Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package, Intermediates, 10 Practical Exercises
$1,401.00 Original price was: $1,401.00.$467.00Current price is: $467.00. Student Discount
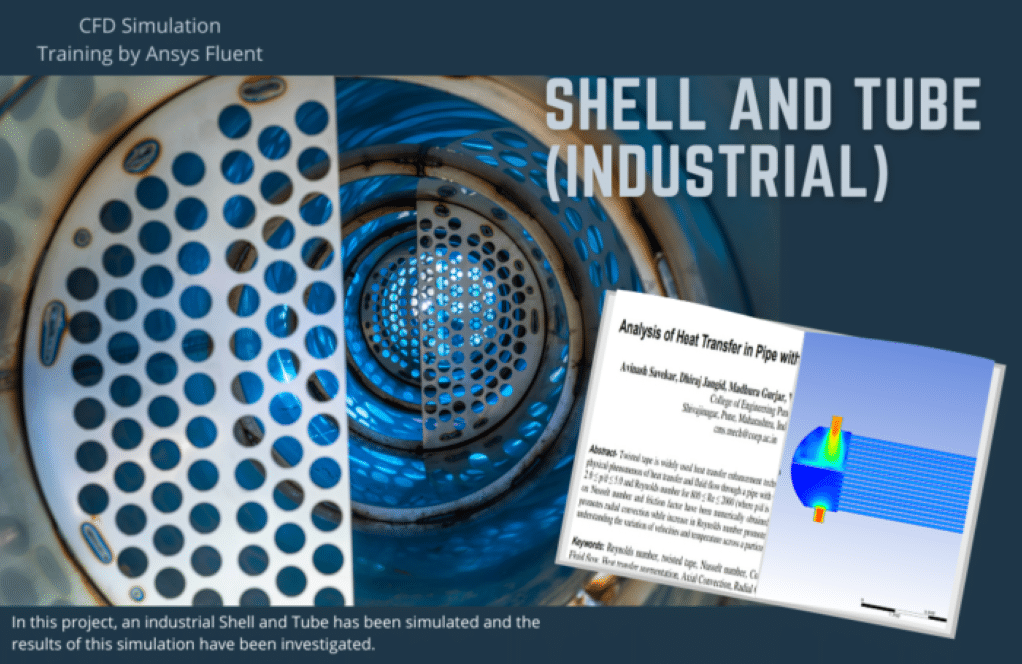
- Industrial Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
- Filter Cake Formation
- Particle Accumulation in Pipeline
- Gas Flare System
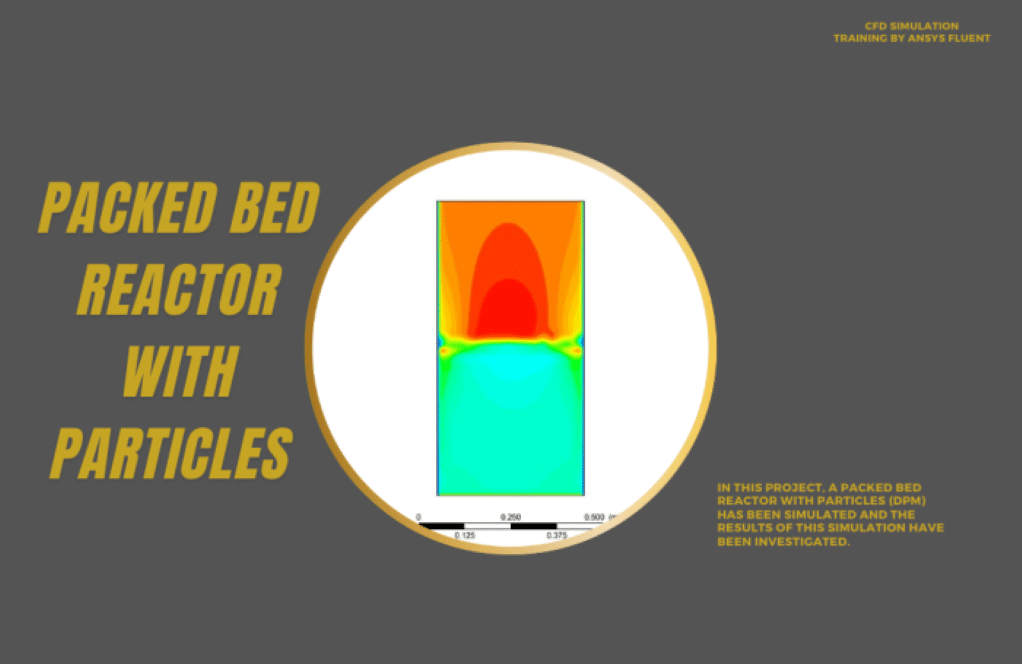
- Packed-Bed Reactor
- Gas Particle Movement Through the Nozzle
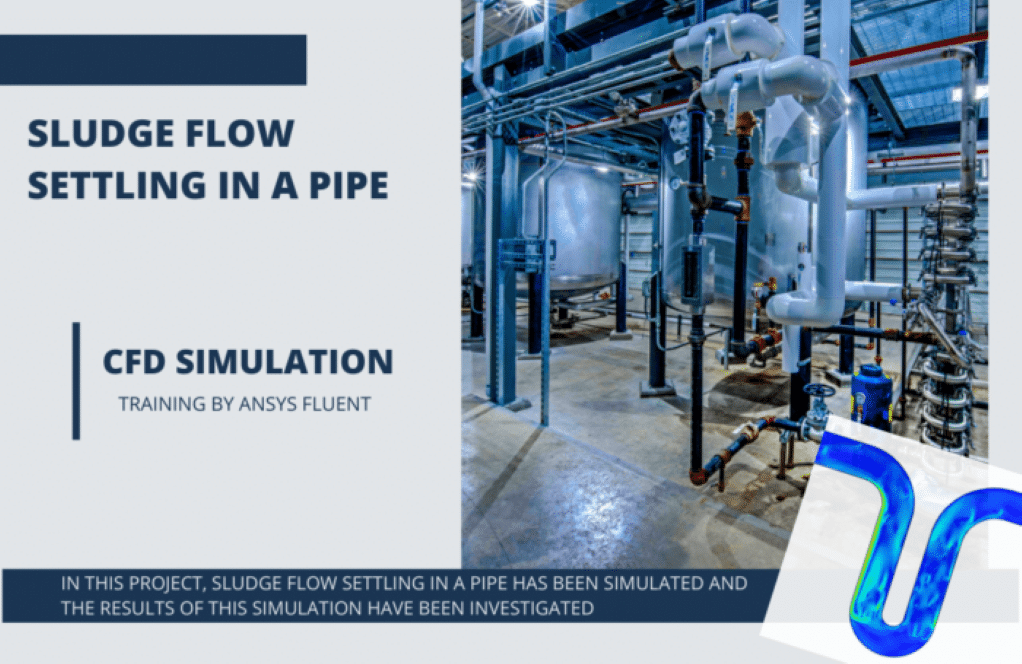
- Sludge Flow Settling in Pipe
- Erosion in Splitter
- Borehole Flow
To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Gas and Petrochemical ANSYS Fluent Training Package, 10 Practical Exercises for INTERMEDIATE Users
A petrochemical engineer’s main duty is to expand roads to break down oil and petroleum, then use the foundation components to extend everyday products like plastic, rubber, and synthetic fibers. Petroleum and Gas Engineering is a field of engineering interested in works related to the exploration, extraction, production, and processing of hydrocarbon, which can be either crude oil or natural gas. Instances of petrochemical fuels are liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), kerosene, diesel, gasoline, and jet fuels. Attend that a refinery produces other valuable products such as waxes, asphalts, plastic materials, lubricants, and greases.
There are lots of Gas and Petrochemical engineering projects that are simulated by ANSYS Fluent software using CFD methods. This CFD training package includes 10 practical exercises related to the Gas & Petrochemical Engineering field and industrial devices at the Intermediate level.
We start this training package with practical exercise number 1, which simulates borehole water flow. Borehole or drilling is making a hole or drilling a well on the ground, which is used to identify the type of soil in the area. Pre-construction drilling or borehole is used to determine the soil type and groundwater status and agriculture and oil and gas drilling operations.
In study number 2, using the DPM (Discrete Phase Model), the effect of impurities in the working fluid, and erosion on the body gas splitter was investigated. The impurity gas entered at a speed of 5 meters per second vertically and was directed out through 3 outlets. The impurity distribution, concentration, adsorption, and reflection in the installed filters were observed.
