Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners, 10 Learning Products
Original price was: $1,200.00.$400.00Current price is: $400.00. Student Discount
This CFD training package is prepared for BEGINNER users of ANSYS Fluent software in the turbomachinery area including 10 practical exercises.
Click on Add To Cart and obtain the Geometry file, Mesh file, and a Comprehensive ANSYS Fluent Training Video.To Order Your Project or benefit from a CFD consultation, contact our experts via email ([email protected]), online support tab, or WhatsApp at +44 7443 197273.
There are some Free Products to check our service quality.
If you want the training video in another language instead of English, ask it via [email protected] after you buy the product.
Description
Turbomachinery CFD Simulation Package, ANSYS Fluent Training for BEGINNER Users
Today, the use of CFD methods in the design and analysis of Turbomachinery has become very important. The application of CFD in the simulation of turbomachines includes the following:
- Performance Predictions
- Internal flow visualization
- Investigation of existing design
- Qualitative and quantitative validation of performance using simulations.
- Optimization
This CFD training package is prepared for BEGINNER users of ANSYS Fluent software in the turbomachinery area including 10 practical exercises. You will learn and obtain comprehensive training on how to simulate projects with ANSYS Fluent software. The achieved knowledge will enable you to choose the most appropriate modeling approaches and methods for applications and CFD simulations.
We start the training package with 3 practical exercises about different Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT).
Study number 1 deals with the airflow on the HAWT blades so the purpose of the problem is to study the distribution of velocity and pressure on the surface of the blades and on their body. There are three areas around the blades for airflow. There is an area around the blades, an area in the front of the blades, and an area behind the blades. Project number 5 is going to simulate an airflow field adjacent to the Liam F1 wind turbine. The geometry included a rotary zone for the turbine walls and a stationary zone for the rest of the domain. The inlet is considered 3 m/s and the turbine zone is rotating with 300 RPM. Practical exercise number 10 is going to simulate an airflow field close to a standard horizontal axis wind turbine. The geometry included a rotary zone for the turbine walls and a stationary zone for the rest of the domain. The inlet is considered to wind with 1 m/s, and the turbine zone is rotating at 16 RPM.
Then, we continue the training package with 3 practical exercises about different Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT).
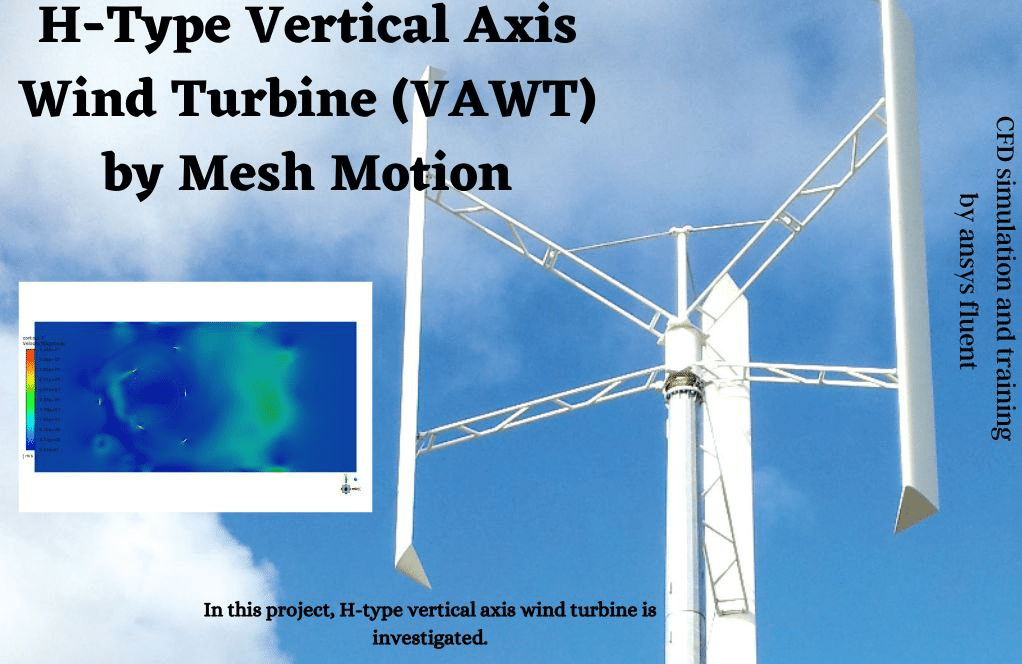
In practical exercise, number 3, steady airflow in the presence of an H-type wind turbine (VAWT) is investigated. Nowadays, turbines are a reliable, clean energy source, which generates electricity using the induced rotation by wind flow. However, turbine wind farms face challenging issues such as low efficiency at lower diameters for horizontal axis wind turbines (HAWT), disruption of the natural view of valleys, and low wind conditions. Project number 7 is going to simulate an airflow field close to a Darrieus (vertical axis wind turbine). The geometry included a rotary zone for the turbine walls and a stationary zone for the rest of the domain. The inlet is considered to wind with 1 m/s, and the turbine zone is rotating with 120 RPM. Practical exercise number 8 is going to simulate an airflow field close to a vertical axis Helical wind turbine. The geometry included a rotary zone for the turbine walls and a stationary zone for the rest of the domain. The inlet is considered to wind with 1 m/s, and the turbine zone is rotating at 120 RPM.
