diversity of exercises in this package for beginners. Are the training materials easy to understand for someone new to ANSYS Fluent?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that you appreciate the variety in the training. Rest assured, our materials are designed with the BEGINNER user in mind, ensuring simplicity and clarity in explanations. Our comprehensive Training Movies walk users through each step of problem-solving to reinforce learning and understanding.
Retha Jacobs –
I’ve just completed the Mechanical Engineering Training Package for Beginners Part 2 and am thrilled with the realistic simulations! It was like bringing theoretical knowledge to life, and the included training movie was so helpful for visual learners like me. Excited to apply these concepts to real-world problems!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear our training package met your expectations and proved to be a valuable learning tool. It’s great to know you found the simulations realistic and the training movie beneficial. We appreciate you choosing our product and we’re excited for you to apply these concepts in your future endeavors!
Gina Walker DVM –
The training package covering different exercise scenarios seems diverse. Would you be able to provide an overall summary of what skills a beginner would attain after completing all these exercises?
MR CFD Support –
Certainly! By completing the 10 exercises in this Beginners’ Part 2 Training Package, a beginner will gain skills in fluid dynamics and thermo-mechanic simulations using ANSYS Fluent. You’ll learn setting boundary and initial conditions, activating various numerical models like k-epsilon for turbulence, discrete phase model for particle tracking, the VOF model for multiphase flows & Ffowcs-Williams & Hawkings model for acoustics pseudonym PARTICULAR SKILLS people teen, assessing the dynamic behavior of materials, simulating phase separation in vortex mechanisms, thermo-mechanic simulations of rotating machinery, understanding the basics of fluid-structure interaction (FSI), and analyzing hydrodynamic behaviors. Moreover, you’ll be acquainted with practical engineering applications like nozzle design, air filtration, sound absorption, multiphase flow management, and more.
Antwan Greenholt Jr. –
Do these exercises cover setting up and solving a CFD simulation in ANSYS Fluent?
MR CFD Support –
Hello! Yes, the exercises in this package are designed to give you a hands-on experience of setting up and solving a CFD simulation in ANSYS Fluent. Remember, we can tailor the exercises to suit your specific needs. We really value your input!
Prof. Leola Witting –
I’ve completed the exercises in the Mechanical Engineering Training Package for Beginners. The projects were intuitive and practical. It has been a valuable resource in learning how to simulate various mechanical engineering scenarios.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our training package was helpful for you. If there’s anything else we can assist you with or if you’re interested in advanced exercises, please let us know. We are here to support your learning journey!
Kamille Ondricka –
This Mechanical Engineering Training Package sounds like a complete and hands-on learning experience for newbies. I appreciate the step-by-step guidance through various practical exercises.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our training package has provided you with a comprehensive learning journey. Your satisfaction with the step-by-step instructions and the variety of exercises is our top priority. If you require further assistance or have any more questions, feel free to reach out. Happy learning!
Onie Ritchie –
The training package covers extensive exercises in ANSYS Fluent, but could you clarify how suitable this package is for individuals who have very little to no prior experience in simulation?
MR CFD Support –
This Mechanical Engineering training package specifically targets BEGINNER users and starts from the basics, ensuring it’s suitable for individuals with minimal to no prior experiences in simulation. It provides step-by-step guidance and includes a comprehensive training movie that demonstrates how to solve the problems, making it easy to follow along and understand the concepts presented.
Benjamin Kilback –
These exercises sound integral for a beginner to progress in mechanical engineering simulations. Do these practical exercises also provide step-by-step tutorials on how to perform the analysis in ANSYS Fluent?
MR CFD Support –
Yes, these practical exercises come with comprehensive Training Movies that guide you through each phase of solving the problems and extracting all the necessary results in ANSYS Fluent. This makes it an excellent learning aid for beginners stepping into the world of mechanical engineering simulations.
Bulah Hagenes –
I found the level of detail in each exercise very instructive! The variety of simulations gave me a broad exposure to different practical issues in mechanical engineering and helped me understand the fundamental principles of CFD in ANSYS Fluent. Keep up the good work!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are thrilled to hear that our training package provided you with valuable insights into the applications of ANSYS Fluent for practical mechanical engineering scenarios. We strive to include a variety of exercises in our packages to cover as many relevant topics and techniques as possible. Your satisfaction with our product encourages us to continue improving and expanding our educational materials. If you have any further questions or need more assistance, don’t hesitate to get in touch. Happy learning!
Kurt Fay PhD –
Thank you for creating the Mechanical Engineering Training Package for beginners! It has been a wonderful resource for me as I’m new to using ANSYS Fluent. I’m halfway through the exercises, and I’ve found the step-by-step approach incredibly helpful for understanding the basics. The variety of problems ensures a broad learning scope, and the training movie is particularly good for visual learners like myself!