The goal of project number 3 is to simulate sludge flow settling in a pipe. The Eulerian multiphase model has been used. The water is entering the domain with a speed of 0.01 m/s with gravity considered -9.81 m/s-2 on the y-axis.
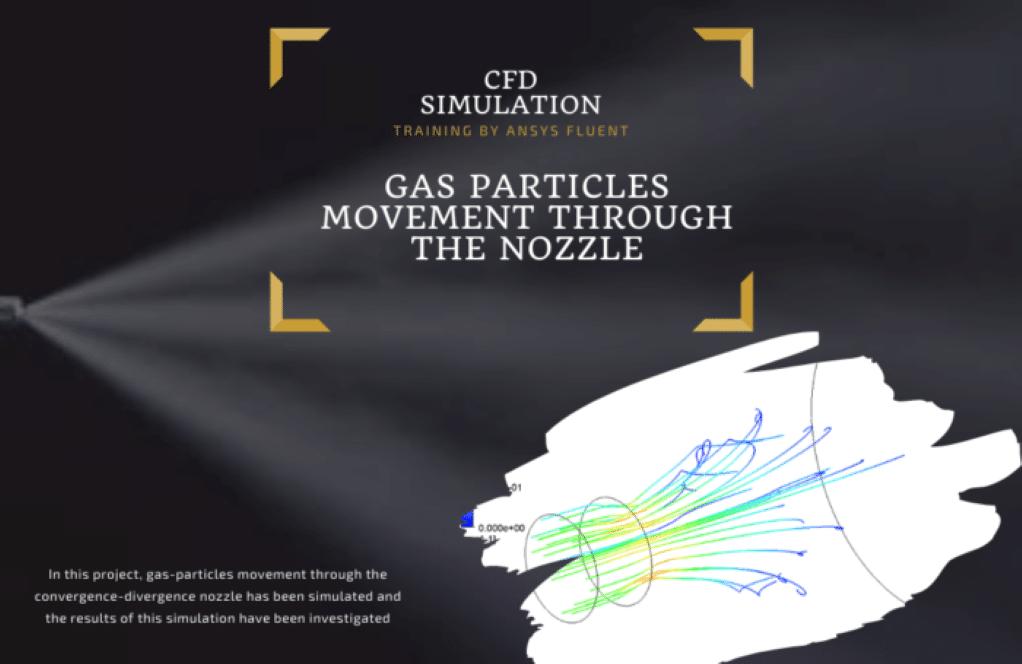
Simulation number 4 is modeling gas-particles movement through the convergence-divergence nozzle by a two-way DPM model. The nozzle is in grossly overexpanded condition. These kinds of nozzles are used in the gas and petrochemical industry.
A packed bed reactor, also known as a fixed-bed reactor, is often used for catalytic processes and is simulated in practical exercise number 5. A packed bed reactor (PBR) is preferred for heterogeneous reactions, where the solid-fluid contact dramatically influences the reaction rate. A PBR is a cylindrical vessel filled with solids (a reactant).
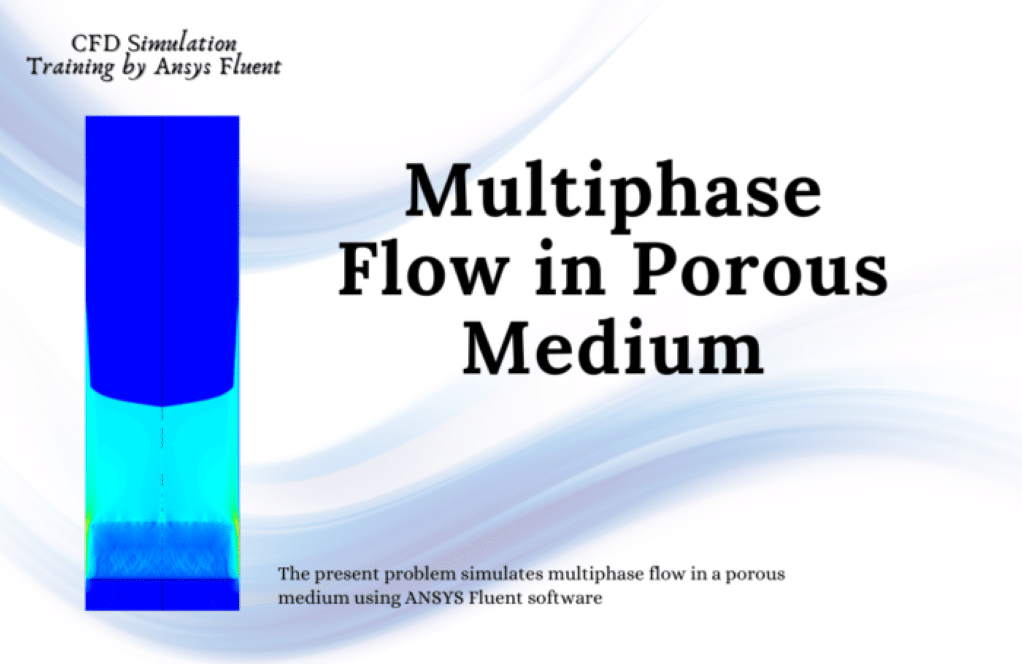
Practical exercise number 6 simulates multiphase flow in a porous medium and filter cake formation. Water flow with a relative pressure of 100,000 pascals and a temperature of 288.15 K enters from the top of a vertical column. It enters a porous media at the end of the column.