Finally, we investigate different Turbomachinery devices in 4 practical exercises.
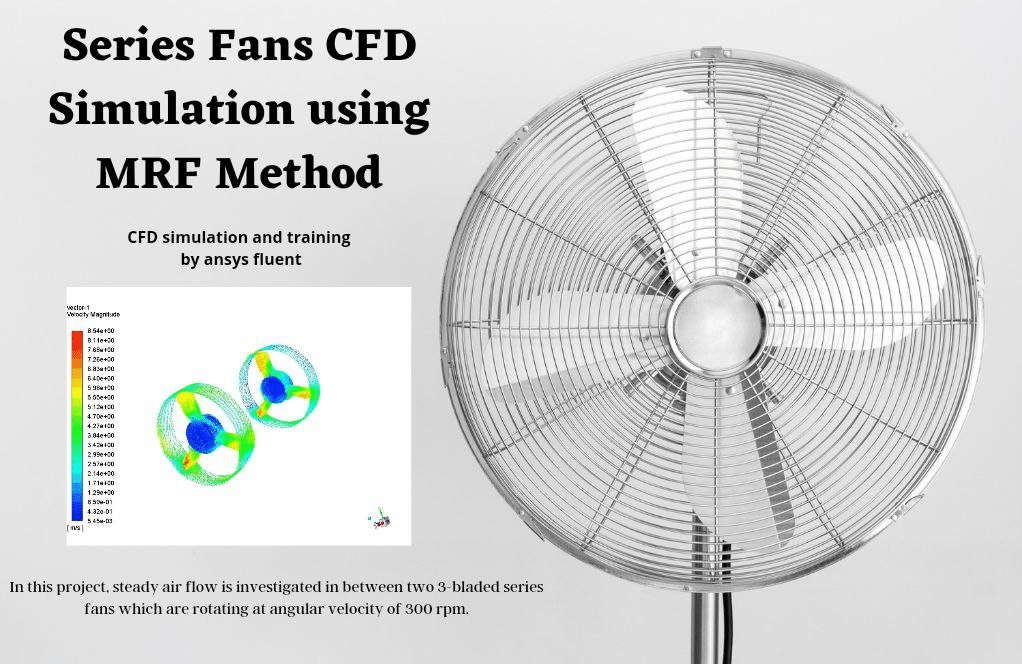
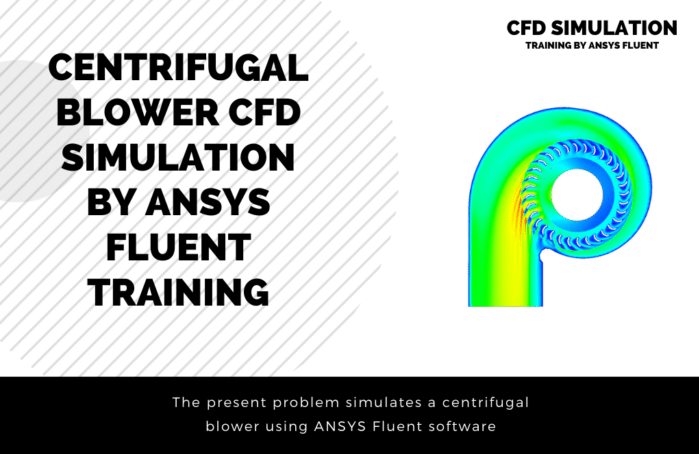
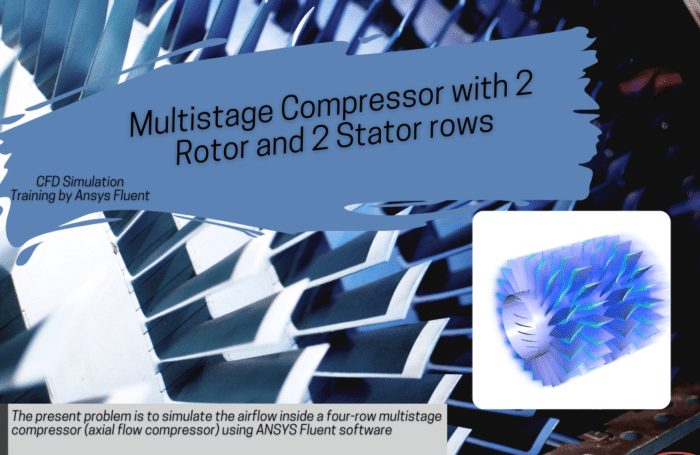
In project number 2, steady airflow is investigated between two 3-bladed series fans which are rotating at an angular velocity of 300 rpm. The rotation of fans generates air suction at the inlet boundary with a flow rate equal to 2.95755 m3/s. The velocity of air reaches values up to 25 m/s on the domain centerline however maximum air velocity in the domain is equal to 47.05 m/s which is captured downstream of the first fan. Problem number 4 simulates a centrifugal blower. The blower is a particular device for blowing high-pressure air, which generally has applications such as dust cleaning and …. For example, a blower is used to clean computer parts and equipment. Practical exercise number 6 simulates a centrifugal compressor with a diffuser. One of the most widely used compressors in the industry is the centrifugal-type compressor. This compressor uses positive pressure while using centrifugal force to compress the gas. Project number 9 simulates the airflow inside a 4-row multistage compressor. The compressor designed in this simulation is of axial type and consists of four rows, including two rows of stator and two rows of the rotor. In general, axial flow compressors are compressors whose airflow is parallel to the axis of rotation. Practical exercise number 10 is going to simulate an airflow field close to a standard horizontal axis wind turbine. The geometry included a rotary zone for the turbine walls and a stationary zone for the rest of the domain. The inlet is considered to wind with 1 m/s, and the turbine zone is rotating at 16 RPM.











Gabe Shanahan –
I recently purchased the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners and found it to be extremely well-structured and informative. As a beginner, the step-by-step approach and clear explanations gave me the confidence to simulate various turbomachinery exercises. The progressive complexity from HAWT simulations to axial compressors allowed for an excellent learning curve. I was particularly intrigued by the unique challenges presented in each project, which sharpened my problem-solving skills.