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear that you’re finding the Mechanical Engineering Training Package beneficial for your ANSYS Fluent learning journey! It’s great that our practical exercises and training movie are effectively aiding your understanding of the basics. We strive to support beginners like you with a comprehensive and clear approach. If you have any further feedback or need assistance as you progress, please let us know. Thank you for the positive review and best wishes for your continued learning!
Murphy Runolfsson –
I’d like to know more about boundary conditions in CFD. Does this package provide information on that?
MR CFD Support –
Hi there! Yes, this package does provide information on boundary conditions, a crucial aspect of CFD. Remember, we can also tailor the exercises to suit your specific needs. Your feedback is really valuable to us!
Romaine Sporer –
I am impressed by the wide range of practical exercises in this Mechanical Engineering Training Package! The mix of exercises involving supersonic flow, acoustic wave modeling, particle trapping mechanisms, as well as multiphase flows seems like a very thorough introduction for beginner users of ANSYS Fluent. It’s great to see DPM, VOF, and mixture multi-phase models included in the learning. Are the training movies clear enough for absolute beginners to follow along with these complex phenomena?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for the kind words about our Mechanical Engineering Training Package (Part 2) for beginners! Yes, the training movies are specifically tailored to guide absolute beginners through each step of the simulation process. We cover everything from creating the geometry and mesh to setting up boundary conditions and solving the exercises. We ensure that complex phenomena are broken down into comprehensive, easy-to-understand tutorials so beginners can fully grasp each concept and apply it on their own.
Emily Tremblay –
I recently delved into the Mechanical Engineering Training Package, Beginners, Part 2, and I must say it has been a mind-blowing experience! Each exercise was perfectly calibrated to enhance my understanding of the fundamentals step by step. Moving from simple to more complex simulations, I was able to grasp critical concepts in mechanical device simulations while also getting hands-on ANSYS Fluent software experience. I especially enjoyed the particle trapping mechanism simulation and the sloshing water in the cube analysis – both were exceptionally enlightening and relevant to my field of study. This training is invaluable for beginners out there!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for taking the time to leave such detailed feedback on the Mechanical Engineering Training Package for Beginners, Part 2! It is wonderful to hear that you enjoyed the exercises, particularly the discrete phase trap simulation and the sloshing water analysis. We are delighted that the steps were both easy to follow and useful for your learning journey. Keep exploring and learning, and we look forward to supporting you as you dive deeper into CFD and mechanical simulations!
Dr. Alessia Kilback –
This training package was incredibly helpful! As a beginner, the step-by-step tutorials in each exercise enhanced my understanding of different mechanical engineering concepts using ANSYS Fluent. The dives into phenomena like sloshing, acoustics, and multi-phase flow were insightful. The inclusion of a training movie for each problem was especially valuable, providing clear visual guidance throughout the learning process.
MR CFD Support –
We are thrilled to hear that our Mechanical Engineering Training Package for Beginners was beneficial to your learning journey. Your positive experiences with our step-by-step tutorials and multimedia resources validate our commitment to providing high-quality and comprehensive learnings tools. We appreciate your kind words and hope you continue to find our products supportive. Thank you for choosing us for your educational needs!
Keshaun Kuvalis –
I’m very impressed with the range of practical exercises included in the Mechanical Engineering Training Package for beginners. These simulations seem like an ideal way to get hands-on experience with ANSYS Fluent across a range of different mechanical engineering scenarios.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are thrilled to hear that you appreciate the diversity and practical applications of our Mechanical Engineering Training Package. Our goal is to provide an engaging learning experience for beginners to build a strong foundation in using ANSYS Fluent. If you ever have any questions or need further assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out. Continue enjoying your learning journey!
Miss Ivory Harvey Jr. –
The simulations included in this Mechanical Engineering Training Package sound impressive! I’m excited to see how these exercises will help beginners understand the real-world physics behind various mechanical systems. The diverse scope of studying everything from fluid flow in nozzles to particle trapping mechanisms to sloshing dynamics provides a rich and hands-on learning experience. Can’t wait to see my skills grow!
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear that you’re excited about the Mechanical Engineering Training Package! It’s wonderful to know that learners like you appreciate the variety of simulations that offer a broad perspective on mechanical phenomena. We are confident that your skills will indeed improve as you work through these engaging and practical exercises. Thank you for choosing our training materials, and we wish you an enriching learning experience!
Tyreek Johns –
I’m on project number 3 about the particle trapping mechanism. Can you explain how gravity affects particle motion in the trap?
MR CFD Support –
In project number 3, gravity plays an essential role since the whole trapping mechanism is heavily dependent on gravitational forces. When gravity is considered in the discrete particle model (DPM), it influences the trajectory and settlement of the particles. The Saffman lift force and pressure gradient forces also contribute to particle dynamics along with gravity, leading to an accurate simulation of the trapping effectiveness for discrete phase particles.