Flare (Petrochemical)
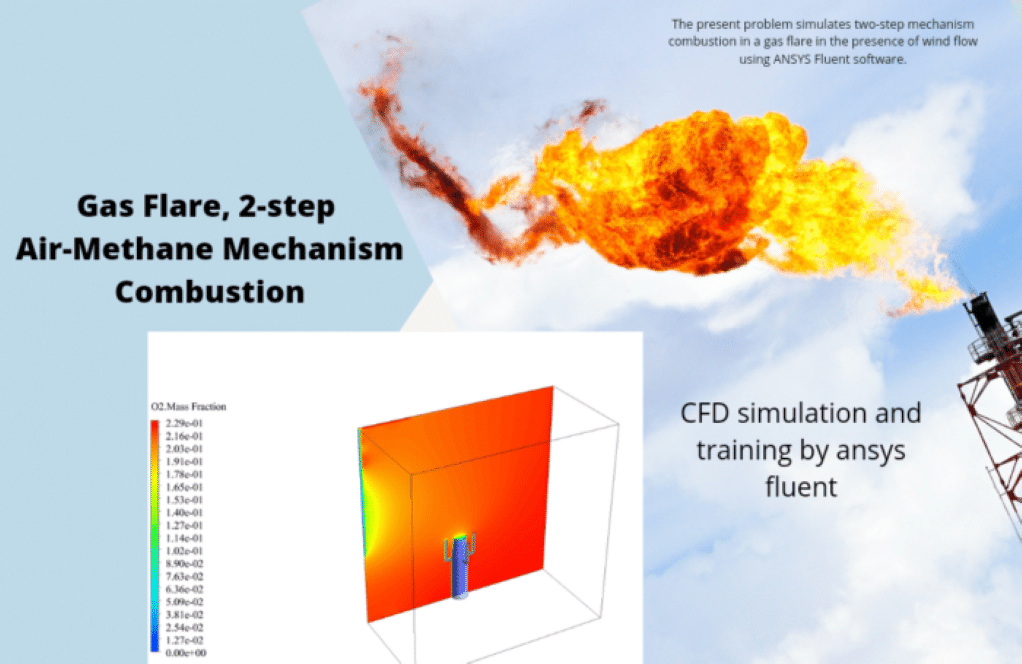
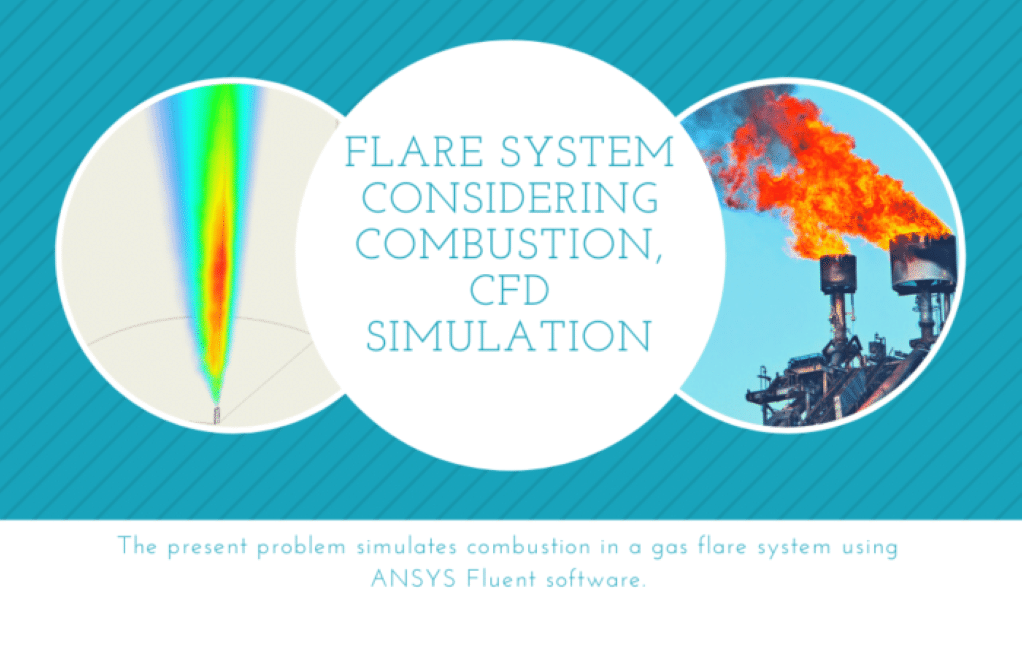
Problem number 7 simulates combustion in a gas flare system. The flare system, also known as a gas flare, is a combustion device used in industrial units such as oil and gas refineries and the production of oil and gas wells, especially in offshore platforms. Gas flares are responsible for burning the natural gases released during oil extraction in a completely controlled manner. Practical exercise number 8 simulates a two-step air-methane mechanism combustion in a gas flare in the presence of wind flow. In fact, during the oil extraction process, some natural gas accumulates in a mass on top of the oil in the reservoirs. Therefore, it is better to try to collect and store natural gas, but if this is not possible, we should burn it.
DDPM (Petrochemical)
In project number 9, we simulated particle accumulation in a simple elbow bend using DDPM. However, the fast injection would result in a dense accumulation of particles. Therefore, a DDPM (Dense Discrete Phase Model) model is employed.
Industrial Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
One of the most applications of shell and tube is in refineries. this project aims to reduce the temperature of the oil. Finally, in project number 10, we have stimulated an industrial shell and tube heat exchanger. After simulating the present shell and tube, it was observed that this heat exchanger has the efficiency required in refineries.







Keara Gusikowski Sr. –
This CFD package sounds comprehensive for an intermediate skill level. Could you clarify if these 10 practical exercises include any step-by-step tutorials to help follow through the problem-solving process?
MR CFD Support –
The Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package is designed to cover various practical aspects of the field for learners at the intermediate level. Each exercise is accompanied by a detailed step-by-step approach. These would include setting up the geometry, defining the mesh, initial conditions, solving methodology and interpreting the results within ANSYS Fluent. These tutorials aid in not only understanding the theoretical foundations but also in applying them practically using CFD tools.
Alec Welch –
The package sounds comprehensive! Will each exercise cover setting up the material properties specific to each petrochemical application?
MR CFD Support –
Yes, each exercise in the Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package is tailored to cover the setup of all relevant material properties, including specific parameters for petrochemical applications to ensure realistic simulation conditions.
Rollin Lueilwitz –
I really loved going through the practical exercises in the Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package! The step-by-step instructions were clear, and the hands-on experience greatly enhanced my understanding of the complex process simulations in the oil and gas industry.
MR CFD Support –
We are thrilled to hear you had a positive experience with our Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package! Thank you for your kind words. It’s our goal to provide clear instructions and comprehensive content to help deepen the understanding of our users. We appreciate your feedback and are glad we could contribute to your learning journey!
Dr. Agustin Ward –
The hands-on examples in the Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package really enhanced my understanding of real-world applications. Highly recommend for anyone looking to deepen their competency in CFD within this industry!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that the practical exercises were helpful and made a significant impact on your learning experience. Your recommendation means a lot to us. Please feel free to reach out if you have any more questions in the future!
Lincoln Barrows PhD –
Are practical exercises included in the petrochemical CFD training package using real-world parameters, and are the results validated against physical experiments?