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear that the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package has provided you with a valuable learning experience! It’s great to know that the structured approach and diverse range of exercises were effective in enhancing your skills in CFD simulation of turbomachinery as a beginner. Thank you for choosing our training content, and if you ever have any further questions or require assistance as you continue your CFD journey, please don’t hesitate to reach out. Your progress and success are what drive us to create comprehensive and user-friendly learning materials.
Liza Effertz DVM –
The training package really gave me a solid understanding of different types of wind turbines and turbomachinery! It was straightforward and engaging, making it easier for a beginner like myself to grasp complex concepts. Each project built upon the last, reinforcing my skills progressively. Thank you for such a thorough and beginner-friendly approach!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re delighted to hear that our Turbomachinery CFD Training Package met your learning needs and helped you gain a solid understanding of the simulation concepts and techniques. If you ever have more questions or need further assistance in your learning journey, feel free to reach out. We’re here to help you succeed!
Jeremie Huels –
In the package, is there a session that covers the post-processing techniques specific to turbomachinery CFD such as visualization of pressure field developments and comparison of efficiency?
MR CFD Support –
The Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners includes exercises on internal flow visualization and qualitative validation of performance, which involve post-processing techniques. Within the sessions, you should be able to learn how to observe and analyze the pressure field and other important physical fields, but the details regarding efficiency comparisons should also be covered purportedly to equip you with the ability to perform a comprehensive analysis of a turbomachinery system.
Demarcus Lesch –
I’ve just completed the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners, and as a novice in ANSYS Fluent, the experience was enlightening. The step-by-step exercises brought clarity to simulation concepts that seemed overwhelming at first. I’m particularly impressed with practical exercises number 4 and 6; they really grounded my understanding of airflow in centrifugal machines. Grateful for such a well-structured pathway into CFD.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your kind words. We’re delighted to hear that you found the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package so helpful and that it clarified complex concepts for you. It’s great to know that exercises number 4 and 6 were particularly beneficial. If you have any further questions or need additional training, don’t hesitate to reach out!
Norma Conn –
This training package seems like a great start for beginners. I particularly appreciate the insightful practical exercises and clear step-by-step approach.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that our training package has provided you with a good introduction and practical experience in turbomachinery CFD simulations using ANSYS Fluent. Should you have any questions or need further assistance, don’t hesitate to reach out. Happy learning!
Emilie Kertzmann Jr. –
I recently went through the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners, and I was amazed at the depth of content covered in each session. The step-by-step guidance on performing different simulations using ANSYS Fluent was easy to follow and exceptionally thorough. The practical exercises varied in complexity and offered an incredible hands-on experience that solidified my understanding of turbomachinery simulations. I particularly found the airflow simulation around the wind turbines to be fascinating – the visualization of flow patterns and the analysis of blade performance crystallized the theoretical aspects I’ve learned in class.
MR CFD Support –
We are thrilled to hear about your positive experience with our Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners. It’s wonderful to know that the practical exercises and detailed guidance provided clarity and reinforced your theoretical understanding of turbomachinery simulations. We sincerely appreciate your feedback and are pleased that the hands-on simulations, like the wind turbine airflow, were engaging and informative. Your enthusiasm for learning encourages us to continue providing high-quality training content. Thank you for choosing our learning products, and we hope you continue to find them beneficial in your studies and future projects!
Shanna Jacobs –
I just completed the ‘Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners’ and was thoroughly impressed with the depth and breadth of the content. The step-by-step guidance on numerous practical exercises helped me understand complex concepts in turbomachinery and CFD simulation. Navigating through the different types of wind turbines and their respective airflow simulations was a highlight. This training package is an invaluable resource for anyone starting in the field of CFD in turbomachinery. Well done, MR CFD Company!
MR CFD Support –
We’re delighted to hear that you found the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package both comprehensive and informative. It’s gratifying to know that the practical exercises and step-by-step instructions aided your understanding of turbomachinery. Thank you for your positive feedback, and we look forward to providing you with continued support in your CFD learning journey!
Jerald Gorczany –
I’ve completed the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners, and I must say, it’s fantastic! The step-by-step exercises led me from the basics to more complex simulations with ease. Kudos to the MR CFD team for putting together such detailed and user-friendly learning material. I particularly appreciated the variety of examples provided, which covered both horizontal and vertical wind turbines, as well as different turbomachinery equipment. Not only did I learn the software, but I also gained conceptual understanding on aerodynamics related to wind turbine design.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words and taking the time to leave this positive review! We’re overjoyed to hear that our Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners met your expectations and provided you with solid foundational knowledge and practical experience. Your feedback is immensely appreciated and assists us in our quest to continuously enhance our learning products. Should you have any further inquiries or need support on your CFD journey, please don’t hesitate to reach out. Happy simulating!
Ms. Anika Miller DDS –
The Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners has helped me as a newcomer in the field. The gradual progression through horizontal and vertical axis wind turbines to intricate devices like multistage compressors laid a strong foundation for understanding how to approach simulations. One thing that wasn’t clear to me, though—how in-depth does the package go into post-processing and data analysis in ANSYS Fluent? It’s vital to draw meaningful conclusions from the results.
MR CFD Support –
The Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners provides step-by-step guidance on post-processing and data analysis in ANSYS Fluent, starting from basics to more complex evaluations. You’ll learn to generate and interpret plots for velocity, pressure, and other crucial flow parameters, as well as how to extract quantitative data for performance evaluation and optimization. Moreover, the package illustrates best practices for creating well-defined graphics to convey your results effectively.