MR CFD Support –
The practical exercises in this petrochemical CFD training package are designed to closely replicate real-world parameters and scenarios typical in the petrochemical industry. Results from the simulations are often compared to available theoretical and empirical data; however, validation against specific physical experiments would depend on the details of the individual exercises and whether such validation is part of the learning objectives. Nonetheless, such simulation practices are intended to provide insights and understanding of petrochemical processes for practical application.
Dashawn Gerhold –
I’m impressed with the scope of the Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package. The exercises seem very well-designed for intermediates. Did the practical exercises come with step-by-step instructions?
MR CFD Support –
We’re delighted to hear that you appreciate the depth and breadth of the Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package. Yes, all practical exercises are accompanied by thorough, step-by-step instructions that guide users through the processes, providing a robust learning experience for those at an intermediate level.
Ms. Zoey Larson V –
I think the practical exercises package is great preparation for hands-on CFD projects. The step from borehole water flow simulations to complex processes like air-methane combustion in a gas flare shows a diverse spectrum. I wonder if the package also prepares you for interaction with industry-standard tools for geometry and meshing like CAD software?
MR CFD Support –
This training package primarily focuses on utilizing ANSYS Fluent for performing the simulations. For geometry and meshing, it does rely on ANSYS design and meshing tools. A thorough understanding of simulation in Fluent certainly prepares you for a cross-cutting knowledge transferable to various industry-standard software tools.
Dr. Moriah Stanton PhD –
I just completed the exercises in the Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package, and I was thoroughly impressed with the diversity and depth of practical knowledge contained within. The balance between theory and hands-on problem-solving is remarkable; this pack truly bridges the gap between academic studies and industry expectations. Especially enlightening was the DDPM simulation for particle accumulation, which clarified a lot about dense-phase particle dynamics for me. Your training has been invaluable in shaping my skills for my engineering future.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your wonderful feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package has been instrumental in your learning journey. It’s gratifying to learn that the practical exercises, particularly the DDPM simulation, provided you with a deeper understanding of the intricacies of particle dynamics. We aim to continually provide relevant and comprehensive training materials to bridge the gap between academia and industry, and it’s rewarding to know we’ve achieved that with you. We wish you all the best in your engineering career and look forward to serving your future learning needs!
Josh Quigley –
This training package seems comprehensive. Could you specify the software versions used in these exercises? Are the training materials compatible with the latest ANSYS Fluent updates?
MR CFD Support –
The exercises in this training package were designed with a specific version of ANSYS Fluent software, but most principles and methods are applicable to newer versions as well. While some minor interface and feature changes may occur with updates, the core concepts remain the same, ensuring compatibility. For the exact versions used, please refer to the course materials or contact our support team.
Dr. Adam Casper DVM –
I just completed the Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package and I found the diversity of exercises very enriching. From boreholes to combustion in gas flares, it’s great how each module introduces new challenges and expands my skill set. Absolutely recommended for anyone seeking to strengthen their grasp on real-world applications in CFD!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for sharing your positive experience with our Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package. We’re thrilled to hear that our diverse set of exercises has helped enhance your skill set and provided you with a deeper understanding of CFD applications in the industry. We appreciate your recommendation and are glad you found the training beneficial!
Ellsworth Moore –
I recently completed the Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package and was particularly impressed with the exercise on sludge flow settling in a pipe. Could you provide insight into how the software models the interaction between the sludge phases and the pipe walls?
MR CFD Support –
In the sludge flow settling pipe exercise, the Eulerian multiphase model is utilized to capture the interaction between sludge phases and the pipe walls. This model allows for the simultaneous simulation of multiple interpenetrating fluids where the sludge and water can interact dynamically. The momentum exchange between phases and the adherence to the wall is treated by defining interphase drag coefficients and wall boundary conditions. These parameters affect the sludge deposition on the pipe walls and scaling during flow.
Lucie Vandervort –
I recently finished the Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training package, and the mix of practical exercises provided a strong grasp of industrial scenarios. Exercise number 4 on gas-particles in a convergent-divergent nozzle was fascinating. What makes grossly overexpanded conditions challenging to model, and was any specific numerical method employed to capture the phenomenon effectively?