Estefania Considine –
The training package for beginners is wonderful! It’s extremely thorough and I’ve gained so much valuable knowledge about simulating different turbomachinery designs with ANSYS Fluent. Understanding airflow interactions and optimizing designs with this toolset has been exciting. Thank you for such a well-prepared and informative package.
MR CFD Support –
We appreciate your compliment and are thrilled to hear that you found the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners valuable and informative. It’s wonderful to know our materials aided your understanding of airflow interactions and design optimization using ANSYS Fluent. If you ever have any questions or need further guidance, our team is here to assist you. Thank you for choosing our training package and for your positive feedback!
Mrs. Millie Kilback II –
The Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners was an excellent and thorough collection of studies. I grasped many essential concepts which were simplified eloquently and appreciate the variety, covering both horizontal and vertical wind turbines as well as different turbomachines. It was particularly helpful how each practical exercise built upon the last, solidifying my understanding of flow physics and CFD applications in wind energy and mechanical design.
MR CFD Support –
We’re so glad to hear that our Turbomachinery CFD Training Package was helpful to you! Thanks for taking the time to provide such positive feedback. It’s wonderful to know that the exercises helped strengthen your understanding of the flow dynamics in wind turbines and turbomachinery. If you have any more questions or need further assistance, feel free to reach out to us.
Henderson Abshire –
I recently completed the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners, which covered various wind turbines and turbomachines. I found the step-by-step guidance remarkably easy to follow and the practical exercises were directly applicable to real-world scenarios. The training solidified my understanding of CFD in turbomachinery design, and helped me visualize internal flows and assess performance metrics efficiently.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your wonderful review! We’re delighted to hear that you found the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package informative and applicable to real-world situations. It’s great to know that our step-by-step guidance was helpful in your learning journey. We appreciate your feedback and we’re glad that you were able to enhance your grasp on CFD for turbomachinery. Keep up the great work!
Prof. Lionel Mueller I –
Very meticulous training package for a beginner! Working through the different practical exercises gave me a solid understanding of the fundamentals of Turbomachinery CFD. The gradual buildup from HAWT to VAWT, and onto more complex turbomachinery devices was really effective. The balance of theory with hands-on ANSYS Fluent simulation was the highlight for me. Looking forward to applying these skills in a professional setting!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your feedback! We’re so glad to hear that our CFD Training Package for Beginners met your expectations. It’s great to know that the theoretical knowledge and the practical exercises with ANSYS Fluent have provided you with the skills you need for professional growth. Keep up the good work, and feel free to reach out if you have any further questions or need more advanced training materials.
Cordia Fadel –
I’m thrilled with the comprehensiveness of the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners. The gradual progression from wind turbines to more complex turbomachinery simulations has effectively solidified my understanding of fluid dynamics within these applications. The variety of practical exercises spanning a good range of scenarios provided an immersive learning experience. Especially helpful was the focus on differentiating the methodologies suitable for horizontal and vertical axis wind turbines, aiding me tremendously in conceptualizing their working principles under various conditions.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re delighted to hear that our training package has been so beneficial to you. Understanding the distinct approaches for HAWT and VAWT simulation is crucial, and it’s fantastic to know our exercises have effectively guided you through these concepts. If you have any more insights or require further information, don’t hesitate to reach out. Your success is very rewarding to us!
Francis Harber –
The comprehensive tutorials for simulating various types of wind turbines and turbomachinery devices have been a game changer for me as a beginner in using ANSYS Fluent. The clear step-by-step instructions allowed me to understand the basic principles of airflow and pressure distribution around turbines, which was not only insightful but also exciting to visualize. The comparison of horizontal and vertical turbines, as well as the inclusion of practical exercises such as simulation of compressors and fans, has been particularly helpful in broadening my knowledge in the field.
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear your experience with our Turbomachinery CFD training package has been so beneficial to your understanding of ANSYS Fluent and CFD simulations. It’s great to know that the variety in practical exercises has helped deepen your knowledge of different airflow mechanisms in turbomachinery. Thank you for taking the time to share your positive feedback, and keep up the excellent work in your learning journey!
Miss Karianne Bosco –
I found the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package extremely thorough and valuable as a beginner. The practical exercises were particularly helpful in understanding both HAWTs and VAWTs, in various operational scenarios. The set-by-step instructions enabled me to simulate different airflow fields and analyze performance effectively, enriching my grasp of turbomachinery dynamics. Fantastic learning tool!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We are thrilled to hear that the training package met your needs and provided valuable insights into turbomachinery CFD simulations. It’s great to know that our practical exercises helped enrich your understanding and enhance your experience. If you have further questions or need assistance in your learning journey, don’t hesitate to reach out. Keep learning and best of luck with your future CFD projects!
Misty Cartwright –
What a fantastic collection for someone new to turbomachinery CFD! Each project seems to build on the last, offering a diverse yet comprehensive look at both horizontal and vertical turbines, as well as distinct turbomachinery devices. As someone aiming to master the basics, this package provides not only a solid starting point but also guides through complex simulations that seem to cover a broad spectrum of issues and applications in the field.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your kind words! We’re thrilled to hear that you’ve found the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package valuable and comprehensive for beginners. It is our goal to provide learners with a solid foundation as well as a deep understanding of different types of simulations within the CFD sphere. Your satisfaction with the variety and depth of the content makes our efforts worthwhile. If you need further assistance or have more feedback in the future, please do not hesitate to reach out. Happy learning!
Dr. Zola Crist –
The training laid out the foundational knowledge so well, I must say, I am deeply impressed with the Big Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners. As someone breaking into the field, the hands-on exercises were intuitive and realistic. Commendable job on including different configurations of both HAWT and VAWT, as well as tackling various turbomachinery devices. It facilitated a smooth learning curve and the practical exercises catered to a comprehensive understanding of airflow dynamics in these systems.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your review! We’re ecstatic to hear that our Turbomachinery CFD Training Package met your educational needs and provided a firm grounding in the simulation of various wind turbines and turbomachinery devices. It’s always our goal to ensure a valuable learning experience through practical and detailed exercises. We appreciate your feedback and look forward to assisting you in your growth in the field of CFD!
Addie Von –
The turbomachinery package for beginners seems quite comprehensive and well-structured. The diverse range of practical exercises provides a great foundation for understanding the nuances of CFD simulations in wind turbines and other turbomachinery devices.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are delighted to hear that you find our Turbomachinery CFD Training Package comprehensive and well-suited for beginners. If there’s any more we can help you with, please don’t hesitate to reach out.
Marina Frami –
The ‘Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners’ is an incredible asset for someone like me who’s starting out with simulations in fluid dynamics within the field of renewable energy. Every project offered diverse scenarios that clearly showed how to set up, run, and analyze simulations. I particularly benefited from the practical exercises involving both HAWT and VAWT. The step-by-step guides clarified several core concepts, which helped me tremendously in understanding the basic principles of turbomachinery flows. Well-crafted materials and spot-on instructions, worth every minute spent studying them!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for taking the time to provide feedback on the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners. We’re delighted to hear that the projects within the training have elucidated the concepts and fundamentals of turbomachinery flows for you in a valuable way. It is our goal to equip beginners with a solid understanding of CFD applications, especially in renewable energy, and we’re pleased to know we’ve achieved that with this material. We appreciate your positive comments and are here to support your learning journey further!
Isaias Hahn –
The Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners has been an outstanding resource for getting up to speed with ANSYS Fluent. The project diversity covering both HAWT and VAWT, as well as axial and centrifugal compressors, provided a comprehensive primer. I particularly appreciate the step-by-step approach that gradually builds up expertise, with thorough explanations making complex phenomena more approachable for a novice.
MR CFD Support –
Your positive feedback on the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package is immensely appreciated. We are thrilled to hear that our approach has effectively facilitated your learning experience with ANSYS Fluent. Your progress and comprehension of the various simulations, including HAWT, VAWT, and different compressors, is exactly what we aim to support with our training packages. Thank you for choosing MR CFD Company as your learning partner in CFD!
Norberto Will –
I have recently completed the ‘Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners’ and I was genuinely impressed with the variety of exercises offered in the package. The progression from horizontal axis wind turbines to vertical ones, and then onto more complex devices like blowers and multistage compressors, really helped me grasp the wide applications of CFD in turbomachinery. The clear instructions and practical work deepen my understanding significanctly.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback! We are delighted to know that the training package met your expectations and provided a comprehensive learning experience. Your success with the exercises is exactly what we aim for. We’re here in case you have more questions or need further assistance. Keep up the great work!