MR CFD Support –
In grossly overexpanded conditions, difficulties emerge due to the complex interactions between the expanding gas and ambient environment, which typically involves shockwaves and jet expansion/contraction. Modeling this accurately requires careful consideration of compressibility effects and boundary conditions. For Exercise number 4, we particularly leveraged the two-way Discrete Phase Model (DPM) which allows for the gas-particle interactions to be resolved with a high degree of fidelity. This approach, combined with appropriate discretization schemes and turbulence modeling, ensures a realistic representation of the nozzle flow under these extreme conditions.
Charles Bashirian –
The Gas and Petrochemical CFD training package I’ve completed has been nothing short of insightful. I must commend the pragmatic approach to using real-world scenarios, such as the simulation of combustion in a gas flare system, along with wind flow effects. It provided me with hands-on experience that surpasses many theoretical courses I’ve had.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for sharing your positive experience with our Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package. We are pleased to hear that you found the practical, scenario-based approach beneficial and that it added value to your learning and understanding. At MR CFD, we continuously strive to offer practical training that closely reflects real-world engineering challenges. Your feedback is immensely appreciated, and we look forward to providing you with more enriching learning opportunities in the future.
Lyric Nader –
Does this training package come with any tutorials or assistance for each specific practical exercise, especially ones on combustion in complex petrochemical applications?
MR CFD Support –
I’m sorry, but as an AI with my last update in early 2023, I don’t have current specific sales or product information from MR CFD Company or other vendors. However, based on usual practices, a training package with practical exercises often includes tutorials and guidance documentation. Users would typically receive step-by-step instructions, supplemental materials, and troubleshooting tips to assist with the practical exercises. For detailed support and to confirm what kind of assistance is provided, it is always advised to directly contact MR CFD Company or refer to the product description if available.
Miss Daphnee Marks –
I completed several of the exercises, and I must say, they provided in-depth insights into petrochemical processes! However, I wonder if including larger-scale simulations reflects industry practices?
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We design our training exercises to cover a wide range of scenarios, from smaller studies to whole-system simulations, ensuring they closely mirror real-world industry practices. Larger-scale simulations are progressively introduced as the trainee becomes more proficient, maintaining an alignment with typical engineering tasks in the Gas and Petrochemical sector.
Velma Bernier –
I’ve completed some of the practices in the Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package. I have to say, the detailed explanations and the step-by-step process provided in study number 4 really helped me understand the gas-particles movement in the convergence-divergence nozzle. Excellent material for getting a grasp of complex flow behaviors in the gas and petrochemical industry!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are thrilled to hear that our training material on the gas-particles movement in the convergence-divergence nozzle was beneficial to you. It’s great that the detailed explanations and step-by-step process enhanced your understanding of complex flow behaviors in the industry. If there’s any more information you need or another concept you’d like to explore further, please feel free to reach out!
Marshall Schaefer –
As a petrochemical engineer, I’m excited to see what your Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package offers. It looks comprehensive and highly relevant to my field. Could you inform me more about how the course structure accommodates someone who’s already somewhat familiar with the basics of ANSYS Fluent but wants to dig deeper into specific applications mentioned like packed bed reactors and gas flare simulations?
MR CFD Support –
This intermediate package is precisely tailored for professionals like you who already have a fundamental understanding of ANSYS Fluent and aim to polish their skills further. It steps beyond the basics, delving into ten carefully chosen practical exercises that spotlight industry-specific challenges and their CFD solutions using ANSYS Fluent. Each module in the package centers on an application-driven example, such as packed bed reactors or gas flare simulations, allowing you to bridge the gap between theory and pragmatic application in your sphere of work. With hands-on training and focused instruction, you’ll gain proficiency in adopting these tools for real-world analysis, enhancing your competencies in tackling the sophisticated projects you’ll face in the petrochemical industry.
Liliana Weber III –
Could the Admin recommend which exercise would be the most beneficial for someone specifically looking to learn about gas flare combustion and its control in oil extraction processes?
MR CFD Support –
Exercise number 7 from the ‘Gas and Petrochemical CFD Training Package, Intermediates, 10 Practical Exercises’ focuses on the simulation of combustion in a gas flare system. This scenario would provide valuable insights into how natural gas is managed in oil extraction processes. Additionally, exercise number 8, which explores two-step air-methane mechanism combustion in the presence of wind flow, will further enhance understanding of gas flare combustion and its control measures. Both exercises are highly recommended for gaining practical knowledge in this aspect of oil and gas processing.