Shanny Rogahn –
The Turbomachinery CFD Training Package has significantly enhanced my understanding of air flows in various wind turbine designs and turbomachinery devices. The step-by-step guidance was indeed tailored for beginners, making it easy for me to follow and apply the knowledge in simulations. I was particularly impressed with the depth of practical exercises that covered both HAWT and VAWT configurations and the simulations of multi-row compressors. Kudos to the team for putting together such an informative and user-friendly learning resource!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for sharing your positive experience with our Turbomachinery CFD Training Package! We’re thrilled to hear that our training exercises equipped you with the necessary skills and knowledge, enabling you to confidently perform simulations. We appreciate your kudos and hope we can continue to support your learning journey in CFD applications.
Jean Balistreri –
I found the practical exercises and their variety quite helpful in understanding turbomachinery CFD simulation. The training seems well-structured, covering both horizontal and vertical axis wind turbines and other machinery. Thanks for a great learning resource!
MR CFD Support –
We’re thrilled to hear that you found the practical exercises useful and the learning structure comprehensive. It’s always our goal to provide helpful resources for understanding CFD simulations, particularly in the area of turbomachinery. Thank you for taking the time to share your positive experience with our training package!
Kirk Willms –
This training package was an amazing journey into turbomachinery CFD simulations! The gradual progress from basic exercises to more advanced simulations gave me a solid ground in understanding both the concept and practical side of fluid dynamics in turbines. Exercises shifted seamlessly from HAWT to VAWT, then concluded with in-depth looks at various turbomachinery devices, greatly expanding my knowledge at each step. The detailed setups and clear explanations allowed me to confidently perform simulations and analyze the results, equipping me with skills directly applicable to my engineering tasks. Incredibly thankful for such a comprehensive learning experience!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you so much for your positive feedback! It’s fantastic to hear how our Turbomachinery CFD Training Package has enhanced your understanding and skills in turbomachinery simulation. We’re proud to assist in your learning and it is great that you found the transition from basic to advanced exercises seamless and informative. If you ever have any questions or need further assistance on your journey, don’t hesitate to reach out. We’re here to help you succeed!
Tomasa Koelpin –
This training package has really deepened my understanding of turbomachinery and how CFD analysis can be applied to it. Each practical exercise was well-structured, guiding me from easy to more complex simulations. The transition from horizontal to vertical axis wind turbines allowed a comprehensive study of aerodynamics in these systems. Moreover, the sessions on blowers, compressors and their optimized use in industry were extremely beneficial. I appreciated the clarity in tutorials that consistently highlighted the critical concepts and techniques.
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We’re thrilled to hear that the turbomachinery CFD training package was effective in enhancing your understanding and skills in the aerodynamics of turbomachinery, as well as in the application of CFD analysis in industry. We are dedicated to providing clear and comprehensive training, and it’s great to know we’ve achieved that. Your success with the practical exercises reaffirms the value of our learning products. Keep up the great work and feel free to reach out if you need further assistance or resources for continuing your journey in CFD analysis.
Lavina Green –
I had a great time learning with the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners. The step-by-step approach in the provided exercises really bolstered my understanding of CFD applications in various types of wind turbines and other turbomachinery. The progression from horizontal axis wind turbines to vertical ones, and finally diving into turbomachinery devices, offered a thorough grasp of the core concepts as well as practical knowing-how. Truly invaluable for a beginner like me!
MR CFD Support –
We are thrilled to hear about your positive experience with our Turbomachinery CFD Training Package for Beginners! It’s fantastic to know that our structured learning modules for various turbomachines have provided you with a solid foundation and practical skills in CFD using ANSYS Fluent. Thank you for choosing our training package, and we wish you continued success in your CFD journey.
Miss Selina Moore Sr. –
This training package has helped me grasp the basics of turbomachinery CFD. The different practical exercises, especially the clear distinction between HAWT and VAWT applications, aided my understanding significantly. The detailed environmental settings and scenarios added depth, showing high application value in real-world problems. Thank you for a well-structured introduction to turbomachinery CFD!
MR CFD Support –
Thank you for your positive feedback! We are delighted to hear that the Turbomachinery CFD Training Package has provided you with a solid foundation in understanding and applying CFD in the turbomachinery field. We are committed to offering high-quality, comprehensive learning materials to our users. Your success is our priority, and we’re thankful that you’ve taken the time to share your learning experience with us.